
Concept explainers
A multinational corporation has a number of divisions, two of which are the North American Division and the Pacific Rim Division. Data on the two divisions are as follows:
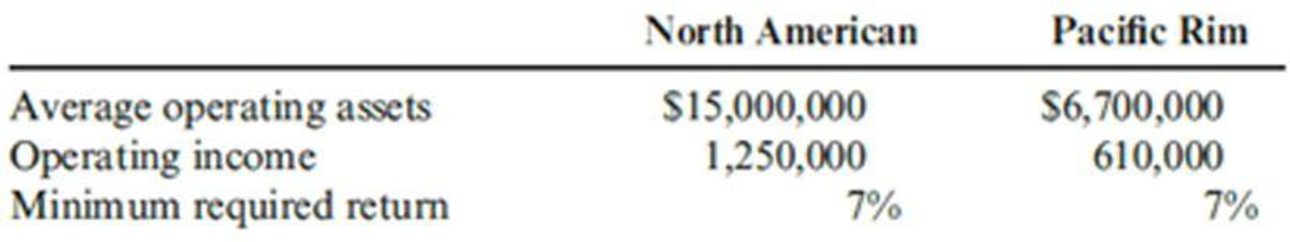
Round all
Required:
- 1. Compute residual income for each division. By comparing residual income, is it possible to make a useful comparison of divisional performance? Explain.
- 2. Compute the residual rate of return by dividing the residual income by the average operating assets. Is it possible now to say that one division outperformed the other? Explain.
- 3. Compute the
return on investment for each division. Can we make meaningful comparisons of divisional performance? Explain. - 4. Add the residual rate of return computed in Requirement 2 to the required rate of return. Compare these rates with the ROI computed in Requirement 3. Will this relationship always be the same?
1.
Compute the residential income for each division and identify whether it is possible to make a useful comparison of divisional performance. Explain the same.
Explanation of Solution
Residual income: It is an amount by which an operating income (earnings) exceeds a minimum acceptable return on the average capital invested.
Compute the residual income:
For NA:
Therefore, the residual income is $200,000.
For PR:
Therefore, the residual income is $141,000.
As the residual income is an absolute dollar amount, it is not adjust for the relative sizes of the division.
Therefore, it is not possible to make a useful comparison of divisional performance
2.
Compute the residual rate of return and identify whether it is possible to make a useful comparison of divisional performance. Explain the same.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the residual rate of return:
For NA:
Therefore, residual rate of return of NA division is 1.33%.
For PR:
Therefore, residual rate of return of NA division is 2.10%.
As the residual rate of return is a percentage, it is possible to make a useful comparison of divisional performance. The above calculations show that the PR Division is more profitable as compared to NA division.
3.
Compute the ROI and identify that whether it makes meaningful comparisons of divisional performance. Explain the same.
Explanation of Solution
Return on investment (ROI): This financial ratio evaluates how efficiently the assets are used in earning income from operations. So, ROI is a tool used to measure and compare the performance of a units or divisions or a companies.
Compute the ROI for each division:
For NA division:
Therefore, ROI for NA division is 8.33%.
For PR division:
Therefore, ROI for PR division is 9.10%.
Yes, it is used to makes meaningful comparisons of divisional performance. ROI of PR division is high.
4.
Whether adding the residual rate of return computed in subpart 2 to the required rate of return. Compare these rates with the ROI computed in the subpart 3. Identify whether this relationship always should be same or not.
Explanation of Solution
Adding the residual rate of return computed in subpart 2 to the required rate of return:
For Division NA:
ROI for Division NA is 8.33%
For Division PR:
ROI for Division PR is 9.10%
ROI for the Division PR is a 9.10%.
The sum of residual rate of return and required rate of return is always equal to the ROI
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Series)
- Quick answer of this accounting questionsarrow_forwardMead Incorporated began operations in Year 1. Following is a series of transactions and events involving its long-term debt investments in available-for-sale securities. Year 1 January 20 Purchased Johnson & Johnson bonds for $20,500. February 9 Purchased Sony notes for $55,440. June 12 Purchased Mattel bonds for $40,500. December 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Johnson & Johnson, $21,500; Sony, $52,500; and Mattel, $46,350. Year 2 April 15 Sold all of the Johnson & Johnson bonds for $23,500. July 5 Sold all of the Mattel bonds for $35,850. July 22 Purchased Sara Lee notes for $13,500. August 19 Purchased Kodak bonds for $15,300. December 31 Fair values for debt in the portfolio are Kodak, $17,325; Sara Lee, $12,000; and Sony, $60,000. Year 3 February 27 Purchased Microsoft bonds for $160,800. June 21 Sold all of the Sony notes for $57,600. June 30 Purchased Black & Decker bonds for $50,400. August 3 Sold all of the Sara…arrow_forwardWhat is the ending inventory?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning



