
Concept explainers
a.
To write: a linear equation for your current monthly wage
a.
Answer to Problem 1PS
Wage of salesperson is
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
As a salesperson, you receive a monthly salary of $2000, plus a commission of 7% of sales. You receive an offer for a new job at $2300 per month, plus a commission of 5% of sales.
Calculation:
Monthly salary = $2000 plus a commission of 7% of sales.
Total Wage is sum of monthly salary and commission.
b.
To write: a linear equation for the monthly wage
b.
Answer to Problem 1PS
Wage of salesperson from new job
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
As a salesperson, you receive a monthly salary of $2000, plus a commission of 7% of sales. You receive an offer for a new job at $2300 per month, plus a commission of 5% of sales. Write
Calculation:
Monthly salary for new job = $2300 plus a commission of 5% of sales.
Total Wage is sum of monthly salary and commission.
c.
To graph: both equations in the same viewing window and then find the point of intersection also what does the point of intersection represent?
c.
Answer to Problem 1PS
The point of intersection is
Explanation of Solution
Given iformation:
As a salesperson, you receive a monthly salary of $2000, plus a commission of 7% of sales. You receive an offer for a new job at $2300 per month, plus a commission of 5% of sales. Use a graphical utility to graph Using a graphical utility the graph formed will be
Graph:
Plotting
Plot the points and join them
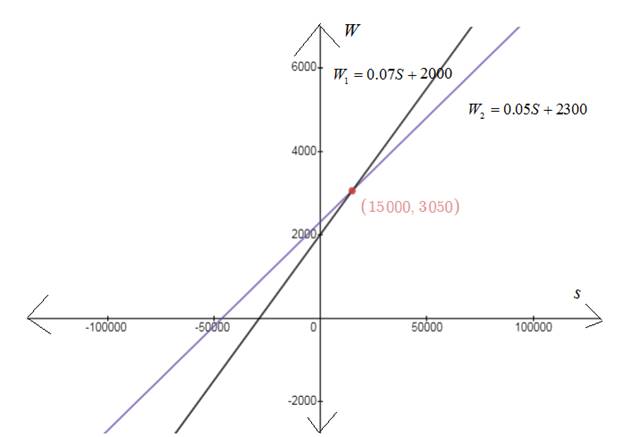
The point of intersection is
d.
To Find: whether to change job or not when expected sale is $20,000 per month.
d.
Answer to Problem 1PS
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
As a salesperson, you receive a monthly salary of $2000, plus a commission of 7% of sales. You receive an offer for a new job at $2300 per month, plus a commission of 5% of sales
Calculation:
Expected sale is of $20,000 per month.
From part (a), we have
From part (b), we have
Now, putting
Here
That implies no need to change the job; you get more money from your current job.
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS W/LIMITS
- 8. For x>_1, the continuous function g is decreasing and positive. A portion of the graph of g is shown above. For n>_1, the nth term of the series summation from n=1 to infinity a_n is defined by a_n=g(n). If intergral 1 to infinity g(x)dx converges to 8, which of the following could be true? A) summation n=1 to infinity a_n = 6. B) summation n=1 to infinity a_n =8. C) summation n=1 to infinity a_n = 10. D) summation n=1 to infinity a_n diverges.arrow_forwardPLEASE SHOW ME THE RIGHT ANSWER/SOLUTION SHOW ME ALL THE NEDDED STEP 13: If the perimeter of a square is shrinking at a rate of 8 inches per second, find the rate at which its area is changing when its area is 25 square inches.arrow_forwardDO NOT GIVE THE WRONG ANSWER SHOW ME ALL THE NEEDED STEPS 11: A rectangle has a base that is growing at a rate of 3 inches per second and a height that is shrinking at a rate of one inch per second. When the base is 12 inches and the height is 5 inches, at what rate is the area of the rectangle changing?arrow_forward
- please answer by showing all the dfalowing necessary step DO NOT GIVE ME THE WRONG ANSWER The sides of a cube of ice are melting at a rate of 1 inch per hour. When its volume is 64 cubic inches, at what rate is its volume changing?arrow_forwardSox & Sin (px) dx 0arrow_forward8 L 8 e ipx dxarrow_forward
- Find the Taylor polynomial T³(×) for the function f centered at the number a. f(x) = xe-2x a = 0 T3(x) =arrow_forwardFor each graph in Figure 16, determine whether f (1) is larger or smaller than the slope of the secant line between x = 1 and x = 1 + h for h > 0. Explain your reasoningarrow_forwardPoints z1 and z2 are shown on the graph.z1 is at (4 real,6 imaginary), z2 is at (-5 real, 2 imaginary)Part A: Identify the points in standard form and find the distance between them.Part B: Give the complex conjugate of z2 and explain how to find it geometrically.Part C: Find z2 − z1 geometrically and explain your steps.arrow_forward
- A polar curve is represented by the equation r1 = 7 + 4cos θ.Part A: What type of limaçon is this curve? Justify your answer using the constants in the equation.Part B: Is the curve symmetrical to the polar axis or the line θ = pi/2 Justify your answer algebraically.Part C: What are the two main differences between the graphs of r1 = 7 + 4cos θ and r2 = 4 + 4cos θ?arrow_forwardA curve, described by x2 + y2 + 8x = 0, has a point A at (−4, 4) on the curve.Part A: What are the polar coordinates of A? Give an exact answer.Part B: What is the polar form of the equation? What type of polar curve is this?Part C: What is the directed distance when Ø = 5pi/6 Give an exact answer.arrow_forwardNew folder 10. Find the area enclosed by the loop of the curve (1- t², t-t³)arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





