
a)
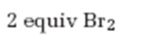
Interpretation:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with 2 equivalents of bromine.
Concept introduction:
In addition reactions,
To give:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with two molar equivalents of bromine.
b)
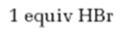
Interpretation:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with 1 equivalent of HBr is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
In addition reactions, alkynes when treated with two molar equivalents of a reagent yield the derivatives of the corresponding alkane as the product. With one molar equivalent of a reagent they yield a derivative of the corresponding alkene as the product. The addition to unsymmetrical alkenes follows Markovnikov regiochemistry. The negative part of the reagent adds on to the more highly substituted carbon in triple bond.
To predict:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with 1 equivalent of HBr.
c)

Interpretation:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with 1 equivalent of HBr is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
In addition reactions, alkynes when treated with excess amount of a reagent yield the derivatives of the corresponding alkane as the product. The addition to unsymmetrical alkenes follows Markovnikov regiochemistry. The negative part of the reagent adds on to the more highly substituted carbon in triple bond.
To predict:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with excess of HBr.
d)
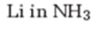
Interpretation:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with Li in ammonia.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes can be reduced by treatment with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. The hydrogenation occurs with anti stereochemistry to give a trans- alkene as product if Li in ammonia is used.
To predict:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with Li in ammonia.
e)
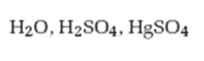
Interpretation:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4 is to be given.
Concept introduction:
When treated with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4 alkynes get hydrated to produce enols. The addition of water to unsymmetrical alkynes follows Markonikov regiochemistry while it cannot be applied in the case of symmetrical alkynes. The enols produced then undergo tautomerization to give a
To predict:
The product formed when 2-hexyne reacts with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? CH₂CH₂ H CI H₂CH₂C H CH₂ Selected Answer: O (35,4R)-4 chloro-3-ethylpentane Correctarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. I I I H Select to Add Arrows HCI, CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and the follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the intermediates and product of the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and the product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forward
- Look at the following pairs of structures carefully to identify them as representing a) completely different compounds, b) compounds that are structural isomers of each other, c) compounds that are geometric isomers of each other, d) conformers of the same compound (part of structure rotated around a single bond) or e) the same structure.arrow_forwardGiven 10.0 g of NaOH, what volume of a 0.100 M solution of H2SO4 would be required to exactly react all the NaOH?arrow_forward3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forward
- 3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forwardConcentration Trial1 Concentration of iodide solution (mA) 255.8 Concentration of thiosulfate solution (mM) 47.0 Concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution (mM) 110.1 Temperature of iodide solution ('C) 25.0 Volume of iodide solution (1) used (mL) 10.0 Volume of thiosulfate solution (5:03) used (mL) Volume of DI water used (mL) Volume of hydrogen peroxide solution (H₂O₂) used (mL) 1.0 2.5 7.5 Time (s) 16.9 Dark blue Observations Initial concentration of iodide in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of thiosulfate in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mA) Initial Rate (mA's)arrow_forwardDraw the condensed or line-angle structure for an alkene with the formula C5H10. Note: Avoid selecting cis-/trans- isomers in this exercise. Draw two additional condensed or line-angle structures for alkenes with the formula C5H10. Record the name of the isomers in Data Table 1. Repeat steps for 2 cyclic isomers of C5H10arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

