
EBK MICROBIOLOGY:W/DISEASES BY BODY...-
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134608242
Author: BAUMAN
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 1VI
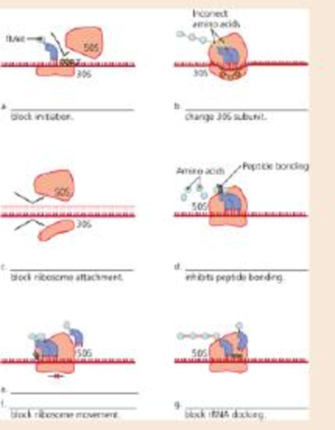
Label each figure below to indicate the class of drug that is stopping polypeptide translation.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Which of the follwowing cells from this lab do you expect to have a nucleus and why or why not? Ceratium, Bacillus megaterium and Cheek epithelial cells?
14. If you determine there to be debris on your ocular lens, explain what is the best way to
clean it off without damaging the lens?
11. Write a simple formula for converting mm to μm when the number of mm's is known. Use
the variable X to represent the number of mm's in your formula.
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK MICROBIOLOGY:W/DISEASES BY BODY...-
Ch. 10 - Prob. 1TMWCh. 10 - Some antimicrobial drugs are harmful to humans....Ch. 10 - Antibiotic Overkill A young woman was taking...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2CCSCh. 10 - Prob. 3TMWCh. 10 - Why is it incorrect to say that an individual...Ch. 10 - Prob. 1EDCSCh. 10 - Prob. 3CCSCh. 10 - Prob. 1MCCh. 10 - In a Kirby-Bauer susceptibility test, the presence...
Ch. 10 - Prob. 3MCCh. 10 - Prob. 4MCCh. 10 - Cross resistance is _____. a. the deactivation of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 6MCCh. 10 - Prob. 7MCCh. 10 - Prob. 8MCCh. 10 - Prob. 9MCCh. 10 - Prob. 10MCCh. 10 - Label each figure below to indicate the class of...Ch. 10 - What specific test for antimicrobial efficacy is...Ch. 10 - What characteristics would an ideal...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2SACh. 10 - Why is the fact that drug Z destroys the NAM...Ch. 10 - Given that both human cells and pathogens...Ch. 10 - Prob. 5SACh. 10 - Prob. 6SACh. 10 - Prob. 7SACh. 10 - Prob. 8SACh. 10 - Compare and contrast the actions of polyenes,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10SACh. 10 - Prob. 1CTCh. 10 - How does Penicillium escape the effects of the...Ch. 10 - How might a colony of Bacillus licheniformis...Ch. 10 - Fewer than 1 % of known antibiotics have any...Ch. 10 - In an issue of News of the Lepidopterists Society,...Ch. 10 - Even though aminoglycosides such as gentamicin can...Ch. 10 - Prob. 7CTCh. 10 - Prob. 8CTCh. 10 - Why might amphotericin B affect the kidneys more...Ch. 10 - Antiparasitic drugs in the benzimidazole family...Ch. 10 - Prob. 11CTCh. 10 - Scientists have cultured bacteria isolated from...Ch. 10 - Prob. 13CTCh. 10 - Prob. 14CTCh. 10 - Enterococcus faecium is frequently resistant to...Ch. 10 - Prob. 1CM
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 13. When a smear containing cells is dried, the cells shrink due to the loss of water. What technique could you use to visualize and measure living cells without heat-fixing them? Hint: you did this technique in part I.arrow_forward10. Write a simple formula for converting μm to mm when the number of μm's are known. Use the variable X to represent the number of um's in your formula.arrow_forward8. How many μm² is in one cm²; express the result in scientific notation. Show your calculations. 1 cm = 10 mm; 1 mm = 1000 μmarrow_forward
- Find the dental formula and enter it in the following format: I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format) Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).arrow_forwardAnswer iarrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
- calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQUESTION 8 For the following pedigree, assume that the mode of inheritance is X-linked recessive, and that the trait has full penetrance and expressivity and occurs at a very low frequency in the hum population. Using XA for the dominant allele and Xa for the recessive allele, assign genotypes for the following individuals (if it is not possible to figure out the second allele of a genotype, that with an underscore): 2 m 1 2 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 IV 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 CO 9 10 12 13 V 1, 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 a. Il-1: b. 11-2: c. III-3: d. III-4: e. If individuals IV-11 and IV-12 have another child, what is the probability that they will have a boy with the disorder?arrow_forwardAnswerrarrow_forward
- please,show workings ahd solutions calculate the questions showing the solution including variables,unit and equations all the questiosn below using the data a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardQuestion about consensus and the relationship to transcriptional activityarrow_forwardQuestion about archaea and eukaryotic general transcription homologsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage LearningSurgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos CareHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337648868Author:AssociationPublisher:Cengage
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage LearningSurgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos CareHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337648868Author:AssociationPublisher:Cengage Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax


Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781305634350
Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. Schroeder
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Surgical Tech For Surgical Tech Pos Care
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337648868
Author:Association
Publisher:Cengage

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax
Drug Abuse, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.; Author: Medical Centric;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b6Dte96WdqM;License: Standard youtube license