
Concept explainers
Draw structures corresponding to the following names:
(a) 3, 3-Dimethyl-4-octyne
(b) 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1, 6, 8-decatriyne
(c) 2, 2, 5, 5-Tetramethyl-3-hexyne
(d) 3, 4-Dimethylcyclodecyne
(e) 3, 5-Heptadien-1-yne
(f) 3-Chloro-4, 4-dimethyl-1-nonen-6-yne
(g) 3-sec-Butyl-1-heptyne
(h) 5-tert-Buty1-2-methyl-3-octyne
a) 3,3-Dimethyl-4-octyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,3-Dimethyl-4-octyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne is
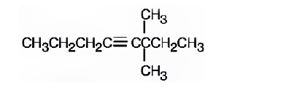
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain eight carbons with a triple bond between C4 & C5 and two methyl groups should be present on C3.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne is

b) 3-Ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne is
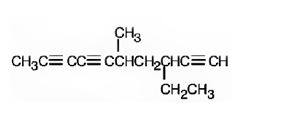
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain ten carbons with three triple bonds, one between C1 & C2, another between C6 & C7 a third one between C8 & C9, an ethyl group on C3 and a methyl group on C5.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-ethyl-5-methyl-1,6,8-decatriyne is

c) 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne is
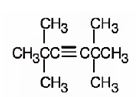
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain six carbons with a triple bond between C3 & C4 and four methyl groups, two on C2 and another two on C5.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 2,2,5,5- tetramethyl-3-hexyne is

d) 3,4-Dimethylcyclodeceyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,4-Dimethylcyclodeceyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,4-dimethyl cyclodeceyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,4-dimethyl cyclodeceyne is
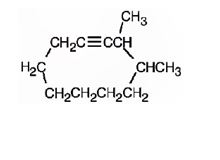
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the compound contains a ring made up of ten carbon atoms with a triple bond attached to two methyl groups on C3 and C4.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,4-dimethyl cyclodeceyne is

e) 3,5-Heptadiene-1-yne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. Compounds containing both double bond and triple bonds are called as enynes. The chain is numbered from the end nearer to the multiple bonds, double or triple. When there is a choice in numbering the double bond is given preference and the lowest number is assigned to it.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne is
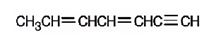
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain seven carbons with a triple bond between C1 & C2 and two double bonds, one between C3 & C4 and another between C5 & C6.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3,5-heptadiene-1-yne is
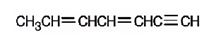
f) 3-Chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain which contains the carbon-carbon triple bond is chosen. The chain is numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Compounds with more than one triple bond are called diynes, triynes and so forth. Compounds containing both double bond and triple bonds are called as enynes. The chain is numbered from the end nearer to the multiple bonds, double or triple. When there is a choice in numbering the double bond is given preference and the lowest number is assigned to it.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne is
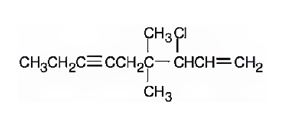
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain nine carbons with a triple bond between C6 & C7, one double bond between C1 & C2, a chlorine atom on C3 and two methyl groups on C4.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-chloro-4,4-dimethyl-1-nonene-6-yne is

g) 3-sec-Butyl-1-heptyne.
Interpretation:
The structure of 3-sec-Butyl-1-heptyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-sec-butyl-1-heptyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-sec-butyl-1-heptyne is
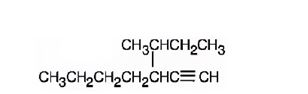
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain seven carbons with a triple bond between C1 & C2 and a sec-butyl group on C3.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 3-sec-butyl-1-heptyne is

h) 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne.
Interpretation:The structure of 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the triple bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkyne name ends with the suffix–yne. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in triple bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the triple bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkyne carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one triple bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diyne, -triyne and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne.
Answer to Problem 27AP
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne is
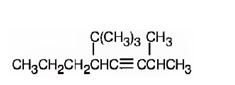
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain eight carbons with a triple bond between C3 & C4, a tert-butyl group on C5 and a methyl group on C2.
The structure corresponding to the IUPAC name 5-tert-Butyl-2-methyl-3-octyne is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- Draw a tetramer of this alternating copolymer.arrow_forwardH I T H HH H -H C. H- Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H CIH H H H HHHH H H 0 ·H H– 冊 CH CHI HH C- H- H H- H H A. H H C H H- -H HH H B. H- -H D. H H H H • H -H E. -H H H HICH T HHH F. H-arrow_forwardPolylactic acid (shown below) is a biodegradable polymer used for food packaging. Identify the monomer(s) used in the production of this polymer using a condensation process.arrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore small byproducts that would evaporate pleasearrow_forwardPoly(ethylene adipate) is a biodegradable polyester (shown below). Identify the type of polymerization process used in the production of this polymer.arrow_forwardPolymers may be composed of thousands of monomers. draw two repeat units(dimer) of the polymer formed in this reaction. assume there are hydrogen atoms on the two ends of the dimer. ignore inorganic byproducts pleasearrow_forward
- Draw the product of the reaction shown below. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardDraw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forward
- Draw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forwardProvide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





