
Concept explainers
A steel tube of 80-mm outer diameter is to carry a 93-kN load P with an eccentricity of 20 mm. The tubes available for use are made with wall thicknesses in increments of 3 mm from 6 mm to 15 mm. Using the allowable-stress method, determine the lightest tube that can be used. Assume E = 200 GPa and σY = 250 MPa.
Fig. P10.105
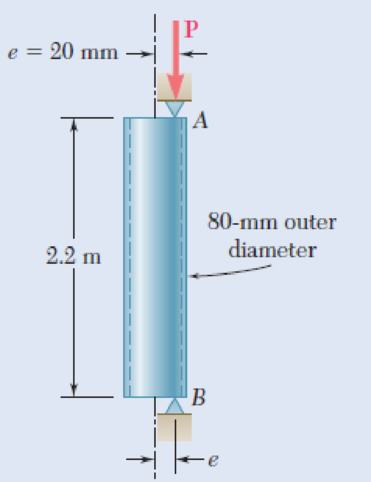
Find the thickness of the lightest tube.
Answer to Problem 105P
The thickness of the lightest steel tube is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The length of the steel tube is
The outer diameter of the steel tube is
The magnitude of the axial load is
The eccentricity of the load in steel tube is
The allowable yield stress of the steel tube is
The modulus of elasticity of the steel tube is
Calculation:
The effective length of the column
Find the inner diameter of the steel tube
Here, the thickness of the steel tube is t.
Substitute 80 mm for
Find the cross sectional area of the steel tube (A) using the equation.
Substitute 80 mm for
Find the moment of inertia of the steel tube (I) using the equation.
Substitute 80 mm for
Find the minimum radius of gyration (r) using the relation.
Substitute
Find the distance between the neutral axis to the extreme fibre (c) using the relation.
Substitute 80 mm for
Find the slenderness ratio
Here, the modulus of elasticity of the material is E and the allowable yield strength is
Substitute 200 GPa for E and 250 MPa for
Find the ratio of the effective length to the minimum radius of gyration.
Consider
Find the effective stress
Substitute 200 GPa for E and
Find the critical stress
Substitute 250 MPa for
Find the allowable stress
Substitute
Find the maximum moment (M) using the relation.
Here, the allowable load is P and the eccentricity of the load is e.
Substitute 93 kN for P and 20 mm for e.
Find the thickness of the lightest tube (t) using the equation.
Substitute
Solve the equation;
The thickness is
The nearest 3 mm increment of the thickness is 12 mm.
Check:
Substitute 12 mm for t in Equation (1).
Therefore, the thickness of the lightest steel tube is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Problem 3.21P: Air at 100F(38C) db,65F(18C) wb, and sea-level pressure is humidified adiabatically with steam. The steam supplied contains 20 percent moisture(quality of 0.80) at 14.7psia(101.3kpa). The air is humidified to 60 percent relative humidity. Find the dry bulb temperature of the humidified air using (a)chart 1a or 1b and (b) the program PSYCH.arrow_forwardPUNTO 4. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 5. Groundarrow_forwardPUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. III IAarrow_forward
- calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7. (Ctrl)arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.given that: summation of K gate valve = 0.25check valve=390 degree elbow= 0.75foot valve= 0.78arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.arrow_forward
- The tensile 0.2 percent offset yield strength of AISI 1137 cold-drawn steel bars up to 1 inch in diameter from 2 mills and 25 heats is reported as follows: Sy 93 95 101 f 97 99 107 109 111 19 25 38 17 12 10 5 4 103 105 4 2 where Sy is the class midpoint in kpsi and fis the number in each class. Presuming the distribution is normal, determine the yield strength exceeded by 99.0% of the population. The yield strength exceeded by 99.0% of the population is kpsi.arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardI tried to go through this problem but I don't know what I'm doing wrong can you help me?arrow_forward
- Generate the kinematic diagram of the following mechanisms using the given symbols. Then, draw their graphs and calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. !!!arrow_forwardCreate a schematic representation of the following mechanisms using the given symbols and draw their graphs. Then, calculate their degrees of freedom (DoF) using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7.arrow_forwardhow the kinematic diagram of the following mechanisms would be represented using the given symbols? PUNTO 0. PUNTO 1. °arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





