
A gas turbine operates with a regenerator and two stages of reheating and intercooling. Air enters this engine at 14 psia and 60°F, the pressure ratio for each stage of compression is 3, the air temperature when entering a turbine is 940°F, the engine produces 1000 hp, and the regenerator operates perfectly. The isentropic efficiency of each compressor is 88 percent and that of each turbine is 93 percent. Which process of the cycle loses the greatest amount of work potential? The temperature of the heat source is the same as the maximum cycle temperature, and the temperature of the heat sink is the same as the minimum cycle temperature. Use constant specific heats at room temperature.
Which process of the cycle loses the greatest amount of work potential.
Answer to Problem 151P
The exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 and 3-4 is
The exergy destruction associated with process 5-6 and 7-8 is
The exergy destruction associated with process 6-7 and 8-9 is
The exergy destruction associated with process 10-1 and 2-3 is
The exergy destruction associated at regenerator is
During the heat rejection process the highest energy destruction occurs.
Explanation of Solution
Draw the
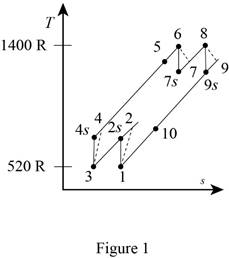
Write the expression for the temperature and pressure relation for the isentropic process 1-2s.
Here, the pressure ratio is
Write the expression for the efficiency of the compressor
Here, the specific heat at constant pressure is
Write the expression for the temperature and pressure relation ratio for the expansion process 6-7s.
Here, temperature at state 7s for isentropic process is
Write the expression for the efficiency of the turbine
Here, temperature at state 7 is
Write the expression to calculate the heat input for the two-stage gas turbine
Here, the specific heat of air at constant pressure is
Write the expression to calculate the heat output for the two-stage gas turbine
Write the expression for the exergy destruction during the process of as steam from an inlet to exit state.
Here, entropy generation is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 1-2
Here, pressure at state 2 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 5-6
Here, pressure at state 5 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 6-7
Here, pressure at state 7 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for process 10-1
Here, pressure at state 10 is
Write the expression of exergy destruction for regenerator
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
The regenerator is ideal, the effectiveness is 100% and therefore,
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 1-2 and 3-4 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 5-6 and 7-8 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 6-7 and 8-9 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated with process 10-1 and 2-3 is
Substitute
Thus, the exergy destruction associated at regenerator is
During the heat rejection process the highest energy destruction occurs.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Note: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting thanks!. Question1: If the following container is 0.6m high, 1.2m wide and half full with water, determine the pressure acting at points A, B, and C if ax=2.6ms^-2.arrow_forwardPlease read the imagearrow_forwardChapter 12 - Lecture Notes.pptx: (MAE 272-01) (SP25) DY... Scoresarrow_forwardConsider a large 6-cm-thick stainless steel plate (k = 15.1 W/m-K) in which heat is generated uniformly at a rate of 5 × 105 W/m³. Both sides of the plate are exposed to an environment at 30°C with a heat transfer coefficient of 60 W/m²K. Determine the value of the highest and lowest temperature. The highest temperature is The lowest temperature is °C. °C.arrow_forwardSketch and explain a PV Diagram and a Temperature Entropy Diagram for a 4 stroke diesel engine please, please explain into detail the difference bewteen the two and referance the a diagram. Please include a sketch or an image of each diagramarrow_forwardDraw left view of the first orthographic projectionarrow_forwardSketch and Describe a timing diagram for a 2 stroke diesel engine emphasis on the 2 stroke as my last answer explained 4 stroke please include a diagram or sketch.arrow_forwardA 4 ft 200 Ib 1000 Ib.ft C 2 ft 350 Ib - за в 2.5 ft 150 Ib 250 Ib 375 300 Ib Replace the force system acting on the frame. shown in the figure by a resultant force (magnitude and direction), and specify where its line of action intersects member (AB), measured from point (A).arrow_forwardA continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ). ive submitted this question twice and have gotten two way different answers. looking for some help thanksarrow_forward15 kg of steel ball bearings at 100 ° C is immersed in 25 kg of water at 20 ° C . Assuming no loss of heat to or from the container, calculate the final temperature of the water after equilibrium has been attained.Specific heat of steel: 0.4857 kJ / kg / ° KSpecific heat of water: 4.187 kJ / kg / ° Karrow_forwardSketch and explain a PV Diagram and a Temperature Entropy Diagram for a 4 stroke diesel enginearrow_forwardA continuous flow calorimeter was used to obtain the calorific value of a sample of fuel and the following data collected: Mass of fuel: 2.25 kgInlet water temperature: 11 ° COutlet water temperature 60 ° CQuantity of water: 360 Liters Calorimeter efficiency: 85%Calculate the calorific value of the sample ( kJ / kg ).arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





