
Organic Chemistry
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780073402772
Author: Janice G. Smith
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 11.64P
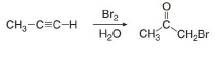
Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following reaction.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4:45 PM Tue Apr 1
K
77%
Problem 9 of 10
Submit
Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting structure, draw the
curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).
Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Then draw any missing organic
intermediates or products for this reaction.
Include all lone pairs in the structures. Ignore inorganic byproducts, counterions, and solvents.
:0:
H
Select to Add Arrows
HI
CH3OH
H+
·HO
CH3OH, H+
0:0
H
H
Select to Add Arrows
tion
Versirate
CH3OH, H*
Select to Draw Product
Can I please get help with this graph? If you can show exactly where it needs to pass through.
G
1.
PPh3, THF
2.
3.
LiH, THF
'
THF
H
H
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Ch. 11 - Draw structures for the three alkynes having...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.2PCh. 11 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound.Ch. 11 - Give the structures corresponding to each of the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.5PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.6PCh. 11 - Which bases can deprotonate acetylene? The pKa...Ch. 11 - Draw the organic products formed when each alkyne...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.9PCh. 11 - Problem 11.9 Draw the products formed when is...
Ch. 11 - Explain the following result. Although alkenes...Ch. 11 - Problem 11.11 Draw the keto tautomer of each...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.13PCh. 11 - a Draw two different enol tautomers of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.15PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.16PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.17PCh. 11 - Problem. 11.17 Show how , and can be used to...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.19PCh. 11 - Draw the products of each reaction. a. b.Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.21PCh. 11 - Problem 11.21 Use retrosynthetic analysis to show...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.23PCh. 11 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a. b.Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.25PCh. 11 - 11.25 Answer the following questions about...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.27PCh. 11 - Give the IUPAC name for each alkyne.Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.29PCh. 11 - Which of the following pairs of compounds...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.31PCh. 11 - 11.30 How is each compound related to A? Choose...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.33PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.34PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.35PCh. 11 - 11.33 Draw the products formed when is treated...Ch. 11 - Draw the products formed when 3-hexyne is treated...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.38PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.39PCh. 11 - What alkynes give each of the following ketones as...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.41PCh. 11 - 11.37 What alkyne gives each compound as the only...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.43PCh. 11 - Draw the structure of compounds A-E in the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.45PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.46PCh. 11 - 11.42 What reactions are needed to convert alcohol...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.48PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.49PCh. 11 - 11.45 Explain the following statement. Although ...Ch. 11 - Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.52PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.53PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.54PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.55PCh. 11 - Synthesize each compound from acetylene. You may...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.57PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.58PCh. 11 - 11.55 Devise a synthesis of the ketone, , from ...Ch. 11 - 11.56 Devise a synthesis of each compound using ...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.61PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.62PCh. 11 - 11.60 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 11 - Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.65PCh. 11 - Write a stepwise mechanism for each of the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.67PCh. 11 - 11.65 Explain why an optically active solution of ...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please EnCircle or Fill-In your Choice CLEARLY: 21. Please Sketch the intermediates for each step below. Draw the Product which would result from the following series of reactions. Name each Type of Rx: 1. Br2, FeBr3 2. Mg, ether 3. ethylene oxide 4. H₂O+ 5. PBr3 6. Mg, ether 7. 8. H3O+, heat (-H₂O 9. HF ?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this question. All required information should be in data table.arrow_forwardesc For the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. Major Product: Explanation Check C ☐ + X NaOH Br F1 F2 80 F3 F4 F5 F6 1 ! @ 2 3 $ 4 % 5 Q W LU E S D A F7 * C Click and dr drawing a 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserv ►II F8 4 F9 6 7 8 9 R T Y U LL F G H Jarrow_forward
- Calculate equilibrium concentrations for the following reaction:N2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇋ 2 NO (g) Kc = 0.10 at 2273K initially [N2] = 0.200M; [O2] = 0.200arrow_forwardFor each scenario below, select the color of the solution using the indicator thymol blue during the titration. When you first add indicator to your Na2CO3solution, the solution is basic (pH ~10), and the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . At the equivalence point for the titration, the moles of added HCl are equal to the moles of Na2CO3. One drop (or less!) past this is called the endpoint. The added HCl begins to titrate the thymol blue indicator itself. At the endpoint, the indicator color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you weren't paying attention and added too much HCl (~12 mL extra), the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you really weren't paying attention and reached the second equivalence point of Na2CO3, the color isarrow_forwardThe following reaction is run in which the initial conditions include only methane (CH4) at a concentration of0.115 M. Once equilibrium was established, the concentration of acetylene (C2H2) was measured to be 0.035M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K?2 CH4 (g) ⇋ C2H2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)arrow_forward
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration of carbon dioxide for the following reaction:2 COF2 (g) ⇋ CF4 (g) + CO2 (g) Kc = 2.00 at 10.00 °C. at equilibrium [COF2] = 0.255M; [CF4] = 0.118Marrow_forwardIn a benzene derivative that has -CH2CH3, indicate how it can be substituted by -COOH.arrow_forwardIn a sulfonated derivative of benzene, indicate how -SO3H can be eliminated.arrow_forward
- What is the equilibrium expression (law of mass action) for the following reaction:CO2 (g) + H2O (l) ⇋ H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)arrow_forwardIndicate the compound resulting from adding NaOH cyclopentane-CH2-CHO.arrow_forwardUse the provided information to calculate Kc for the following reaction at 550 °C: H2(g) + CO2(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2O(g) Kc = ?CoO(s) + CO(g) ⇌ Co(s) + CO2(g) Kc1 = 490CoO(s) + H2(g) ⇌ Co(s) + H2O(g) Kc2 = 67arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Nomenclature: Crash Course Chemistry #44; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7wavimfNFE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY