
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule that corresponds to the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:
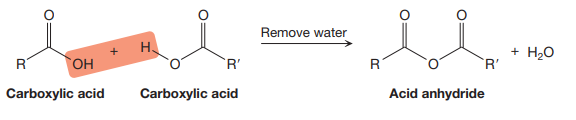
If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are the same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic anhydride in which the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule that corresponds to the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are the same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydrides are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule is to be drawn that corresponds to the given IUPAC name.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydride are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
Substituents attached to the carbon chain of any carboxylic acid portion are written as prefix in the IUPAC name.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule is to be drawn that corresponds to the given IUPAC name.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydride are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
Substituents attached to the carbon chain of any carboxylic acid portion are written as prefix in the IUPAC name.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter F Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





