
A research paper published in the summer of 2012 presented a method to obtain the whole-genome sequence of a fetus without any invasive procedure such as amniocentesis that could on rare occasions cause miscarriage. This new technique is based on the fact that some fetal cells leak into the mother’s bloodstream and then break down, releasing their DNA. Assume that exactly 10% of the DNA fragments in the mother’s blood serum come from the fetus, while the remaining 90% of the DNA fragments in the serum come from the mother’s genome.
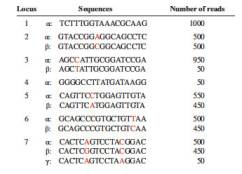
The investigators collected cell-free DNA from a pregnant woman’s bloodstream and subjected it to an advanced high-throughput sequencing method. The table at the end of this problem looks at seven unlinked loci; the number of reads of particular alleles (identified by Greek letters) are shown. You should assume for the sake of simplicity that all numerical differences are statistically significant (even though actual data are never this clean).
| a. | Determine whether each locus is autosomal, X-linked, or Y-linked. |
| b. | Describe the diploid genomes of the mother and fetus by using Greek letters for the alleles, or a dash (–) if no Greek letter is appropriate. |
| c. | Is the fetus male or female? |
| d. | At an eighth locus, 1500 reads of a single type of sequence were found. Provide a possible explanation for this result, being as specific as possible. |
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- Explain in a small summary how: What genetic information can be obtained from a Punnet square? What genetic information cannot be determined from a Punnet square? Why might a Punnet Square be beneficial to understanding genetics/inheritance?arrow_forwardIn a small summary write down:arrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Noggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





