
Concept explainers
(a)
To add a column showing the experimental probability of landing on each given color with the next spin.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The following is the table showing the results of various spins
| Color | Frequency |
| Red | 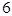 |
| Blue | 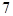 |
| Yellow | |
| Orange | |
| Purple | |
| Green | |
| Total |
The total number of spins is
The probability for any event
For the red color favorable cases are
Make the table again by calculating the probabilities as shown.
| Color | Frequency | Probability |
| Red | 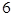 | |
| Blue | 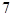 | |
| Yellow | ||
| Orange | ||
| Purple | ||
| Green | ||
| Total |
The table shows the probabilities for different color spinners.
(b)
Draw the bar diagram showing the experimental probabilities.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
GRAPH:
The following bar graph shows the experimental probabilities.
Take color on x - axis and probability on y - axis and draw the bar graph as shown below.
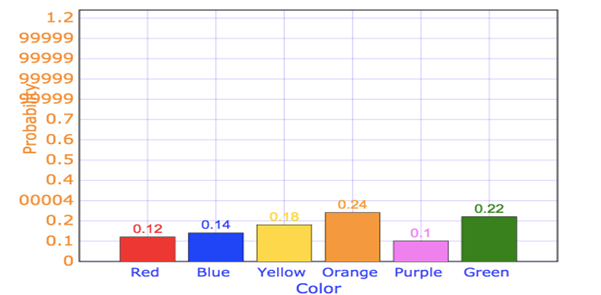
Bar graph for the experimental probabilities.
(c)
Draw a table by adding a column that showing the theoretical probability of the spinner.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
There are six colors and all colors have equal probabilities.
Since, the total probability is
The following table shows the theoretical probabilities in the table.
| Color | Frequency | Probability |
| Red | 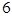 | |
| Blue | 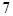 | |
| Yellow | ||
| Orange | ||
| Purple | ||
| Green | ||
| Total |
The table showing the theoretical probabilities.
(d)
Create a bar diagram showing the theoretical probabilities.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
GRAPH:
To plot the bar graph, proceed as follows.
Take color on x - axis and probability on y - axis and draw the bar graph as shown below.
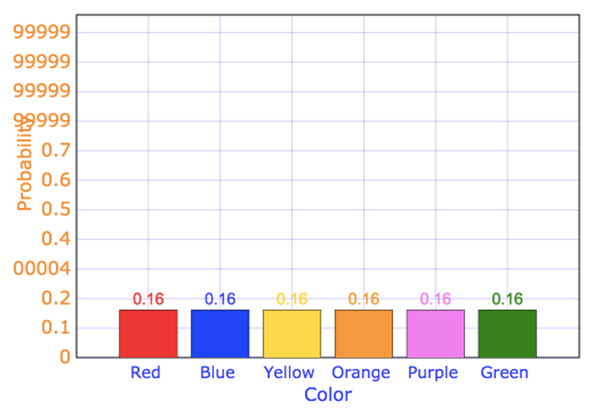
Bar graph for the theoretical probabilities.
(e)
Interpret the graph by comparing the graphs created in above parts (b) and (d)
(e)
Explanation of Solution
In the first bar graph the experimental probabilities are given which is maximum for orange. Therefore, the probability of spinner landing on orange is more than green. So according the bar graph higher the length of bar, higher the probability of landing on that color.
But in the second bar graph all the bars have equal length implying that probability of landing on all the colors is same. All the colors have equal probability.
Chapter 0 Solutions
Glencoe Algebra 2 Student Edition C2014
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- In simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forwardIn simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forward
- In simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forwardWrite each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forward
- Step by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step how do you find the zeros of y = 6x2 + 24x - 192arrow_forwardStep by step Find the zeros of each quadratic relation. a) y = x2 - 16xarrow_forward
- In simplest step by step terms, how do you find the zeros of y = x2 - 16arrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Describe the shape and position of the parabola relative to the graph of y = x 2 y = - 80( x + 9) 2 + 10.8arrow_forwardas a Identify each equation Parabola, circle, ellipse perbola without completio the square. x²-6x-14 y = 33-y² 14y ofarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





