Define both transcription and translation. In addition, describe the role(s) of each of the following in the processes of gene expression and protein synthesis: DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, ribosome(s), RNA polymerase, codon, anticodon, amino acid(s) and polypeptide(s). Be detailed in your answer.
Define both transcription and translation. In addition, describe the role(s) of each of the following in the processes of gene expression and protein synthesis: DNA, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, ribosome(s), RNA polymerase, codon, anticodon, amino acid(s) and polypeptide(s). Be detailed in your answer.
Transcription:
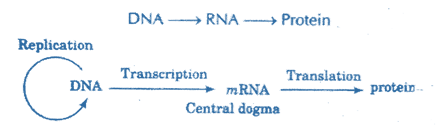
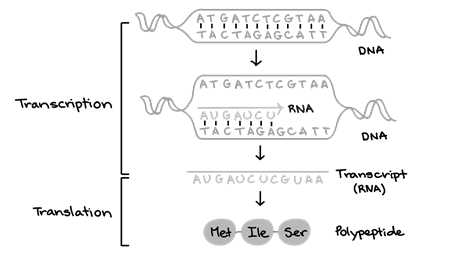
During transcription, DNA is used as a template to make a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA) or copying the DNA sequence of a gene. Then molecule of mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a Ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs.
The process of transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell. For a protein-coding gene, the RNA copy, or transcript, carries the information that is required for making a polypeptide.
RNA polymerase is the enzyme requires in the process of transcription and enzyme use the template (single-stranded) of DNA. Enzyme builds an RNA into direction 5’ to 3’ and ads each nucleotide to 3’ end of the strand. The three stages of transcription are :
Initiation - During initiation, the initiation factor binds to the regulatory region of the gene and recruit the RNA polymerase to the promoter. Because to begin transcription, RNA polymerase binds to the DNA to the gen at a region called the promoter. Promoter addresses the site of transcribing to the polymerase.
Elongation – RNA polymerase synthesizes the RNA strand by polymerizing nucleotides together. Two strands of DNA helix are separated by disrupting H-bonds. Base-pair rules are used to build mRNA. And Builds RNA strand only in 5' → 3' direction. New nucleotides are added.
Termination - There is DNA sequence-based information & RNA structure-based info that tells RNA Polymerase when it should stop.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images