
Essential University Physics Volume 1, Loose Leaf Edition (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780135264669
Author: Richard Wolfson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 65P
A disk of radius R has an initial mass M. Then a hole of radius R/4 is drilled, with its edge at the disk center (Fig. 10.29). Find the new rotational inertia about the central axis. (Hint: Find the rotational inertia of the missing piece, and subtract it from that of the whole disk. You’ll Find the parallel-axis theorem helpful.)
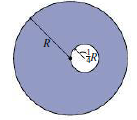
FIGURE 10.29 Problems 65 and 70
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Suppose you exert a force of 192 N tangential to a 0.255 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at
least 2 decimal places.)
(a) What torque (in N· m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.)
N. m
(b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.)
rad/s2
(c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) if there is an opposing frictional force of 20.6N exerted 3.00 cm from the axis?
(Enter the magnitude.)
rad/s2
A square metal plate 0.180 m on cach side is pivoted about
an axis through point O at its center and perpendicular to the plate
(Fig. 10.39). Calculate the net torque about this axis due to the
three forces shown in the figure if the magnitudes of the forces are
F = 18.0 N, F2 = 26.0 N, and F3 = 14.0 N. The plate and all
forces are in the plane of the page.
F1
0.180 m
45°
0.180 m
Suppose you exert a force of 227 N tangential to a 0.295 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.)
(a) What torque (in N · m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.)
N.m
(b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.)
rad/s2
(c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) if there is an opposing frictional force of 22.6 N exerted 2.50 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.)
rad/s2
Chapter 10 Solutions
Essential University Physics Volume 1, Loose Leaf Edition (4th Edition)
Ch. 10.1 - A wheel undergoes constant angular acceleration,...Ch. 10.2 - The forces in Figs. 10.5 and 10.6 all have the...Ch. 10.3 - Would the rotational inertia of the two-mass...Ch. 10.3 - Explain why the rotational inertia of the solid...Ch. 10.3 - The figure shows two identical masses m connected...Ch. 10.4 - A wheel is rotating at 100 rpm. To spin it up to...Ch. 10.5 - The wheels of trains, subway cars, and other rail...Ch. 10 - Do all points on a rigid, rotating object have the...Ch. 10 - A point on the rim of a rotating wheel has nonzero...Ch. 10 - Why doesnt it make sense to talk about a bodys...
Ch. 10 - Two forces act on an object, but the net force is...Ch. 10 - Is it possible to apply a counterclockwise torque...Ch. 10 - A solid sphere and a hollow sphere of the same...Ch. 10 - A solid cylinder and a hollow cylinder of the same...Ch. 10 - A circular saw lakes a long time to stop rotating...Ch. 10 - A solid sphere and a solid cube have the same...Ch. 10 - The lower part of a horses leg contains...Ch. 10 - Given a fixed amount of a material, what shape...Ch. 10 - A ball starts from rest and rolls without slipping...Ch. 10 - Exercises and Problems Exercises Section 10.1...Ch. 10 - Whats the linear speed of a point (a) on Earths...Ch. 10 - Express each of the following in radians per...Ch. 10 - A 25-cm-diameter circular saw blade spins at 3500...Ch. 10 - A compact discs rotation varies from about 200 rpm...Ch. 10 - During startup, a power plants turbine accelerates...Ch. 10 - A merry-go-round starts front rest and accelerates...Ch. 10 - Section 10.2 Torque A 320-N frictional force acts...Ch. 10 - A 110-N m torque is needed to start a revolving...Ch. 10 - A car tune-up manual calls for tightening the...Ch. 10 - A 55-g mouse runs out to the end of the 17-cm-long...Ch. 10 - You have your bicycle upside down for repairs. The...Ch. 10 - Section 10.3 Rotational Inertia and the Analog of...Ch. 10 - The shaft connecting a power plants turbine and...Ch. 10 - The chamber of a rock-tumbling machine is a hollow...Ch. 10 - A wheels diameter is 92 cm, and its rotational...Ch. 10 - Three equal masses m are located at the vertices...Ch. 10 - (a) Estimate Earths rotational inertia, assuming...Ch. 10 - A neutron star is an extremely dense, rapidly...Ch. 10 - A 108-g Frisbee is 24 cm in diameter and has half...Ch. 10 - At the MIT Magnet Laboratory, energy is stored in...Ch. 10 - Section 10.4 Rotational Energy A 25-cm-diameter...Ch. 10 - Humankind uses energy at the rate of about 16 TW....Ch. 10 - A 150-g baseball is pitched at 33 m/s spinning at...Ch. 10 - (a) Find the energy stored in the flywheel of...Ch. 10 - A solid 2.4-kg sphere is rolling at 5.0 m/s. Find...Ch. 10 - What fraction of a solid disks kinetic energy is...Ch. 10 - A rolling ball has total kinetic energy 100 J, 40...Ch. 10 - A wheel turns through 2.0 revolutions while...Ch. 10 - Youre an engineer designing kitchen appliances,...Ch. 10 - An eagle with 2.1-m wingspan flaps its wings 20...Ch. 10 - A compact disc (CD) player varies the rotation...Ch. 10 - You rev your cars engine and watch the tachometer...Ch. 10 - A circular saw spins at 5800 rpm, and its...Ch. 10 - Full-circle rotation is common in mechanical...Ch. 10 - A pulley 12 cm in diameter is free to rotate about...Ch. 10 - A square frame is made from four thin rods, each...Ch. 10 - A thick ring has inner radius 12R, outer radius R,...Ch. 10 - A uniform rectangular flat plate has mass M and...Ch. 10 - Each propeller on a King Air twin-engine airplane...Ch. 10 - The cellular motor driving the flagellum in E....Ch. 10 - Verify by direct integration Table 10.2s entry for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 55PCh. 10 - A skaters body has rotational inertia 4.2 kgm2...Ch. 10 - A 2.4-kg block rests on a slope and is attached by...Ch. 10 - Youve got your bicycle upside down for repairs,...Ch. 10 - A potters wheel is a stone disk 90 cm in diameter...Ch. 10 - A ships anchor weighs 5.0kN. Its cable passes over...Ch. 10 - Starting from rest, a hollow ball rolls down a...Ch. 10 - A hollow ball rolls along a horizontal surface at...Ch. 10 - As an automotive engineer, youre charged with...Ch. 10 - A solid ball of mass M and radius R starts at rest...Ch. 10 - A disk of radius R has an initial mass M. Then a...Ch. 10 - A 50-kg mass is tied to a massless rope wrapped...Ch. 10 - Each wheel of a 320-kg motorcycle is 52 cm in...Ch. 10 - A solid marble starts from rest and rolls without...Ch. 10 - A disk of radius R and thickness w has a mass...Ch. 10 - The disk in Fig. 10.29 is rotating freely about a...Ch. 10 - Youre asked to check the specifications for a wind...Ch. 10 - In bicycling, each foot pushes on the pedal for...Ch. 10 - Calculate the rotational inertia of a solid,...Ch. 10 - A thick ring of mass M has inner radius R1 and...Ch. 10 - A thin rod of length L and mass M is free to pivot...Ch. 10 - The local historical society has asked your...Ch. 10 - Youre skeptical about a new hybrid car that stores...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.31 shows an object of mass M with one...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.32 shows an apparatus used to measure...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
8. Studies of DNA support which of the following?
a. Members of the group called australopiths were the first t...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
In your own words, briefly distinguish between relative dates and numerical dates.
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
The number of named species is about __________, but the actual number of species on Earth is estimated to be a...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
WRITE ABOUT A THEME: INTERACTIONS In Batesian mimicry, a palatable species gains protection by mimicking an unp...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a bar that extends from x = 0 m to x = 4 m. The linear mass density of the rod is given by λ(x) = 7 + 7 x (kg/m). Calculate the rotational inertia of the beam about x = 0, in kg m2. (Please answer to the fourth decimal place - i.e 14.3225)arrow_forwardBe sure to review Examples 10.11 and 10.12 (Section 10.6) before attempting these problems. Suppose that instead of hitting the center of the door, the bullet in (Figure 5) strikes the door at the edge farthest away from the hinge and embeds itself there. What is the angular speed of the door just after the bullet embeds itself? Take Vbullet = 320 m/s. Express your answer in radians per second. 1να ΑΣφ. W = rad/s Submit Request Answer Figure 5 of 5 > Part F Hinge What fraction of the initial kinetic energy of the bullet remains as kinetic energy after the collision? l= 0.50m Express your answer using two significant figures. m = 10g Bullet να ΑΣ φ. Voullet d = 1.00m M =15kg K2/K1 = Submit Request Answer Before Afterarrow_forwardSuppose you exert a force of 172 N tangential to a 0.295 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.) (a) What torque (in N · m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.) N. m (b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.) |rad/s? (c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) if there is an opposing frictional force of 22.6 N exerted 1.75 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.) |rad/s?arrow_forward
- Suppose you exert a force of 172 N tangential to a 0.295 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.) (a) What torque (in N · m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.) 50.74 N. m (b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.) 15.55 rad/s? (c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) if there is an opposing frictional force of 22.6 N exerted 1.75 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.) 15.44 ]× rad/s²arrow_forwardSuppose you exert a force of 207 N tangential to a 0.275 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.) (a) What torque (in N· m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.) N. m (b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s²) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.) |rad/s2 (c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) if there is an opposing frictional force of 24.6 N exerted 1.25 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.) rad/s2 Additional Materials O Readingarrow_forwardSuppose you exert a force of 212 N tangential to a 0.295 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.) (a) What torque (in N· m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.) N: m (b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.) rad/s2 (c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) if there is an opposing frictional force of 24.6 N exerted 2.00 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.) rad/s2arrow_forward
- Suppose you exert a force of 167 N tangential to a 0.255 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.) (a) What torque (in N m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.) 42.585 N.m (b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s²) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.) 2.44 X rad/s² (c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s²) if there is an opposing frictional force of 22.6 N exerted 1.75 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.) rad/s²arrow_forwardSuppose you exert a force of 192 N tangential to a 0.235 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.) (a) What torque (in N · m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.) N · m (b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.) rad/s2 (c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) if there is an opposing frictional force of 20.6 N exerted 2.50 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.) rad/s2arrow_forwardA hollow sphere (Icom plane, which is tilted 0 = 18.9 degrees above horizontal. The ball rolls up the incline plane, again without slipping. How far does the ball go up the plane (L) before it comes to a momentary stop? Assume there is negligible loss due to any friction in this process. MR?) of mass 1.25 kg and radius 0.151 m rolls without slipping at a speed of 8.33 m/s toward an inclined Image size: s ML Maxarrow_forward
- Suppose you exert a force of 192 N tangential to a 0.255 m radius 75.0 kg grindstone (a solid disk). (Give your answers to at least 2 decimal places.) (a)What torque (in N · m) is exerted? (Enter the magnitude.) (b) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) assuming negligible opposing friction? (Enter the magnitude.) (c) What is the angular acceleration (in rad/s2) if there is an opposing frictional force of 21.6 N exerted 2.50 cm from the axis? (Enter the magnitude.)arrow_forwardNote: 1. Mass in units of Kgs, length in unit of meters At equilibrium, the meter stick must be horizontal to ground. 3. This experiment should be performed on a flat surface. 2. Procedure: To find center of mass of the ruler Experimental setup: Part A: Prove Sum of Torques = 0 CHAR Step 1 Step 2 Step 3a Step 3 Step 1: Gently insert one end of ball bearing at the center of the Styrofoam cup as shown in step 1 Step 2: Apply tape at the center of the ruler followed by placing ruler on the ball bearing, such that the ruler is balanced. Step 3, 3a: Record center of mass, the point where the ruler is balanced is the center of mass of ruler, record the observation (indicated by arrow) The center of mass of the ruler = re = cm = CHARLYS LE Step 4 Step 4: Hang m, = 50g and m;=100g mass on the ruler with a string (see fig above) followed by gently moving m, or m, left or right on ruler, such that the meter stick is balanced as in step 2 Step 5: Find the distance ri and rz from re, record data…arrow_forwardWhat is the rotational inertia of a rod if the mass of the rod is 13.1 kg and a length of 2.5 m?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Rotational Kinetic Energy; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s5P3DGdyimI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY