
Concept explainers
The couple
Answer to Problem 10.31P
The couple
Explanation of Solution
Given:
For equilibrium the value of
The value of force
Concept used:
To determine the couple
Draw the kinematic diagram for the mechanism as shown below:
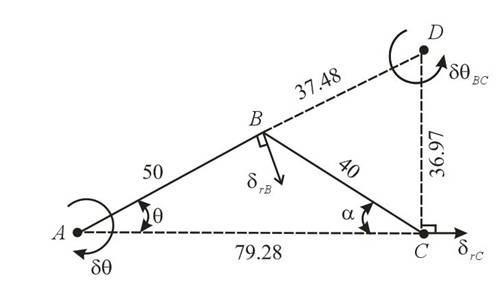
The instantaneous center of the system is at point D after theapplication of virtual angular displacement at point A the bar AB rotates about point A and bar BC will rotate about point D.
From above figure, by help of geometry angle
Simplify further for
Here,
Write the expression for the distance between points A and C.
Here,
Write the expression for the distance between point C and D.
Here,
Write the expression for the distance between point A and D.
Here,
Write the expression for the distance between point B and D.
Here,
Write the expression for displacement of point B fro bar AB.
Here,
Write the expression for displacement of point B for bar BC.
Here,
Write the expression for displacement of point C for bar BC.
Here,
Write the expression for net virtual work done on the system.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The couple
Conclusion:
Thus, the couple
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
- The answer should equal to 1157. Please sent me the solution. Thank you!arrow_forwardBONUS: If the volume of the 8cm x 6.5cm x 6cm Block of Aluminum was 312cm3 before machining, find how much material was removed when the fixture below was machined. +2 2.00 cm 6.00 cm 2.50 cm 6.50 cm 1.00 cm 2.50 cm 11.00 cm 8.00 cm 30 CP 9411 FL.4) (m² 1157 Area of triangle = 1/2*B*H Area of circle = лR² Circumference of a circle = 2πR 6.00 cm 6.50 cm 1.50 cm Radius 1.50 cm 1.00 cmarrow_forwardConsider a 5m by 5m wet concret patio with an average water film thickness of .2mm. Now wind at 50 km/h is blowing over the surface. If the air is at 1 atm, 15oC and 35 percent relative humidity, determine how long it will take for the patio to completely dry.arrow_forward
- 70. Compute the number of cubic centimeters of iron required for the cast-iron plate shown. The plate is 3.50 centimeters thick. Round the answer to the nearest cubic centimeter. 50.0 cm 40.0 cm Radius 150° 115.0 cm- 81.0 cmarrow_forwardLaw of Sines Solve the following problems using the Law of Sin 7. Find side x. All dimensions are in inches. -°-67°-37° 81° x Sin A 8.820 X 67°00' 32°00' a sin A b C sin B sin Carrow_forward35. a. Determine B. b. Determine side b. c. Determine side c. 5.330 in.- ZB 73°30'arrow_forward
- Consider a 12 cm internal diameter, 14 m long circular duct whose interior surface is wet. The duct is to be dried by forcing dry air at 1 atm and 15 degrees C throught it at an average velocity of 3m/s. The duct passes through a chilled roo, and it remains at an average temp of 15 degrees C at all time. Determine the mass transfer coeeficient in the duct.arrow_forwardnote n=number of link(dont include the ground link (fixed))arrow_forward6.(单选题) The DOF of the following mechanism is E A F=3x4-2x5-0=2 B F=3x3-2x4-0=1 F=3x3-2x3-2=1 D F=3x4-2x5-1=1arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
