
a)

Interpretation:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst.
Concept introduction:
To predict:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst.
Answer to Problem 32AP
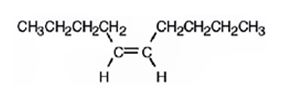
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is cis-5-decene
Explanation of Solution
When 5-decyne reacts with hydrogen in the presence of Lindlar catalyst, the addition of hydrogens to both carbons in triple bond takes place resulting in the formation of cis-5-decene.
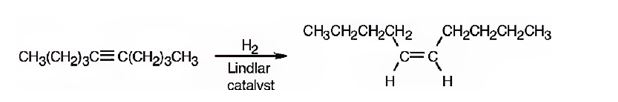
The product expected when 5-decyne reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst is cis-5-decene.

b)

Interpretation:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with Li in ammonia.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes can be reduced by treatment with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. The hydrogenation occurs with anti stereochemistry to give a trans-alkene as product if Li in ammonia is used.
To predict:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with Li in ammonia.
Answer to Problem 32AP
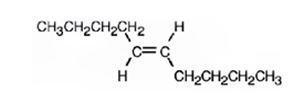
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with Li in ammonia is trans-5-decene.
Explanation of Solution
When 5-decyne reacts with hydrogen in the presence of Li in ammonia, the addition of hydrogens to both carbons in triple bond takes place following antistereochemistry resulting in the formation of trans-5-decene.
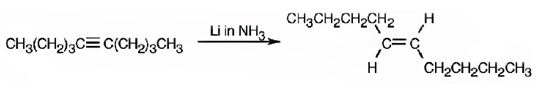
The product expected when 5-decyne reacts with Li in ammonia is trans-5-decene.

c)
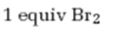
Interpretation:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with one equivalent of bromine.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes undergo addition reactions with anti stereochemistry when treated with bromine. When treated with one equivalent of bromine a trans-dibromoalkene results as product by the addition of bromine atoms to the carbons in triple bond from opposite faces.
To predict:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with one equivalent of bromine.
Answer to Problem 32AP
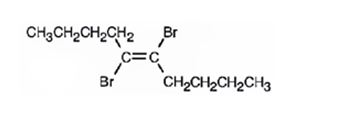
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with one equivalent of bromine is trans-5,6-dibromo-5-hexene.
Explanation of Solution
When 5-decyne reacts with bromine, the addition of bromine to both carbons in triple bond takes place following anti stereochemistry, resulting in the formation of trans-5,6-dibromo-5-decene as the product.
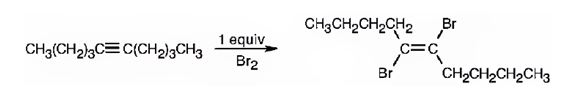
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with one equivalent of bromine is trans-5,6-dibromo-5-decene.

d)
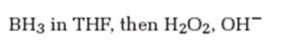
Interpretation:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with BH3 in THF followed by with H2O2, OH-.
Concept introduction:
Alkynes get hydrated in the hydroboration oxidation reaction. The reaction occurs with syn stereochemistry following anti Markovnikov regiochemistry to produce an enol. The enol then tautomerizes to yield a
To predict:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with BH3 in THF followed by with H2O2, OH-.
Answer to Problem 32AP
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with BH3 in THF followed by with H2O2, OH- is 6-decanone.
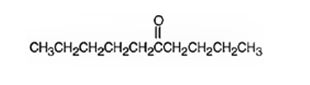
Explanation of Solution
When 5-decyne is treated with BH3 in THF followed by with H2O2, OH-, the reaction occurs with syn stereochemistry following anti Markovnikov regiochemistry to produce an enol. The enol then tautomerizes to yield a ketone as the product. The Boron and hence the OH group adds to the less highly substituted carbon in triple bond and H adds to the more highly substituted carbon atom in the triple bond to produce an enol. The enol then tautomerizes to yield the ketone as the product.
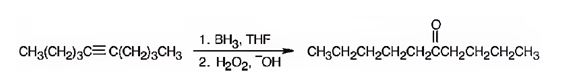
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with BH3 in THF followed by with H2O2, OH-is 6-decanone.

e)
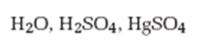
Interpretation:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4 is to be given.
Concept introduction:
When treated with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4 alkynes get hydrated to produce enols. The addition of water to unsymmetrical alkynes follows Markonikov regiochemistry while it cannot be applied in the case of symmetrical alkynes. The enols produced then undergo tautomerization to give a ketone as the product.
To predict:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4.
Answer to Problem 32AP
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4 is 5-decanone.
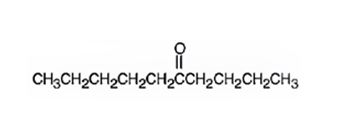
Explanation of Solution
5-Decyne is a symmetrical alkyne. Hence Markonikov regiochemistry is not applicable. When treated with dilute H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4, the OH group adds to a carbon in triple bond and H adds to the other carbon in triple bond to yield an enol. The enol then tautomerizes to yield the ketone, 5-decanone.

The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with H2O, H2SO4 in the presence of HgSO4 is 5-decanone.

f)
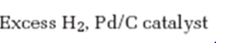
Interpretation:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with excess H2 in the presence of Pd/C is to be given.
Concept introduction:
When treated with excess H2, Pd/C catalyst the alkynes react with two molar equivalents of hydrogen to give the parent
To predict:
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with excess H2 in the presence of Pd/C.
Answer to Problem 32AP
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with excess H2 in the presence of Pd/C is n-decane.
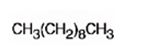
Explanation of Solution
When 5-Decyne is treated with excess H2 in the presence of Pd/C, two molar equivalents of hydrogens add to the triple bond. The corresponding alkane, n-decane is the product.
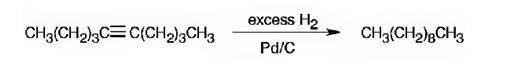
The product formed when 5-decyne reacts with excess H2 in the presence of Pd/C is n-decane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- When anisole is treated with excess bromine, the reaction gives a product which shows two singlets in 1H NMR. Draw the product.arrow_forward(ii) Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction: CI NaOH heat OH (hint: SNAr Reaction) :arrow_forwardDraw the major product in each of the following reaction:arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for the following Friedel-Craft reaction. AlBr3 Brarrow_forward(a) Draw the structures of A and B in the following reaction. (i) NaNH2, NH3(1) A + B (ii) H3O+arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Consider the following decomposition reaction of N2O5(g): For the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 → NO2 + NO3 (K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5 → NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: d[N2O5] = -k₁[N₂O₂] + K¸₁[NO₂][NO3] - K¸[NO₂]³ dtarrow_forwardIn a reaction of A + B to give C, another compound other than A, B or C may appear in the kinetic equation.arrow_forwardFor the reaction 2 N2O5(g) → 4 NO2(g) + O2(g), the following mechanism has been proposed: N2O5 →> NO₂+ NO3_(K1) NO2 + NO3 → N2O5 (k-1) NO2 + NO3 → → NO2 + O2 + NO (K2) NO + N2O5- NO2 + NO2 + NO2 (K3) d[N₂O5] __2k‚k₂[N2O5] Indicate whether the following rate expression is acceptable: dt k₁₁+ k₂arrow_forward
- Given the reaction R + Q → P, indicate the rate law with respect to R, with respect to P and with respect to P.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardk₁ Given the reaction A B, indicate k-1 d[A] (A). the rate law with respect to A: (B). the rate law with respect to B: d[B] dt dtarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





