
HeLa Cells Are a Genetic Mess HeLa cells can vary in chromosome number. Defects in proteins that orchestrate cell division result in descendant cells with too many or too few chromosomes, an outcome that is one of the ha1lmarks of cancer cells. The panel of chromosomes in FIGURE 11.9, originally published in 1989, shows all of the chromosomes in a single metaphase HeLa cell.
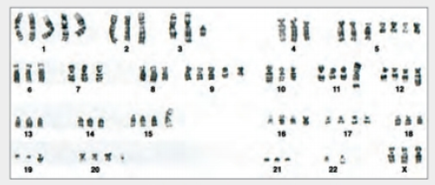
FIGURE 11.9 Karyotype of HeLa showing chromosomes in one cell.
Can you tell that this cell came from a female? How?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
- If four babies are born on a given day What is the chance all four will be girls? Use genetics lawsarrow_forwardExplain each punnet square results (genotypes and probabilities)arrow_forwardGive the terminal regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the terminal line: Give the first residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line : Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the first residual line: Give the second residual regression line equation and R or R2 value: Give the x axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: Give the y axis (name and units, if any) of the second residual line: a) B1 Solution b) B2 c)hybrid rate constant (λ1) d)hybrid rate constant (λ2) e) ka f) t1/2,absorb g) t1/2, dist h) t1/2, elim i)apparent central compartment volume (V1,app) j) total AUC (short cut method) k) apparent volume of distribution based on AUC (VAUC,app) l)apparent clearance (CLapp) m) absolute bioavailability of oral route (need AUCiv…arrow_forward
- You inject morpholino oligonucleotides that inhibit the translation of follistatin, chordin, and noggin (FCN) at the 1 cell stage of a frog embryo. What is the effect on neurulation in the resulting embryo? Propose an experiment that would rescue an embryo injected with FCN morpholinos.arrow_forwardParticipants will be asked to create a meme regarding a topic relevant to the department of Geography, Geomatics, and Environmental Studies. Prompt: Using an online art style of your choice, please make a meme related to the study of Geography, Environment, or Geomatics.arrow_forwardPlekhg5 functions in bottle cell formation, and Shroom3 functions in neural plate closure, yet the phenotype of injecting mRNA of each into the animal pole of a fertilized egg is very similar. What is the phenotype, and why is the phenotype so similar? Is the phenotype going to be that there is a disruption of the formation of the neural tube for both of these because bottle cell formation is necessary for the neural plate to fold in forming the neural tube and Shroom3 is further needed to close the neural plate? So since both Plekhg5 and Shroom3 are used in forming the neural tube, injecting the mRNA will just lead to neural tube deformity?arrow_forward
- Can I get this answered with the colors and what type of connection was formed? Hydrophobic, ionic, or hydrogen.arrow_forwardCan I please get this answered with the colors and how the R group is suppose to be set up. Thanksarrow_forwardfa How many different gametes, f₂ phenotypes and f₂ genotypes can potentially be produced from individuals of the following genotypes? 1) AaBb i) AaBB 11) AABSC- AA Bb Cc Dd EE Cal bsm nortubaarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





