
Concept explainers
What is the molecular formula for each of the following hydrocarbons?
- a. 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexane
- b. 1,3-Dimethylcyclohexane
- c. 2,2-Dimethylhexane
- d. 2,3-Dimethylhexane
(a)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Cycloalkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that contain a ring of carbon atoms with or without alkyl substituents on it. The general molecular formula for cycloalkanes is
In a line-angle structural formula of cycloalkanes, the intersection of two lines represent a methylene group (
Answer to Problem 1.107EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of cycloalkane is 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane. From the name it is understood that the parent cycloalkane is six carbon cyclic ring which is cyclohexane. The substituent present on the cyclohexane ring are two methyl groups, each at first and second carbon. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane can be drawn as shown below,
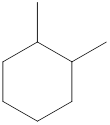
The above structure is a line-angle structural formula representation. This structure has a total of six intersections and two end lines. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is found to be eight.
The molecular formula for the given cycloalkane can be found using the general molecular formula. General molecular formula for cycloalkane is
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found to be
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found as
(b)
Interpretation:
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be found.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Cycloalkanes are a class of saturated hydrocarbons that contain a ring of carbon atoms with or without alkyl substituents on it. The general molecular formula for cycloalkanes is
In a line-angle structural formula of cycloalkanes, the intersection of two lines represent a methylene group (
Answer to Problem 1.107EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of cycloalkane is 1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. From the name it is understood that the parent cycloalkane is six carbon cyclic ring which is cyclohexane. The substituent present on the cyclohexane ring are two methyl groups, each at first and third carbon. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 1,3-dimethylcyclohexane can be drawn as shown below,
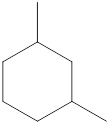
The above structure is a line-angle structural formula representation. This structure has a total of six intersections and two end lines. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is found to be eight.
The molecular formula for the given cycloalkane can be found using the general molecular formula. General molecular formula for cycloalkane is
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found to be
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is found as
(c)
Interpretation:
Molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Molecular formula of the alkanes can be found by using the general formula
Answer to Problem 1.107EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alkane is 2,2-dimethylhexane. From the name it is understood that the parent alkane is six carbon chain which is hexane. The substituent present on the hexane are two methyl groups, on the second carbon atom. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 2,2-dimethylhexane can be drawn as shown below,
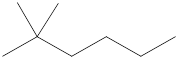
In line-angle structural representation of molecule, carbon atom is present where two lines meet and at the end of the lines. In the above structure there are four points where the lines meet and four end points. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is 8.
To determine the molecular formula of alkane, the value of “n” has to be substituted as 8 in the general formula of alkane.
Therefore, the molecular formula of the given hydrocarbon is determined as
The molecular formula of the hydrocarbon was determined as
(d)
Interpretation:
Molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Organic compounds are the important basis of life. They include gasoline, coal, dyes, and clothing fibers etc. The compounds that are obtained from living organisms are termed as organic compounds and those obtained from the earth are known as inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are found in earth also apart from living organisms. All the organic compounds contain the element carbon. Urea was synthesized in the laboratory which is an organic compound.
Hydrocarbons are the organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms. Hydrocarbon derivatives are the one in which the compounds contain hydrogen and carbon atoms along with one or more additional elements. The additional elements that can be present in hydrocarbon derivatives are oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, chlorine, bromine etc.
Hydrocarbons are further classified into two categories. They are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbons that contain single bonds between carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as saturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons that contain atleast one double or triple bond between two carbon atoms in the entire molecule is known as unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Molecular formula of the alkanes can be found by using the general formula
Answer to Problem 1.107EP
The molecular formula for the given hydrocarbon is
Explanation of Solution
Given name of alkane is 2,3-dimethylhexane. From the name it is understood that the parent alkane is six carbon chain which is hexane. The substituent present on the hexane are two methyl groups, each at second and third carbon. Therefore, the line-angle structural formula for 2,3-dimethylhexane can be drawn as shown below,
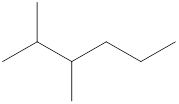
In line-angle structural representation of molecule, carbon atom is present where two lines meet and at the end of the lines. In the above structure there are four points where the lines meet and four end points. Therefore, the total number of carbon atoms present in the given structure is 8.
To determine the molecular formula of alkane, the value of “n” has to be substituted as 8 in the general formula of alkane.
Therefore, the molecular formula of the given hydrocarbon is determined as
The molecular formula of the given hydrocarbon was determined as
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC AND BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY
- A unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alanine and histidine write the amididation reaction mechanism using arrows then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction and the one letter code for the product of the reaction.arrow_forwardWrite the amididation reaction mechanism of p-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophen please use arrows.arrow_forward
- Write the amididation reaction mechanism of a-aminophenol and acetic acid to produce acetaminophenarrow_forwardFor the condensation reaction between Alamine and histamine, please help me write the amididation reaction mechanism. Then write the three letter code for the product of the reaction, then write the one letter code for the product of the reaction. arrow_forwardHow to draw the reaction mechasnism belowarrow_forward
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning




