
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780133858501
Author: Bruice
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 9, Problem 43P
Interpretation Introduction
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction should be proposed.
Concept introduction:
Epoxide: It is 3 membered ring in which 2 carbons and 1 oxygen atom present.
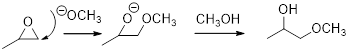
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Ph3P-CHCH3
H₂C
H3C
Aldehydes and ketones are converted into alkenes by means of a direct nucleophilic addition called the Wittig reaction. In the reaction, a triphenylphosphorine ylide, also called a phosphorane, adds to
an aldehyde/ketone to give a four-membered cyclic intermediate called an oxaphosphetane. The oxaphosphetane is not isolated but instead spontaneously decomposes to release triphenylphosphine
oxide and an alkene.
CH3
00
+
The ylide is formed by reaction of triphenylphosphine, a good nucleophile, with a primary alkyl halide in an SN2 reaction, followed by deprotonation of the carbon with a strong base, such as
butyllithium. The carbonyl carbon and the carbon originally bonded to the halogen become the two carbons with the double bond in the product alkene
X m
CH3
The real value of the Wittig reaction lies in its ability to yield an alkene of predictable structure, as the C=C bond is precisely where the C=O bond was in the reactant and no isomers (other than E/Z
isomers)…
CH3
Ph3P-CHCH3
H3C
H3C
Aldehydes and ketones are converted into alkenes by means of a direct nucleophilic addition called the Wittig reaction. In the reaction, a triphenylphosphorine ylide, also called a phosphorane, adds to
an aldehyde/ketone to give a four-membered cyclic intermediate called an oxaphosphetane. The oxaphosphetane is not isolated but instead spontaneously decomposes to release triphenylphosphine
oxide and an alkene.
Ph3P-CHCH3
H3C
The ylide is formed by reaction of triphenylphosphine, a good nucleophile, with a primary alkyl halide in an S 2 reaction, followed by deprotonation of the carbon with a strong base, such as
butyllithium. The carbonyl carbon and the carbon originally bonded to the halogen become the two carbons with the double bond in the product alkene
:0:
CH3
Com
The real value of the Wittig reaction lies in its ability to yield an alkene of predictable structure, as the C-C bond is precisely where the C=O bond was in the reactant and no isomers (other than…
What are the three alkenes formed in the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-pentanol? Propose the mechanism of their formation.
Chapter 9 Solutions
EP ESSENTIAL ORG.CHEM.-MOD.MASTERING
Ch. 9.1 - Draw the structures of straight-chain alcohols...Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 2PCh. 9.1 - Prob. 3PCh. 9.2 - Why are NH3 and CH3NH2 no longer nucleophiles when...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 9.2 - The observed relative reactivities of primary,...Ch. 9.4 - Which of the following alcohols would dehydrate...Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 10PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 11PCh. 9.4 - Prob. 12P
Ch. 9.4 - Prob. 13PCh. 9.5 - What product will be obtained from the reaction of...Ch. 9.5 - Prob. 15PCh. 9.6 - a. What is each ethers systematic name? 1....Ch. 9.8 - Draw the structure of the following: a....Ch. 9.8 - Prob. 20PCh. 9.8 - Would you expect the reactivity of a five-membered...Ch. 9.9 - Explain why the two arene oxides in Problem 22...Ch. 9.9 - Which compound is more likely to be...Ch. 9.11 - The following three nitrogen mustards were studied...Ch. 9 - What are the common and systematic names of the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 28PCh. 9 - Prob. 29PCh. 9 - Prob. 30PCh. 9 - Prob. 31PCh. 9 - What is the major product obtained from the...Ch. 9 - Draw structures for the following: a....Ch. 9 - Prob. 34PCh. 9 - Prob. 35PCh. 9 - Prob. 36PCh. 9 - Prob. 37PCh. 9 - Ethylene oxide reacts readily with HO.because of...Ch. 9 - Propose a mechanism for each of the following...Ch. 9 - Which of the following ethers would be obtained in...Ch. 9 - Show how each of the following syntheses could be...Ch. 9 - Prob. 42PCh. 9 - Prob. 43PCh. 9 - Prob. 44PCh. 9 - Propose a mechanism for each of the following...Ch. 9 - a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:...Ch. 9 - Three arene oxides can be obtained from...Ch. 9 - Prob. 48PCh. 9 - The following reaction takes place several times...Ch. 9 - Show how each of the following compounds could be...Ch. 9 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 9 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 9 - What alkenes would you expect to be obtained from...Ch. 9 - Triethylenemelamine (TEM) is an antitumor agent....Ch. 9 - When a diol that has OH groups on adjacent carbons...Ch. 9 - What product is obtained when...Ch. 9 - Prob. 58P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ethylene oxide is the starting material for the synthesis of 1,4-dioxane. Propose a mechanism for each step in this synthesis.arrow_forwardThe pyrolysis of acetic esters to give an alkene and acetic acid is thought to involve a planar transition state and cyclic redistribution of (4n + 2) electrons. Propose a mechanism for pyrolysis of the following ester.arrow_forwardEnamines normally react with methyl iodide to give two products: one arising from alkylation at nitrogen and the second arising from alkylation at carbon. For example, Heating the mixture of C-alkylation and N-alkylation products gives only the product from C-alkylation. Propose a mechanism for this isomerization.arrow_forward
- Following is the structural formula of the tranquilizer meparfynol (Oblivon). Propose a synthesis for this compound starting with acetylene and a ketone. (Notice the -yn- and -ol in the chemical name of this compound, indicating that it contains alkyne and hydroxyl functional groups.)arrow_forwardA problem often encountered in the oxidation of primary alcohols to acids is that esters are sometimes produced as by-products. For example, oxidation of ethanol yields acetic acid and ethyl acetate: Propose a mechanism to account for the formation of ethyl acetate. Take into account the reversible reaction between aldehydes and alcohols:arrow_forwardSelect the best answer. Briefly explain the selection. A mechanism is an acceptable explanation.arrow_forward
- the organic compound 2-heptanone, belonging to the ketone family, is responsible for the strong penetrating odor in Roquefort cheeses. Starting from acetylene as the starting reagent, propose a synthesis line with the reaction mechanisms involved for the synthetic obtaining of 2-heptanone and use it as a food additive in analogous cheeses.arrow_forwardb) The Wolf-Kishner reduction is a reaction used in Organic Chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene group. The reaction was used to convert an aldehyde or ketone to an alkane using hydrazine, base and thermal conditions. The mechanism begins with the attack of hydrazine of the aldehyde or ketone. Stage 1: The reaction of aldehyde/ketone with hydrazine to produce hydrazine Stage 2: Reaction with the base and heat to convert hydrozone to alkane Write the mechanism of the reaction.arrow_forwardDraw the principal organic product for the reaction of 1-bromopentane with lithium in diethyl ether, followed by formaldehyde in diethyl ether, and then followed by dilute acid.arrow_forward
- Describe how 3-methyl-1-phenyl-3-pentanol can be prepared from benzene. You can use any inorganic reagents and solvents, and any organic reagents provided they contain no more than two carbons.arrow_forwardPropose the reaction mechanism for the two possible products formation from the following reaction of acetophenone and butanal using naoh.arrow_forwardA synthetic organic molecule, G, which contains both aldehyde and ether functional groups, is subjected to a series of reactions in a multi-step synthesis pathway. In the first step, G undergoes a Wittig reaction, leading to the formation of an alkene, H. Subsequently, H is treated with an ozone (O3) reagent followed by a reducing agent in an ozonolysis reaction, resulting in the formation of two different products, I and J. Considering the functional groups present in G and the nature of the reactions involved, what are the most probable structures or functional groups present in products I and J? A. I contains a carboxylic acid group, and J contains an aldehyde group. B. I contains a ketone group, and J contains an alcohol group. C. I and J both contain aldehyde groups. D. I contains an ester group, and J contains a ketone group. Don't use chat gpt.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Coenzymes and cofactors; Author: CH15 SWAYAM Prabha IIT Madras;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bubY2Nm7hVM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Aromaticity and Huckel's Rule; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-BguH4_WBQ;License: Standard Youtube License