
The U.S. Postal Service printed a bar code on every envelope that represented a five- (or more) digit zip code using a format called POSTNET (this format was deprecated in favor of a new system, OneCode, in 2009). The bar code consists of long and short bars as shown: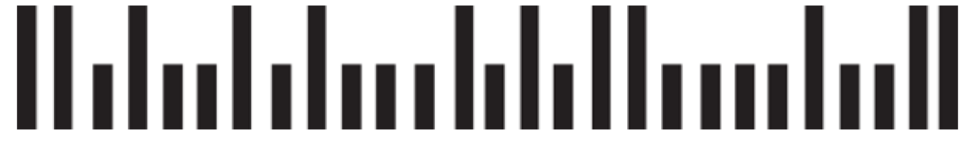
For this
Therefore, the bar code would be represented in our program as
| 110100101000101011000010011 |
The first and last digits of the bar code are always 1. Removing these leaves 25 digits. If these 25 digits are split into groups of 5 digits each, we have
| 10100 10100 01010 11000 01001 |
Next, consider each group of 5 digits. There will always be exactly two 1s in each group of digits. Each digit stands for a number. From left to right, the digits encode the values 7, 4, 2, 1, and 0. Multiply the corresponding value with the digit and compute the sum to get the final encoded digit for the zip code. The table below shows the encoding for 10100.
| Bar Code Digits | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Value | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Product of Digit 4 Value |
| Zip Code Digit = 7 + 0 + 2 + 0 + 0 = 9 |
Repeat this for each group of 5 digits and concatenate to get the complete zip code. There is one special value. If the sum of a group of 5 digits is 11, then this represents the digit 0 (this is necessary because with two digits per group it is not possible to represent zero). The zip code for the sample bar code decodes to 99504. Although the POSTNET scheme may seem unnecessarily complex, its design allows machines to detect if errors have been made in scanning the zip code.
Write a zip code class that encodes and decodes 5-digit bar codes used by the U.S. Postal Service on envelopes. The class should have two constructors. The first constructor should input the zip code as an integer, and the second constructor should input the zip code as a bar code string consisting of 0s and 1s, as described above. Although you have two ways to input the zip code, internally, the class should store the zip code using only one format (you may choose to store it as a bar code string or as a zip code number). The class should also have at least two public member functions, one to return the zip code as an integer, and the other to return the zip code in bar code format as a string. All helper functions should be declared private. Embed your class definition in a suitable test program. Your program should print an error message if an invalid bar code is passed to the constructor.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Problem Solving with C++ (9th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
- 3) Finite State Automata Given the FSA below, answer the following questions. a b a b 0 1 2 b b 3 A. Give three 4-letter words that can be accepted by this FSA; B. Give three 4-letter words that cannot be accepted by this FSA; C. How could you describe the words accepted by this FSA? D. Is this FSA deterministic or non-deterministic?arrow_forwardConsidering the TM below, answer the following questions. a/x,R €/E,L €/E,R €/E,L x/E,R c/c,R b/E.L c/c,L x/x,R I J K L M F b/E.L D A. Give three 4-letter words that can be accepted by this TM; B. Give three 4-letter words that cannot be accepted by this TM; C. How could you describe the words accepted by this TM? D. What is the alphabet of the language accepted by this TM?arrow_forwardWhat is the generator? Explain motor generator motorarrow_forward
- This battle room is focused on entry level tasks for a network analyst where you will be given trials and reconnaissance, sensor tuning, log aggregation, SIEM queries, and network analysis. For this week’s project, complete the following tasks: From your Project Ares portal, LOG IN Click on LAUNCH GAME. Select the region NORTH AMERICA Click on Battle School Under the BATTLE SCHOOL pop-up window, click on START TRAINING. Under the BATTLE ROOMS tile, click on ENTER. Under the NETWORK ANALYST tile, click on PLAY. Wait for the Battle Room to load. While loading, the BATTLE ROOM button will display red. Once the Battle Room is loaded, the BATTLE ROOM button will turn yellow and the center of the disk display will indicate CONNECTED. Click on the BATTLE ROOM button to enter the Battle Room. Below the TASKS folder, make sure you click on INSTRUCTIONS to download the Network Analyst Fundamentals material. In the Battle Room, under the TASKS menu select task INTRUSION DETECTION. Complete…arrow_forwardCreate a relationship between the common field (Technician Number) of the two tables. Make sure that each client must have 1 and only 1 technician assigned, and each technician can have multiple clients. 2. Create a query to show the Client Number, Client Name, Billed, Paid for clients in Anderson city. Save the query. 3. Create a query to show the Technician Number, Last Name, First Name, YTD Earnings for technicians whose Hourly Rate is greater than or equal to 30. Save the query. 4. Create a query to show Client Number, Client Name, Billed, Paid for clients whose technician number is 22 and whose Billed is over 300. Save the query. 5. Create a query to show the Technician Number, Last Name, First Name, Client Number, Client Name for clients whose technician number 23. Save the query. 6. Create a query to show the Technician Number, Last Name, First Name, Client Number, Client Name for clients whose technician number 23 or 29. Save the query Help please Microsoft office accessarrow_forwardDijkstra's Algorithm (part 1). Consider the network shown below, and Dijkstra’s link-state algorithm. Here, we are interested in computing the least cost path from node E (note: the start node here is E) to all other nodes using Dijkstra's algorithm. Using the algorithm statement used in the textbook and its visual representation, complete the "Step 0" row in the table below showing the link state algorithm’s execution by matching the table entries (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv) with their values. Write down your final [correct] answer, as you‘ll need it for the next question.arrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology PtrProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology PtrProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781305480537Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781305480537Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





