
Concept explainers
The couple
Answer to Problem 10.21P
The couple
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of each uniform bar is
Concept used:
Apply the Principle of virtual work by providing a small angular virtual displacement of
By applying the virtual angular displacement to bar AB then bar AB will rotate, Bar BC will translate and bar CD will rotate
The virtual kinematic diagram after the angular displacement of
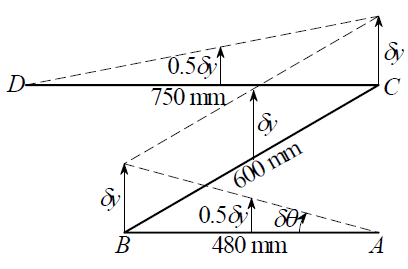
Write the expression to calculate linear displacement of bar AB.
Here,
Write the expression to calculate linear displacement of bar CD.
Here,
The weight force is the only force applied on the system thus, but similar triangle the displacement of center of bars AB and CD is
Write the expression for the weight of bar.
Here,
Write the expression for virtual work done on system.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
Displacement of bar BC will be equal to displacement of end B as there is no constraint therefore,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The couple
Conclusion:
Thus, the couple
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
- 1. Calculation Calculate the DOF of the following mechanis m 2 3 1 Please enter the answerarrow_forwarda) Determine state of stress at all points (a, b and c). These points are located on the exteriorsurface of the beam. Point a is located along the centreline of the beam, point b is 15mmfrom the centreline and point c is located on the edge of the beam. Present yourresults in a table and ensure that your sign convention is clearly shownb) Construct Mohrs circle at this point andcalculate the principal stresses and maximum in‐plane shear stress (τmax) at pointc. sketch the resulting state of stress at this point clearly indicating themagnitude of the stresses and any angles associated with the state of stress (principal ormaximum in‐plane shear).arrow_forwardparts e,f,garrow_forward
- Figure 9-6 9-49 An aluminum alloy plate with dimensions 20 cm x 10 cm × 2 cm needs to be cast with a secondary dendrite arm spacing of 10-2 cm (refer to Figure 9-6). What mold constant B is required (assume n = 2 )? Secondary dendrite arm spacing (cm) - 10-1 10-2 10-3 10 41 0.1 1 Copper Zinc alloys Aluminum alloys 10 100 1,000 10,000 100,000 Solidification time (s)arrow_forward9-72 Figure 9-29 shows a cylindrical riser attached to a casting. Compare the solidification times for each casting section and the riser and determine whether the riser will be effective. Figure 9-29 Т 3 6 3 8 3 6 Details A diagram shows the step-block casting. A cylinder of height "7" and diameter "3" is kept on a platform consisting of 2 steps. The width of the second step of the platform is labeled as "3". The horizontal length of the first step is labeled as "6." The horizontal length, width and height of the first step are labeled "6", "8" and "3".arrow_forward6/94 Determine the minimum coefficient of static friction for which the bar can be in static equilibrium in the config- uration shown. The bar is uniform and the fixed peg at C is small. Neglect friction at B. A L PROBLEM 6/94 B L 22arrow_forward
- Q2. For the following situation, estimate the minimum required compressive strength of 20/40 proppant. If intermediate-strength proppant is used, estimate the permeability of the proppant pack: Formation depth: 10,000 ft Overburden density: 165lbm/ft3 Poison’s ratio: 0.25 Biot constant: 0.7 Reservoir pressure: 6,500 psi Production drawdown: 2,000 and 4,000 psiarrow_forwardA 3-in.-radius drum is rigidly attached to a 5-in.-radius drum as shown. One of the drums rolls without sliding on the surface shown, and a cord is wound around the other drum. Knowing that at the instant shown. point A has a velocity of 4.875 in./sin./s and an acceleration of 15.50 in./s2in./s2 , both directed to the right, determine the accelerations of points A, B, and C of the drums. The cord is wound around the 3 inch radius drum. Point B is at the bottom of the 5 inch radius drum. Point A is at the bottom of the 3 inch radius drum. Point C is on the right edge of the 5 inch radius drum. The accelerations of point B is______ in./s2 . The accelerations of point A is ______ in./s2 ______ ⦨ °. at what angle/direction The accelerations of point C is______ in./s2 ______ ⦪ °. at what angle/direction?arrow_forwardA total volume of mud is 1,000 bbls that has a mud weight of 9.1 ppg. Calculate the volumefractions of water, Bentonite, and the weight of Bentonite used. Density of powder Bentonite is 156 lbm/ft3arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
