
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the following molecule has a liquid crystalline phase or not should be determined.
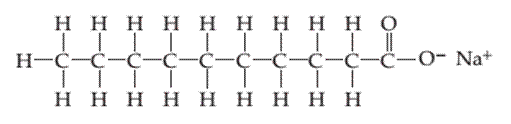
Concept introduction:
Liquid crystals are defined as a phase in which substance exhibits properties of both liquids and solids. Liquid crystal flow like a liquid but their arrangement of the molecule as well as intermolecular forces is like solid.
Liquid crystal molecules are made up of six-membered rings with on terminal polar group, a linkage group and a side chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in liquid crystal molecules has trigonal planar geometry.
The molecules are rigid. The rigidity is increased due to the presence of double-bonded linkage groups such as
The terminal polar groups exhibit strong intermolecular forces such as strong dipole-dipole interaction or dipole−induced dipole interaction and hydrogen bond.
Types of liquid crystal are as follows:
- Nematic Liquid crystal.
- Smectic Liquid crystal.
1. Nematic Liquid crystal: The molecules in the nematic phase are in the same direction and can move around freely very much like that of liquid. In this, the axis is parallel but the ends are not aligned.
2. Smectic Liquid crystal: The molecules in the smectic phase are perpendicular to the plane and are aligned in layers. In these, the long axis is parallel and also their ends are aligned.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the following molecule has a liquid crystalline phase or not should be determined.
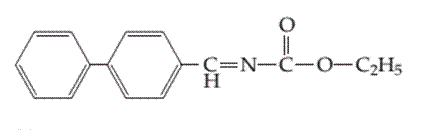
Concept introduction:
Liquid crystals are defined as a phase in which substance exhibits properties of both liquids and solids. Liquid crystal flow like a liquid but their arrangement of the molecule as well as intermolecular forces is like solid.
Liquid crystal molecules are made up of six-membered rings with on terminal polar group, a linkage group and a side chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in liquid crystal molecules has trigonal planar geometry.
The molecules are rigid. The rigidity is increased due to the presence of double-bonded linkage groups such as
The terminal polar groups exhibit strong intermolecular forces such as strong dipole-dipole interaction or dipole−induced dipole interaction and hydrogen bond.
Types of liquid crystal are as follows:
- Nematic Liquid crystal.
- Smectic Liquid crystal.
1. Nematic Liquid crystal: The molecules in the nematic phase are in the same direction and can move around freely very much like that of liquid. In this, the axis is parallel but the ends are not aligned.
2. Smectic Liquid crystal: The molecules in the smectic phase are perpendicular to the plane and are aligned in layers. In these, the long axis is parallel and also their ends are aligned.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the following molecule has a liquid crystalline phase or not should be determined.
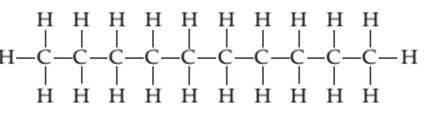
Concept introduction:
Liquid crystals are defined as a phase in which substance exhibits properties of both liquids and solids. Liquid crystal flow like a liquid but their arrangement of the molecule as well as intermolecular forces is like solid.
Liquid crystal molecules are made up of six-membered rings with on terminal polar group, a linkage group and a side chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in liquid crystal molecules has trigonal planar geometry.
The molecules are rigid. The rigidity is increased due to the presence of double-bonded linkage groups such as
The terminal polar groups exhibit strong intermolecular forces such as strong dipole-dipole interaction or dipole−induced dipole interaction and hydrogen bond.
Types of liquid crystal are as follows:
- Nematic Liquid crystal.
- Smectic Liquid crystal.
1. Nematic Liquid crystal: The molecules in the nematic phase are in the same direction and can move around freely very much like that of liquid. In this, the axis is parallel but the ends are not aligned.
2. Smectic Liquid crystal: The molecules in the smectic phase are perpendicular to the plane and are aligned in layers. In these, the long axis is parallel and also their ends are aligned.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
CHEMISTRY-TEXT
- Can you explain how I get these here and show the steps plz?arrow_forwardGive the IUPAC name for this compound Hydrocarbon Condensed Formulas Hint C2H5 CH2CH3 expand that in all the formula Part A: (CH3)2CHCH(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part B: CH2=C(C2H5)CH2CH2CH3 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part C: (CH3)2C=CHC(C2H5)=CH2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part D: CH3C=CCH(C2H5)2 Give the IUPAC name for this compound. Part E: (CH3)3CC=CCH2CH=C(CH3)2arrow_forwardSelect/ Match the correct letter from the image below for the IUPAC names given below: A B C D 3 E F G H K L Part 1. 4-methylheptane For example.mmmm Answer Letter H _for part 1 Part 2. 2,4-dimethylhexane Part 3. 2,3-dimethylpentane Part 4. 2,2-dimethylhexane Part 5. 2-ethyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethylcyclopentane Part 6. 3-ethyl-2-methylpentanearrow_forward
- Can u show the process as to how to get these?arrow_forwardSketch the expected 'H NMR spectra for the following compound. Label all of the H's in the structure and the corresponding signal for the spectra you sketch. Make sure you include the integration value and the splitting pattern for each signal Indicate how many signals you would expect in the 13C NMRarrow_forwardUse IUPAC naming rules to name the following hydrocarbon compounds: CH2-CH3 | a) CH-CH-CH2-CH-CH-CH3 b) | CH2 CH3 | CH3 CH3 \ / C=C H 1 H CH2-CH3 c) d) CH=C-CH3 e) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 f) CH2=CH-CH2-CH=CH-CH3 g) CH3-CH2-C = C-CH2-CH3 h)arrow_forward
- Q5 Name the following : a. b. C. d. e.arrow_forward25. Predict the major product of the following reaction. 1 equivalent of each of the starting materials was used. H₂C CH3 CH3 H3C H3C H3C. CH2 + H3C. heat CH3 CH H.C. CH3 H.C H.C CH3 CH CH3 CH3 A B C Earrow_forwardFind chemical structures based on the below information. a) Chemical formula C6H8O Compound is aromatic plus has two 1H NMR peaks that integrated for 3 each that are singlets (it could have more peaks in the 1H NMR b) Chemical Formula: C6H100 Compounds is conjugated 'H NMR has a signal that integrates for 6 and is a doublet IR spectra has a signal at 1730 cm-1arrow_forward
- Jaslev Propose a synthesis of the following starting from benzene and any other reagents and chemicals. No mechanisms are required. Indicate the condition for each step plus the major product for each step. More than two steps are required. Step 1 Step 2 مہد Brarrow_forwardPart C: The line formula for another branched alkane is shown below. i. In the IUPAC system what is the root or base name of this compound? ii. How many alkyl substituents are attached to the longest chain? iii. Give the IUPAC name for this compound.arrow_forwardPart D: Draw the Structural Formula for 4-ethyl-2-methylhexane Part E. Draw the Structural Formula for 1-chloro-3,3-diethylpentane (Chloro = Cl)arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





