
a)
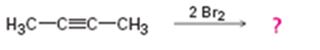
Interpretation:
Assuming that halogens add to
Concept introduction:
Alkynes when treated with one equivalent of a halogen yield a dihaloalkene as the product. They react with two equivalents of the halogens to yield a tetrahaloalkane derivative. In the first step of the addition reaction the nucleophilic attack of the π electrons of the double/triple bond in alkene/alkyne on a halogen results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. In the second step the halide ion attacks the cyclic halonium ion to yield the product.
To propose:
A mechanism and to predict the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Br2 adds to 2-butyne assuming that bromine adds to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes.
b)
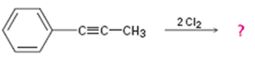
Interpretation:
Assuming that halogens add to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes, a mechanism is to be proposed and the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Cl2 adds to 1-phenylpropyne is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes when treated with one equivalent of a halogen yield a dihaloalkene as the product. They react with two equivalents of the reagents to yield a tetrahaloalkane as the product. In the first step of the addition reaction, the nucleophilic attack of the π electrons of the double/triple bond in alkene/alkyne on a halogen results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. In the second step the halide ion attacks the cyclic halonium ion to yield the product.
To propose:
A mechanism and to predict the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Cl2 adds to 1-phenylpropyne assuming that chlorine adds to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes.
c)
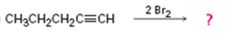
Interpretation:
Assuming that halogens add to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes, a mechanism is to be proposed and the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Br2 adds to 1-pentyne is/are to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes when treated with one equivalent of a halogen yield a dihaloalkene as the product. They react with two equivalents of the reagents to yield a tetrahaloalkane as the product. In the first step of the addition reaction the nucleophilic attack of the π electrons of the double/triple bond in alkene/alkyne on a halogen results in the formation of a cyclic halonium ion with the simultaneous elimination of a halide ion. In the second step the halide ion attacks the cyclic halonium ion to yield the product.
To propose:
A mechanism and to predict the product(s) expected for the reaction in which two equivalents of Br2 adds to 1-pentyne assuming that bromine adds to alkynes in the same manner as they add to alkenes.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- On the next page is an LC separation of the parabens found in baby wash. Parabens are suspected in a link to breast cancer therefore an accurate way to quantitate them is desired. a. In the chromatogram, estimate k' for ethyl paraben. Clearly indicate what values you used for all the terms in your calculation. b. Is this a "good" value for a capacity factor? Explain. c. What is the resolution between n-Propyl paraben and n-Butyl paraben? Again, indicate clearly what values you used in your calculation. MAU | Methyl paraben 40 20 0 -2 Ethyl paraben n-Propyl paraben n-Butyl paraben App ID 22925 6 8 minarrow_forwardd. In Figure 4, each stationary phase shows some negative correlation between plate count and retention factor. In other words, as k' increases, N decreases. Explain this relationship between k' and N. Plate Count (N) 4000 3500 2500 2000 1500 1000 Figure 4. Column efficiency (N) vs retention factor (k') for 22 nonionizable solutes on FMS (red), PGC (black), and COZ (green). 3000 Eluent compositions (acetonitrile/water, A/W) were adjusted to obtain k' less than 15, which was achieved for most solutes as follows: FMS (30/70 A/W), PGC (60/40), COZ (80/20). Slightly different compositions were used for the most highly retained solutes. All columns were 50 mm × 4.6 mm id and packed with 5 um particles, except for COZ, which was packed with 3 um particles. All other chromatographic conditions were constant: column length 5 cm, column j.§. 4.6 mm, flow rate 2 mL/min, column temperature 40 °C, and injection volume 0.5 μL Log(k'x/K'ethylbenzene) FMS 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 ཐྭ ཋ ཤྩ བྷྲ ; 500 0 5 10…arrow_forwardf. Predict how the van Deemter curve in Figure 7 would change if the temperature were raised from 40 °C to 55 °C. Figure 7. van Desmter curves in reduced coordinates for four nitroalkane homologues (nitropropane, black; nitrobutane, red; nitropentane, blue; and nitrohexane, green) separated on the FMS phase. Chromatographic conditions: column dimensions 50 mm × 4.6 mm id, eluent 30/70 ACN/water, flow rates 0.2-5.0 mL/min, injection volume 0.5 and column temperature 40 °C. No corrections to the plate heights have been made to account for extracolumn dispersion. Reduced Plate Height (h) ° 20 40 60 Reduced Velocity (v) 8. (2) A water sample is analyzed for traces of benzene using headspace analysis. The sample and standard are spiked with a fixed amount of toluene as an internal standard. The following data are obtained: Ppb benzene Peak area benzene Peak area toluene 10.0 252 376 Sample 533 368 What is the concentration of benzene in the sample?arrow_forward
- Liquid chromatography has been used to track the concentration of remdesivir (a broad-spectrum antiviral drug, structure shown at right) in COVID patients undergoing experimental treatments. Intensity The authors provide the following details regarding standard solutions preparation: HN CN HO OH NH2 Remdesivir (RDV) stock solution (5000 µg/mL) was prepared by dissolving RDV drug powder using the mixture of DMSO: MeOH (30:70 v/v). The RDV working standard solutions for calibration and quality controls were prepared using methanol in concentrations of 100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01 µg/mL. 1, 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 25, 50, 75, 100, 250, 500, 1000, and 5000 ng/mL sample solutions were prepared freshly by spiking calibration standard solutions into the blank human plasma samples for method calibration. a) What type of calibration method is being described? Why do you think the authors chose this method as opposed to another? b) Based on the details provided in part a, describe an appropriate method blank…arrow_forwardRecent advancements in liquid chromatography include the development of ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) and an increased use of capillary columns that had previously only been used with gas chromatography. Both of these advances have made the development of portable LC systems possible. For example, Axcend Corp. makes a portable system that uses a capillary column with an internal diameter of 150-μm-that is packed with 1.7-um stationary phase particles. In contrast, a traditional LC column has a 4.6 mm internal diameter and utilizes 5-um stationary phase particles. a) Explain one advantage that is afforded by the use of a capillary column in liquid chromatographic separation. Explain one disadvantage of capillary columns. b) Explain how the use of smaller stationary phase particles can improve the resolution of a separation. Include any relevant equations that support your explanation. c) A scientist at Rowan University is using the Axcend LC to conduct analyses of F…arrow_forwardThis paper describes the use of fullerene molecules, also known as buckyballs, as a stationary phase for liquid chromatography. The performance of the fullerene-modified stationary phase (FMS) is compared to that of a more common C18 stationary phase and to two other carbon-based stationary phases, PGC and COZ. A. 10A OM B. - Figure 1. Idealized drawing of the cross-section of a pore inside a silica particle, showing the relative densities of aminopropylsilyl (red/green) and fullerene (blue) groups: (A) full cross- section; (B) detailed view of covalent bonding of fullerene to the silica surface. Surface densities of silyl and fullerene groups were inferred from elemental composition results obtained at each stage of the synthesis (see Table 1). Absorbance (mAU, 220 nm) 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 a. Define selectivity, a, with words and an equation. b. Explain how the choice of stationary phase affects selectivity. c. Calculate the resolution of the nitrobenzene and toluene peaks in…arrow_forward
- Normalized Intensity (a. u.) 0.5 1.0 A 3D-printed GC column (shown below) was created for use with "micro" gas chromatography applications. To prove its utility, it was used to separate a mixture of alkanes (C9-C18, C22, C24). For the separation shown below, the column temperature was ramped from 40 °C to 250 °C at a rate of 30 °C per minute. (a) 9 10 = 1 mm 12 13 15 22 0.0 0 100 200 300 400 Time (sec) a) What detector would you use for this analysis? Justify your selection. b) Explain how the chromatogram would change if the separation was run isothermally. c) Explain how the chromatogram would change if the temperature ramp were increased to 50 °C per minute.arrow_forwardDevise a synthesis of each compound from the indicated starting material. You may also use any organic compounds with one or two carbons and any needed inorganic reagents. a. Brarrow_forwardPlease help me with #2b & #3 using the data.arrow_forward
- Heparin is used as an anti-coagulant. A risk of heparin use is thrombocytopenia, or low platelet count. This risk is minimized with the use of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH), therefore it is desirable to separate LMWH from higher molecular weight heparins. The method of choice to do this is molecular exclusion chromatography. Below is a chromatogram from a molecular exclusion chromatographic run. Peaks ranging from A to J are clearly distinguishable. The heparin mixture that was analyzed had anywhere from 6 to 30 repeat units of monomer (where the heparin with 30 repeat units would be roughly five times the size of the heparin with six repeat units). a. Which letter most likely represents the peak with 6 repeat units given these heparin polymers were separated with molecular exclusion chromatography? b. Explain your reasoning describing the mechanism of retention in molecular exclusion chromatography. 100 80 60 60 Relative Abundance 40 40 E GH 20 20 B A 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50 50…arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! URGENT!arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



