
Concept explainers
What
a. 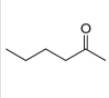 b
b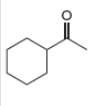 . c.
. c. 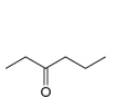 d.
d. 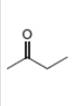
(a)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.36P
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
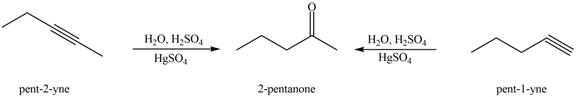
Figure 1
The terminal alkynes,
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
(b)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.36P
The alkyne that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkyne that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
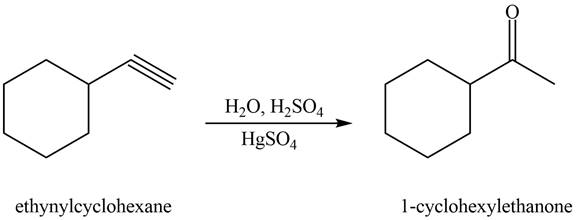
Figure 2
The terminal alkyne, ethynylcyclohexane reacts with the reagents
The alkyne that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
(c)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.36P
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
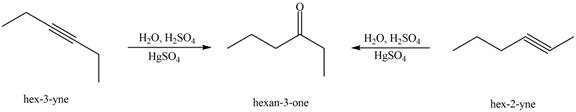
Figure 3
The terminal alkynes,
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
(d)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.36P
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
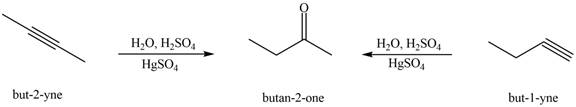
Figure 4
The terminal alkynes,
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Loose Leaf For Integrated Principles Of Zoology
Organic Chemistry
- Using what we have learned in CHEM 2310 and up through class on 1/31, propose a series of reaction steps to achieve the transformation below. Be sure to show all reagents and intermediates for full credit. You do not need to draw mechanism arrows, but you do need to include charges where appropriate. If you do not put your group name, you will get half credit at most. ? Brarrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the formation of 2-bromovanillin using bromonium ion as the reactive electrophile.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





