
a)
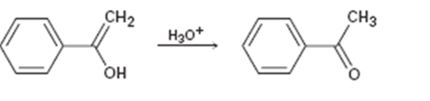
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation ion then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
b)
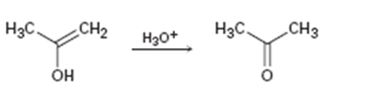
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an alkyne under acidic conditions is the tautomerization of the enol intermediate to give the corresponding ketone. The mechanism involves protonation followed by deprotonation. Based on this information a mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
c)
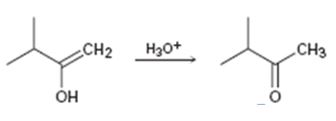
Interpretation:
Given that the final step in the hydration of an alkyne under acidic conditions is the tautomerization of the enol intermediate to give the corresponding ketone. The mechanism involves protonation followed by deprotonation. Based on this information a mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The enol picks up a proton from H3O+ using the unshared pair of electrons on oxygen and the π electrons in the double bond to yield a carbocation. The carbocation then loses a proton and the electrons in the O-H bond are moved towards the positively charged carbon to yield the ketone.
To propose:
A mechanism for the tautomerization reaction shown.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Q5: Label each chiral carbon in the following molecules as R or S. Make sure the stereocenter to which each of your R/S assignments belong is perfectly clear to the grader. (8pts) R OCH 3 CI H S 2pts for each R/S HO R H !!! I OH CI HN CI R Harrow_forwardCalculate the proton and carbon chemical shifts for this structurearrow_forwardA. B. b. Now consider the two bicyclic molecules A. and B. Note that A. is a dianion and B. is a neutral molecule. One of these molecules is a highly reactive compound first characterized in frozen noble gas matrices, that self-reacts rapidly at temperatures above liquid nitrogen temperature. The other compound was isolated at room temperature in the early 1960s, and is a stable ligand used in organometallic chemistry. Which molecule is the more stable molecule, and why?arrow_forward
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

