
Concept explainers
The relative rate of radical bromination is 1;82;1640 for 1°;2°;3° hydrogens, respectively. Draw all of the monobrominated products that you might obtain from the radical bromination of the compounds below. Calculate the relative percentage of each.
(a) methylcyclobutane
(b) 3,3-dimethylpentane
(c) 3-methylpentane
a) Methylcyclobutane
Interpretation:
The relative rate of radical bromination is 1:82:1640 for 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens respectively. The structures of all the monobrominated products obtainable from the radical bromination of methylcyclobutane are to be drawn. The relative percentage of their formation is also to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
During radical bromination all types of hydrogens present in a compound are replaced by bromine to yield different products. The number of each type of hydrogen present in the compound and their relative rates of bromination are calculated seperately. The relative percentage of formation of a particular type of hydrogen can be calculated from the total rate of bromination of all types of hydrogens and that of the particular hydrogen.
To draw:
The structures of all the monobrominated products obtainable from the radical bromination of methylcyclobutane.
To calculate:
The relative percentage of formation of each monobromination product.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Four different monochlorination products are possible by the radical bromination of methylcyclohexane. They are bromomethylcyclobutane(I), 1-bromo-1-methylcyclobutane(II), 1-bromo-2-methylcyclobutane(III) and 1-bromo-3-methylcyclobutane(IV).
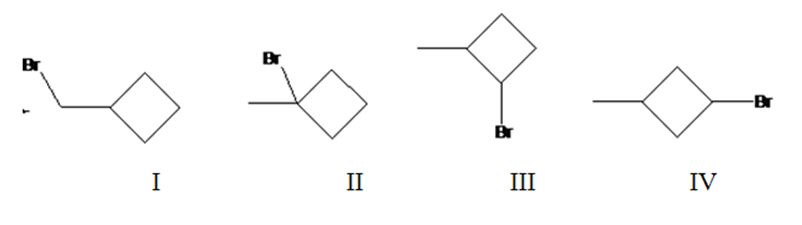
The relative percentage of 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens in methylcyclobutane is 0.15: 23.1: 76.8.
Explanation of Solution
Methylcyclobutane has four types of hydrogens, one in methyl, a second on C1 to which methyl group is attached, a third one on C2 and C4 and a fourth one on C3. It has three 1° hydrogens, six 2° hydrogens and one 3° hydrogen. Hence four monochlorination products are possible.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 1° hydrogens = 3 x 1 = 3.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 2° hydrogens = 6 x 82 = 492.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 3° hydrogens = 1 x 1640 = 1640.
Total rate of radical bromonation of all hydrogens = 3+492+1640 = 2135.
Therefore the relative percentage of
Radical bromonation of 1° hydrogens = 3/2135 x 100= 0.15%.
Radical bromonation of 2° hydrogens = 492/2135 x 100= 23.1%.
Radical bromonation of 3° hydrogens = 1640/2135 x 100= 76.8%.
Four different monochlorination products are possible by the radical bromination of methylcyclohexane. They are bromomethylcyclobutane(I), 1-bromo-1-methylcyclobutane(II), 1-bromo-2-methylcyclobutane(III) and 1-bromo-3-methylcyclobutane(IV).

The relative percentage of 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens in methylcyclobutane is 0.15: 23.1: 76.8.
b) 3,3-dimethylpentane
Interpretation:
The relative rate of radical bromination is 1:82:1640 for 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens respectively. The structures of all the monobrominated products obtainable from the radical bromination of 3,3-dimethylpentane are to be drawn. The relative percentage of their formation is also to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
During radical bromination all types of hydrogens present in a compound are replaced by bromine to yield different products. The number of each type of hydrogen present in the compound and their relative rates of bromination are calculated seperately. The relative percentage of formation of a particular type of hydrogen can be calculated from the total rate of bromination of all types of hydrogens and that of the particular hydrogen.
To draw:
The structures of all the monobrominated products obtainable from the radical bromination of 3,3-dimethylpentane.
To calculate:
The relative percentage of formation of each monobromination product.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Three different monochlorination products are possible by the radical bromination of 3-bromomethyl-3-methylpentane. They are bromomethylcyclobutane(I), 2-bromo-3,3-dimethylpentane(II) and 1-bromo-3,3-dimethylpentane (III).
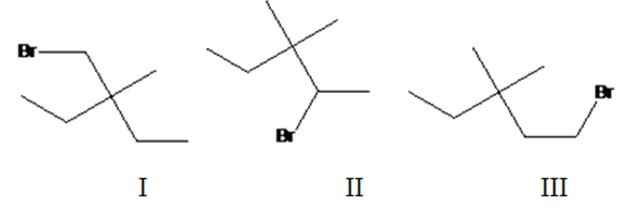
The relative percentage of 10and 20 hydrogens in 3,3-dimethylpentane is 3.6:96.4.
Explanation of Solution
3,3-Dimethylpentane has two types of hydrogens, one in methyl groups and other in CH2 attached to methyl group. Hence two monochlorination products are possible. It has twelve 1° hydrogens and four 2° hydrogen atoms.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 1° hydrogens = 12 x 1 = 12.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 2° hydrogens = 4 x 82 = 328.
Total rate of radical bromonation of all hydrogens = 12+328 = 340.
Therefore the relative percentage of
Rdical bromonation of 1° hydrogens = 12/340 x 100= 3.6%.
Rdical bromonation of 2° hydrogens = 328/340 x 100=96.4%.
Three different monochlorination products are possible by the radical bromination of 3-bromomethyl-3-methylpentane. They are bromomethylcyclobutane(I), 2-bromo-3,3-dimethylpentane(II) and 1-bromo-3,3-dimethylpentane (III).

The relative percentage of 1° and 2° hydrogens in 3,3-dimethylpentane is 3.6:96.4.
c) 3-methylpentane
Interpretation:
The relative rate of radical bromination is 1:82:1640 for 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens respectively. The structures of all the monobrominated products obtainable from the radical bromination of 3-methylpentane are to be drawn. The relative percentage of their formation is also to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
During radical bromination all types of hydrogens present in a compound are replaced by bromine to yield different products. The number of each type of hydrogen present in the compound and their relative rates of bromination are calculated seperately. The relative percentage of formation of a particular type of hydrogen can be calculated from the total rate of bromination of all types of hydrogens and that of the particular hydrogen.
To draw:
The structures of all the monobrominated products obtainable from the radical bromination of 3-methylpentane.
To calculate:
The relative percentage of formation of each monobromination product.
Answer to Problem 48AP
Four different monochlorination products are possible by the radical bromination of 3-methylpentane. They are bromomethylpentane(I), 3-bromo-3-methylpentane(II), 2-bromo-3-methylpentane(III) and 1-bromo-3-methylpentane(IV).
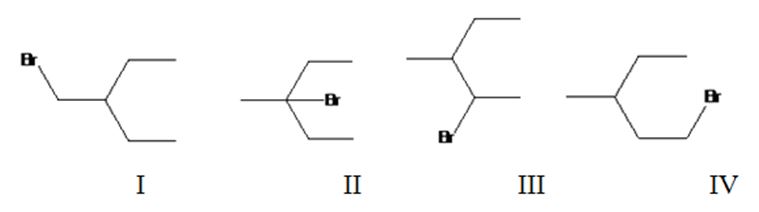
The relative percentage of 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens in 3,3-dimethylpentane is 0.46:16.6:82.9.
Explanation of Solution
3,3-Dimethylpentane has four types of hydrogens, one in methyl at C1, another methyl groups attached to CH2, a third in C2 and a fourth in CH2. It has nine 1° hydrogens, four 2° hydrogens and one 3° hydrogen. Hence four monochlorination products are possible.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 1° hydrogens = 9 x 1 = 9.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 2° hydrogens = 4 x 82 = 328.
The relative rate of radical bromonation of 3° hydrogens = 1 x 1640 = 1640.
Total rate of radical bromonation of all hydrogens = 9+328+1640 = 1977.
Therefore the relative percentage of
Radical bromonation of 1° hydrogens = 9/1977x100= 0.46%.
Radical bromonation of 2° hydrogens = 328/1977x100= 16.6%.
Radical bromonation of 3° hydrogens = 1640/1937x100= 82.9%.
Four different monochlorination products are possible by the radical bromination of 3-methylpentane. They are bromomethylpentane(I), 3-bromo-3-methylpentane(II), 2-bromo-3-methylpentane(III) and 1-bromo-3-methylpentane(IV).

The relative percentage of 1°, 2° and 3° hydrogens in 3,3-dimethylpentane is 0.46:16.6:82.9.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
