
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product obtained by the reaction of the given
Concept Introduction:
Hydrogenation reaction is nothing but the addition of hydrogen to an alkene. In this reaction two bonds are simultaneously broken, one is carbon-carbon double bond, and second one is hydrogen-hydrogen bond, finally forms two carbon-hydrogen bonds. The general reaction can be represented as follows,
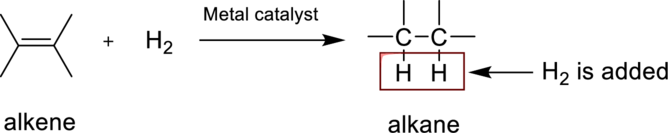
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained by the reaction of the given alkene with hydrogen and palladium catalyst has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Interpretation:
The product obtained by the reaction of the given alkene with hydrogen and palladium catalyst has to be identified.
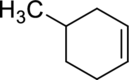
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Interpretation:
The product obtained by the reaction of the given alkene with hydrogen and palladium catalyst has to be identified.
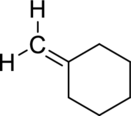
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
- Rank the labeled protons (Ha-Hd) in order of increasing acidity, starting with the least acidic. НОН НЬ OHd Онсarrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? ? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C :0 T Add/Remove step Garrow_forwardThe following equations represent the formation of compound MX. What is the AH for the electron affinity of X (g)? X₂ (g) → 2X (g) M (s) → M (g) M (g) M (g) + e- AH = 60 kJ/mol AH = 22 kJ/mol X (g) + e-X (g) M* (g) +X (g) → MX (s) AH = 118 kJ/mol AH = ? AH = -190 kJ/mol AH = -100 kJ/mol a) -80 kJ b) -30 kJ c) -20 kJ d) 20 kJ e) 156 kJarrow_forward
- A covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forwardWhich one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forward
- All of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





