
a)

Interpretation:
How to convert 1-butyne in to butanone is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Terminal
To show:
How to convert 1-butyne in to butanone.
b)
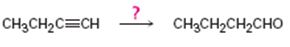
Interpretation:
How to convert 1-butyne in to butanal is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Terminal alkynes when hydrated using hydroboration-oxidation reaction yield an enol with OH group attached to the terminal carbon as the reaction follows anti-Markovnikov regiochemistry. The enol obtained then tautomerizes to an
To show:
How to convert 1-butyne in to butanal is to be shown.
c)
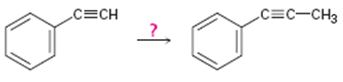
Interpretation:
How to convert ethynylbenzene in to propynylbenzene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Terminal alkynes are converted in to acetylides by treating with NaNH2 in liquid ammonia. The acetylides can be converted to higher alkynes by treating with
To show:
How to convert ethynylbenzene in to propynylbenzene.
d)
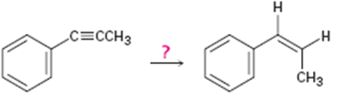
Interpretation:
How to convert propynylbenzene in to cis-1-propenylbenzene is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes can be converted in to the corresponding
To show:
How to convert 1-propynylbenzene in to 1-propenylbenzene.
e)

Interpretation:
How to convert 1-butyne in to propanoic acid is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes gets cleaved when treated with powerful oxidizing agents like KMnO4. Internal alkynes give carboxylic acids as products. Terminal alkynes give CO2 also along with a
To show:
How to convert 1-butyne in to propanoic acid.
f)
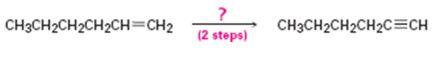
Interpretation:
How to convert 1-hexene in to 1-hexyne in two steps is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Alkenes when treated with bromine yield a dibromo
To show:
How to convert 1-hexene in to 1-hexyne in two steps
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


