
Concept explainers
(a)
To find: The temperature change in degree per inch for the gypsum wallboard.
(a)
Answer to Problem 42E
The temperature change in degree per inch for the gypsum wallboard is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The given figure is as follows.
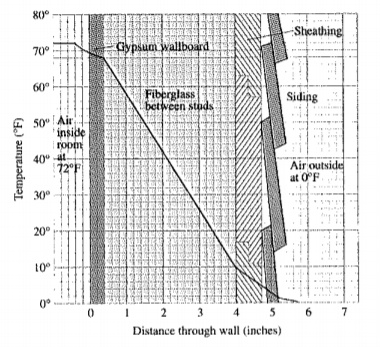
Calculation:
The formula to calculate the temperature change is given by,
Find the temperature change in degree per inch for the gypsum wallboard as follows.
Therefore, the temperature change in degree per inch for the gypsum wallboard is
(b)
To find: The temperature change in degree per inch for the fiberglass insulation.
(b)
Answer to Problem 42E
The temperature change in degree per inch for the fiberglass insulation is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The given figure is as follows.
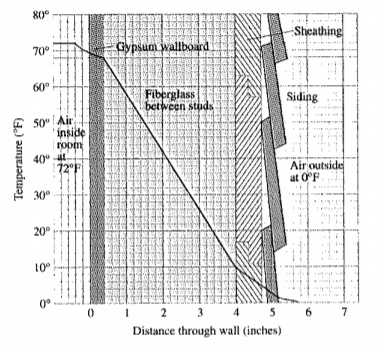
Calculation:
The formula to calculate the temperature change is given by,
Find the temperature change in degree per inch for the gypsum wallboard as follows.
Therefore, the temperature change in degree per inch for the fiberglass insulation is
(c)
To find: The temperature change in degree per inch for the wood sheathing.
(c)
Answer to Problem 42E
The temperature change in degree per inch for the wood sheathing is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given figure is as follows.
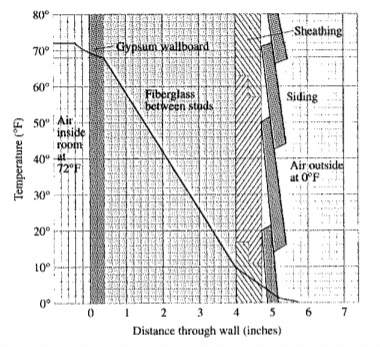
Calculation:
The formula to calculate the temperature change is given by,
Find the temperature change in degree per inch for the wood sheathing as follows.
Therefore, the temperature change in degree per inch for the wood sheathing is
(d)
To find: The best and poorest insulating material.
(d)
Answer to Problem 42E
The best insulator is fiberglass insulation and poorest insulator is Gypsum wallboard.
Explanation of Solution
Given information: The given figure is as follows.
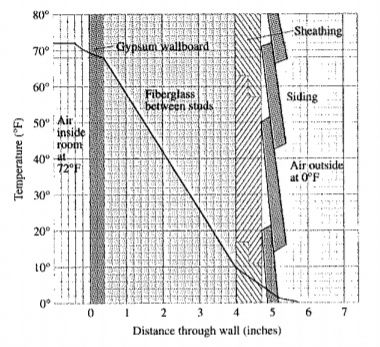
The best insulating material will have the highest temperature change per inch, because that will allow larger temperature difference on opposite sides of thinner layers.
From the above calculation, it can be concluded that the fiberglass insulation has highest temperature change so it will be best insulator.
The Gypsum wallboard has lowest temperature change so it will be poorest insulator.
Therefore, the temperature change in degree per inch for the wood sheathing is
Chapter 1 Solutions
Calculus: Graphical, Numerical, Algebraic
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics
College Algebra (7th Edition)
- For each graph in Figure 16, determine whether f (1) is larger or smaller than the slope of the secant line between x = 1 and x = 1 + h for h > 0. Explain your reasoningarrow_forwardPoints z1 and z2 are shown on the graph.z1 is at (4 real,6 imaginary), z2 is at (-5 real, 2 imaginary)Part A: Identify the points in standard form and find the distance between them.Part B: Give the complex conjugate of z2 and explain how to find it geometrically.Part C: Find z2 − z1 geometrically and explain your steps.arrow_forwardA polar curve is represented by the equation r1 = 7 + 4cos θ.Part A: What type of limaçon is this curve? Justify your answer using the constants in the equation.Part B: Is the curve symmetrical to the polar axis or the line θ = pi/2 Justify your answer algebraically.Part C: What are the two main differences between the graphs of r1 = 7 + 4cos θ and r2 = 4 + 4cos θ?arrow_forward
- A curve, described by x2 + y2 + 8x = 0, has a point A at (−4, 4) on the curve.Part A: What are the polar coordinates of A? Give an exact answer.Part B: What is the polar form of the equation? What type of polar curve is this?Part C: What is the directed distance when Ø = 5pi/6 Give an exact answer.arrow_forwardNew folder 10. Find the area enclosed by the loop of the curve (1- t², t-t³)arrow_forward1. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: t X== y = t +1 2 te(-∞, ∞) 42,369 I APR 27 F5 3 MacBook Air stv A Aa T 4 DIIarrow_forward
- Middle School GP... Echo home (1) Addition and su... Google Docs Netflix Netflix New folder 9. Find the area enclosed by x = sin²t, y = cost and the y-axis.arrow_forward2. Graph and find the corresponding Cartesian equation for: (4 cos 0,9 sin 0) θ ε [0, 2π) 42,369 I APR 27 3 MacBook Air 2 tv A Aaarrow_forward30 Page< 3. Find the equation of the tangent line for x = 1+12, y = 1-3 at t = 2 42,369 APR A 27 M . tv NA 1 TAGN 2 Aa 7 MacBook Air #8arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





