
Interpretation:
The stereoisomers formed in the reaction of acid catalysed dehydration of 3,4-dimethyl-3-hexanol and the major product has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction, for example
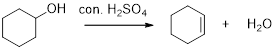
Alcohols are reacts with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid to yield the corresponding carbocation intermediates and then the carbocation intermediate undergoes elimination reaction to give a corresponding
The stability of carbocation is given below,
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary and primary.
Cis–trans isomerism (or) geometric isomerism or configurational isomerism:
- If the
functional groups are in the same side of the carbon chain, then it is called cis isomer. - If the functional groups are in opposite to each other in the carbon chain, then it is called Trans isomer.
- If two similar functional groups are in same side which is called as Z-isomer.
- If two similar functional groups are opposite side which is called as E-isomer.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
- Briefly indicate the coordination forms of B and Si in borates and silicates, respectively.arrow_forwardCan you please draw out the Lewis structure for these two formulasarrow_forwardIn a rotational Raman spectrum of a diatomic molecule it is correct to say that:a) anti-Stokes lines occur at frequencies higher than the excitatory oneb) Stokes lines occur at frequencies higher than the excitatory onec) Rayleigh scattering is not observedd) Rayleigh scattering corresponds to delta J = 0arrow_forward
- Of the molecules: H2, N2, HCl, CO2, indicate which ones can give Raman vibration-rotation spectra:a) H2, N2 and HClb) H2, N2, HCl and CO2c) H2 and N2d) all of themarrow_forwardCan you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!arrow_forwardCan you please help me with drawing the Lewis structure of each molecular formula?I truly appreciate you!arrow_forward
- Describe each highlighted bond in terms of the overlap of atomic orbitals. (a) Н Н H H [References] HIC H H C H H-C-CC-N: H σ character n character (b) HIC H H H H-C-C-C HIC H Н H O-H σ character n character Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remainingarrow_forward11 Naming and drawing alcohols Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: structure OH HO OH Explanation Check name ☐arrow_forwardwhat is the drawn mechanism for diethyl carbonate and 4 - bromo - N, N -dimethylaniline to create crystal violet?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning



