
Organic Chemistry
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781118875766
Author: T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle, Scott A. Snyder
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 3LGP
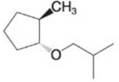
Synthesize the compound shown below from methylcyclopentane and 2-methylpropane using those compounds as the source of the carbon atoms and any other reagents necessary. Synthetic tools you might need include Markovnikov or anti-Markovnikov hydration, Markovnikov or anti-Markovnikov hydrobromination, radial halogenation, elimination, and nuceleophilic substitution reactions.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
EFFICIENTS
SAMPLE READINGS
CONCENTRATIONS
Pigiadient)
TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR)
TOMATO (REDUCED SALT)
TOMATO SAUCE (REGULAR)
TOMATO (REDUCED SALT)
58
6.274
3.898
301.7
151.2
14150
5.277
3.865
348.9
254.8
B
5.136
3.639
193.7
85.9
605
4.655
3.041
308.6
199.6
05
5.135
3.664
339.5
241.4
0139
4.676
3.662
160.6
87.6
90148
5.086
3.677
337.7
242.5
0092
6.348
3.775
464.7
186.4
PART3
5.081
3.908
223.5
155.8
5.558
3.861
370.5
257.1
4.922
3.66
326.6
242.9
4.752
3.641
327.5
253.3
50
5.018
3.815
336.1
256.0
84
4.959
3.605
317.9
216.6
38
4.96
3.652
203.8
108.7
$3
5.052
3.664
329.8
239.0
17
5.043
3.767
221.9
149.7
052
5.058
3.614
331.7
236.4
5.051
4.005
211.7
152.1
62
5.047
3.637
309.6
222.7
5.298
3.977
223.4
148.7
5.38
4.24
353.7
278.2
5
5.033
4.044
334.6
268.7
995
4.706
3.621
305.6
234.4
04
4.816
3.728
340.0
262.7
16
4.828
4.496
304.3
283.2
0.011
4.993
3.865
244.7
143.6
AVERAGE
STDEV
COUNT
95% CI Confidence Interval (mmol/L)
[Na+] (mg/100 mL)
95% Na+ Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)
If we have two compounds: acetone (CH₃COCH₃) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH), applying heat to them produces an aldol condensation of the two compounds. If this is correct, draw the formula for the final product.
If we have two compounds: acetone (CH3COCH3)
and acetic acid (CH3COOH); if we apply heat (A),
what product(s) are obtained?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 11 - Prob. 1PPCh. 11 - Practice Problem 11.2 Give bond-line formulas and...Ch. 11 - Prob. 3PPCh. 11 - Prob. 4PPCh. 11 - Prob. 5PPCh. 11 - Prob. 6PPCh. 11 - Prob. 7PPCh. 11 - Practice Problem 11.8 Show how you would prepare...Ch. 11 - Prob. 9PPCh. 11 - Prob. 10PP
Ch. 11 - Practice Problem 11.11
An exception to what is...Ch. 11 - Prob. 12PPCh. 11 - Prob. 13PPCh. 11 - Prob. 14PPCh. 11 - Prob. 15PPCh. 11 - Prob. 16PPCh. 11 - Prob. 17PPCh. 11 - Prob. 18PPCh. 11 - Practice Problem 11.19
Propose structures for each...Ch. 11 - Prob. 20PPCh. 11 - Prob. 21PPCh. 11 - Prob. 22PPCh. 11 - Prob. 23PPCh. 11 - Prob. 24PPCh. 11 - Give an IUPAC substitutive name for each of the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 26PCh. 11 - Prob. 27PCh. 11 - Prob. 28PCh. 11 - Prob. 29PCh. 11 - 11.30. Show how you might prepare 2-bromobutane...Ch. 11 - Prob. 31PCh. 11 - Prob. 32PCh. 11 - Prob. 33PCh. 11 - Considering A-L to represent the major products...Ch. 11 - Write structures for the products that would be...Ch. 11 - Prob. 36PCh. 11 - Provide the reagents necessary for the following...Ch. 11 - 11.38. Predict the major product from each of the...Ch. 11 - Predict the products from each of the following...Ch. 11 - Provide the reagents necessary to accomplish the...Ch. 11 - 11.41. Provide reagents that would accomplish the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 42PCh. 11 - 11.43. A synthesis of the -receptor blocker called...Ch. 11 - Prob. 44PCh. 11 - Prob. 45PCh. 11 - 11.46. For each of the following, write a...Ch. 11 - 11.47. Vicinal halo alcohols (halohydrins) can be...Ch. 11 - Prob. 48PCh. 11 - Prob. 49PCh. 11 - Prob. 50PCh. 11 - Prob. 51PCh. 11 - Prob. 52PCh. 11 - Outlined below is a synthesis of the gypsy moth...Ch. 11 - Prob. 54PCh. 11 - Prob. 55PCh. 11 - Prob. 56PCh. 11 - 11.57. When the 3-bromo-2-butanol with the...Ch. 11 - 11.58. Reaction of an alcohol with thionyl...Ch. 11 - Prob. 59PCh. 11 - Prob. 60PCh. 11 - Prob. 1LGPCh. 11 - Prob. 2LGPCh. 11 - Synthesize the compound shown below from...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Microbiology: An Introduction
What main advantage do microbial plastics have over synthetic plastics?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
Name each of the following:
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
2 Of the uterus, small intestine, spinal cord, and heart, which is/are in the dorsal body cavity?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
43. Why does X-chromosome inactivation occur?
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
79. Complete and balance each acid-base reaction.
a.
b.
c.
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardYou need to make a buffer by dissolving benzoic acid and sodium benzoate in water. What is the mass of benzoic acid that you would weigh out, in mg, to create 50 mL of a buffer at pH = 4.7 that will change pH no more than 0.10 units with the addition of 0.001 moles of acid or base? Enter just the answer without the units (mg) - just the number will do!arrow_forwardDraw the formula for 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride.arrow_forward
- QUESTION: Fill out the answers to the empty green boxes attached in the image. *Ensure you all incorporate all 27 values (per column)*arrow_forwardComplete the following reactions- hand written pleasearrow_forwardGive the organic product: O A O B Ос ○ D -NH–CH3 + CH3 CH3 NEN C ? A CH3 CH3 NH- CH3 B CH3 CH3 N=N- C CH3 CH3 N=NNH CH3 D CH3 N=N CH3 NHCH3 LNH CHOarrow_forward
- Finish the reaction- hand written pleasearrow_forwardGive the organic products: (benzyne) Br ? CH3 + K* :NH, liq NH3 HINT: Two products are formed. Each is a substituted aniline; they are isomers of each other. NH2 II I H₂N. CH3 CH3 III Select one: ○ A. I and II ○ B. I and III O C. I and IV O D. II and III O E. III and IV H₂N CH3 IV CH₂-NH2arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: HBr (1 equiv) cold ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of this reaction in the drawing area below. • You can draw the products in any arrangement you like. • Pay careful attention to the reaction conditions, and only include the major products. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • Note that there is only 1 equivalent of HBr reactant, so you need not consider the case of multiple additions. Erase something Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terarrow_forward
- Q14. Fill this chart: (please refer to ppt notes/browser to answer these questions) What alcohol is also called wood alcohol? What is the common name of ethanol? Draw the structure of phenol and thiophene? Are bigger chain alcohol like heptanol and octanol are soluble or insoluble in water and explain it ? Are ethers soluble or insoluble in water? What suffix and prefix are used for alcohol while naming alcohol and ether? What the process called when we add water to any alkene to make alcohol? Q16. Draw the diagram of following aromatic compound (practice from previous module) Aniline Phenol Benzoic acid Methyl benzoate Q17. a. Write the oxidation reactions for the 2 propanol. b. Write the oxidation reaction of the ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 11 of 18 (1 point) Question Attempt: 3 of How many signals do you expect in the 'H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. 1 For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule Check For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box…arrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry Esterification reactions 1. Write the steps to prepare ester. 2. Write complete reaction of ethanol and acetic acid to make ester. 3. What does ester smell like? What are the uses of ester. 4. What the role of sulfuric acid in the esterification reactionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides: Crash Course Organic Chemistry #24; Author: Crash Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j04zMFwDeDU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY