
Concept explainers
a
To sketch: a line which shows a set of points equidistant from F and T as shown in the figure below.

a
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Points F, T and P are shown as below in the diagram and a sketch has to be made of a line that specifies a set of points which are equidistant from F and T.

Sketch: Take a centimeter ruler and find a point midway between F and T and mark it. Now draw a line through that point perpendicular to the line joining F and T, which is the required line.
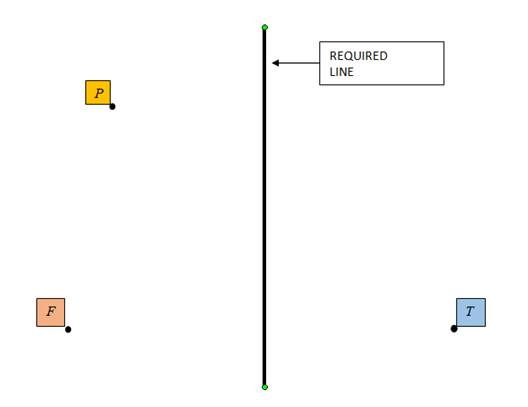
Interpretation: The required line is equidistant from points F and T which can be checked using a centimeter ruler.
b
To sketch: a

b
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Points F, T and P are shown as below in the diagram and a sketch has to be made of a circle whose radius is 6 cm and the center is at P as shown below.

Sketch: Use a ruler to set the distance from the point of the compass needle to the pencil's lead at 6 cm. Place the compass needle at P and rotate it about 360 degrees. The required object in the plane is a circle of radius 6 cm.
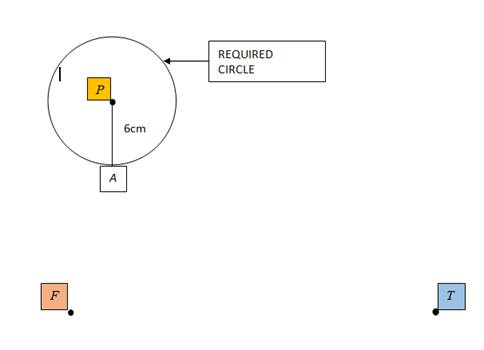
Interpretation: The circle so formed has a radius of 6 cm which can be checked by a centimeter ruler.
c
To sketch: the points 6 cm from P which are equidistant from F and T as shown in the figure below,

c
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Points F,T and P are shown as below in the diagram; it is to be found that how many points are equidistant from F and T and are also 6 cm away from P.

Graph: Take a centimeter ruler and find a point midway between F and T and mark it. Now draw a line through that point perpendicular to the line joining F and T. Use a ruler to set the distance from the point of the compass needle to the pencil's lead at 6 cm. Place the compass needle at P and rotate it about 360 degrees. The required object in the plane is a circle of radius 6 cm.
So there are two points of intersection as a result.
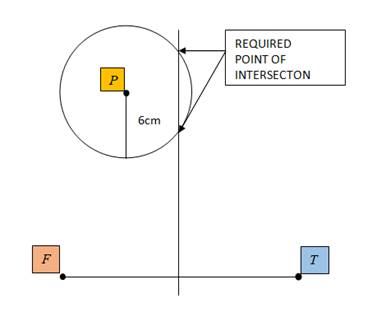
Interpretation: There are two points which are equidistant from F and T and also 6 cm away from P.
Chapter 1 Solutions
McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Intro Stats, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
- 5. 156 m/WXY = 59° 63 E 7. B E 101 C mFE = 6. 68° 8. C 17arrow_forward1/6/25, 3:55 PM Question: 14 Similar right triangles EFG and HIJ are shown. re of 120 √65 adjacent E hypotenuse adjaca H hypotenuse Item Bank | DnA Er:nollesup .es/prist Sisupe ed 12um jerit out i al F 4 G I oppe J 18009 90 ODPO ysma brs & eaus ps sd jon yem What is the value of tan J? ed on yem O broppo 4 ○ A. √65 Qx oppoEF Adj art saused taupe ed for yem 4 ○ B. √65 29 asipnisht riod 916 zelprisht rad √65 4 O ○ C. 4 √65 O D. VIS 9 OD elimiz 916 aelonsider saused supsarrow_forwardFind all anglesarrow_forward
- Find U V . 10 U V T 64° Write your answer as an integer or as a decimal rounded to the nearest tenth. U V = Entregararrow_forwardFind the area of a square whose diagonal is 10arrow_forwardDecomposition geometry: Mary is making a decorative yard space with dimensions as shaded in green (ΔOAB).Mary would like to cover the yard space with artificial turf (plastic grass-like rug). Mary reasoned that she could draw a rectangle around the figure so that the point O was at a vertex of the rectangle and that points A and B were on sides of the rectangle. Then she reasoned that the three smaller triangles resulting could be subtracted from the area of the rectangle. Mary determined that she would need 28 square meters of artificial turf to cover the green shaded yard space pictured exactly.arrow_forward
- 7. 11 m 12.7 m 14 m S V=B₁+ B2(h) 9.5 m 16 m h+s 2 na 62-19 = 37 +, M h² = Bu-29arrow_forwardwhat would a of a interscribed angle be with an arc of 93 degrees and inside abgles of 111 and 98arrow_forwardPlease complete through GeoGebra and present the screenshots of the results. Thanks! (This supports on how to submit it.)arrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

