
(a)
Interpretation:
The constitutional isomer, which is formed greatest yield in the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction, for example
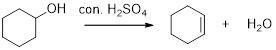
Alcohols are react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic to yields the corresponding carbocation intermediates, this carbocation intermediate undergoes elimination reaction to give a corresponding
The stability of carbocation is given below,
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary and primary.
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The
The functional groups are in opposite to each other in the carbon chain is called trans isomer.
Two similar functional groups are in same side which is called as Z-isomer.
Two similar functional groups are opposite side which is called as E-isomer.
Stereoisomers: same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space.
(b)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer, which is formed greatest yield in the given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction, for example
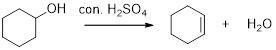
Alcohols are react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic to yields the corresponding carbocation intermediates, this carbocation intermediate undergoes elimination reaction to give a corresponding alkene as a product.
The stability of carbocation is given below,
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary and primary.
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
The functional groups are in the same side of the carbon chain is called cis isomer.
The functional groups are in opposite to each other in the carbon chain is called trans- isomer.
Two similar functional groups are in same side which is called as Z-isomer.
Two similar functional groups are opposite side which is called as E-isomer.
Stereoisomers: same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Pearson eText Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- Feedback (7/10) Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining Ο (CH3CH2)2NH, TSOH Select to Draw V N. 87% Retryarrow_forwardIf I want to obtain (1,1-dipropoxyethyl)benzene from 1-bromopropene, indicate the product that I have to add in addition to NaOH.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when fluorobenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when chlorobenzene acid reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting benzenesulfonic acid with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting ethylbenzene with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained when tert-butylbenzene reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained when acetophenone reacts with a sulfonitric acid mixture (HNO3 + H2SO4). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile with a sulfonitric mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained in the reaction of p-Toluidine with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained from the reaction of 4-methylbenzonitrile with a sulfonitric acid mixture (H2SO4 + HNO3). Indicate the majority if necessary.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


