
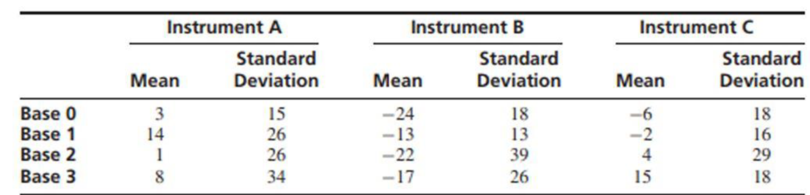
The article “Combined Analysis of Real-Time Kinematic GPS Equipment and Its Users for Height Determination” (W. Featherstone and M. Stewart, Journal of Surveying Engineering. 2001:31–51) presents a study of the accuracy of global positioning system (GPS) equipment in measuring heights. Three types of equipment were studied, and each was used to make measurements at four different base stations (in the article a fifth station was included, for which the results differed considerably from the other four). There were 60 measurements made with each piece of equipment at each base. The means and standard deviations of the measurement errors (in mm) are presented in the following table for each combination of equipment type and base station.
- a. Construct an ANOVA table. You may give
ranges for the P-values. - b. The question of interest is whether the
mean error differs among instruments. It is not of interest to determine whether the error differs among base stations. For this reason, a surveyor suggests treating this as a randomized complete block design, with the base stations as the blocks. Is this appropriate? Explain.
a.
Construct the ANOVA.
Answer to Problem 9SE
The ANOVA table is,
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F | P |
| Base | 3 | 13,495 | 4498.3 | 7.5308 | 0.000 |
| Instrument | 2 | 90,990 | 45,495 | 76.164 | 0.000 |
| Interaction | 6 | 12,050 | 2,008.3 | 3.3622 | 0.003 |
| Error | 708 | 422,912 | 597.33 | ||
| Total | 719 | 539,447 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is based on the accuracy of the global positioning system (GPS) which has 3 instruments that have to make measurements at four different base stations have 60 measurements with each piece of instrument at each base.
Let us denote the main effects of Instruments (I) with
The aim is to find the ANOVA.
State the hypothesis:
Main effect of Instruments:
Null hypothesis:
Alternative hypothesis:
Main effect of Base:
Null hypothesis:
Alternative hypothesis:
Interaction:
Null hypothesis:
Alternative hypothesis:
ANOVA table:
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F |
| Treatment | ||||
| Blocks | ||||
| Interaction | ||||
| Error | ||||
| Total |
Where,
Where, N is the sample size, I denotes the number of treatments,
Here, the number of treatments (I) is 3, the number of blocks (J) is 4 and the number of replicates (K) is 60.
Test the hypothesis on 5% level of significance:
Here, Instrument is the treatments and Base is the blocks.
Level of significance:
The level of significance is
Degrees of freedom:
Base degrees of freedom:
Instrument degrees of freedom:
Interaction degrees of freedom:
Error degrees of freedom:
Total degrees of freedom:
The treatment and block means are tabulated below:
| Base | Instruments | Block mean | ||
| Instrument A | Instrument B | Instrument C | ||
| 0 | 3 | –24 | –6 | –9 |
| 1 | 14 | –13 | –2 | –0.33 |
| 2 | 1 | –22 | 4 | –5.667 |
| 3 | 8 | –17 | 15 | 2 |
| Treatment mean | 6.5 | –19 | 2.75 | |
By observing the data, the values of
For Base:
The value of SSB (Base) is:
Substitute
The value of MSB (Base) is:
Substitute
For Instruments:
The value of SSTr ( Instruments) is:
Substitute
The value of MSTr (Instruments) is:
Substitute
For Interaction Factor (AB):
The value of SSAB is:
Substitute
The value of MSAB is:
Substitute
The value of MSE is:
Substitute
The value of SSE is:
The value of SST is:
The value of F statistic is:
For Base:
Substitute
Thus, the value of F statistic for Base is 7.5308.
For Instruments:
Substitute
Thus, the value of F statistic for Instruments is 76.164.
For Interaction factor (AB):
Substitute
Thus, the value of F statistic for interaction is 3.3622.
The ranges of P-values are:
For Base
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical-value using the MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘F’ distribution.
- Enter Numerator Df as 3.
- Enter Denominator Df as 708.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose X Value and Right Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Data value as 7.5308.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
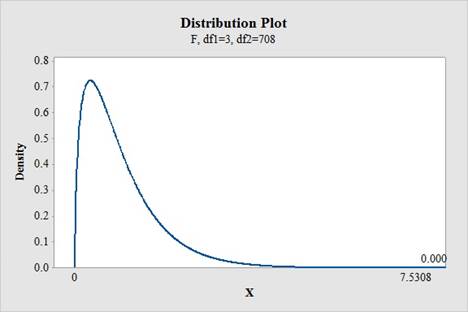
From the MINITAB output, the value of
For Instruments
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical-value using the MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘F’ distribution.
- Enter Numerator Df as 2.
- Enter Denominator Df as 708.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose X Value and Right Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Data value as 76.164.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
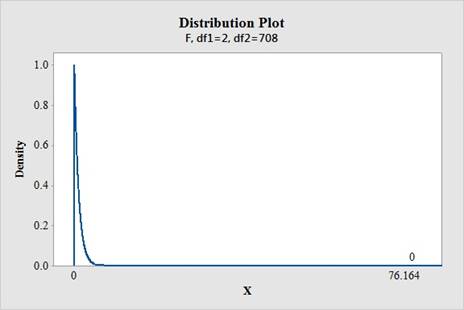
From the MINITAB output, the value of
For interaction
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the critical-value using the MINITAB software is given below:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability> OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘F’ distribution.
- Enter Numerator Df as 6.
- Enter Denominator Df as 708.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose X Value and Right Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Data value as 3.3622.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
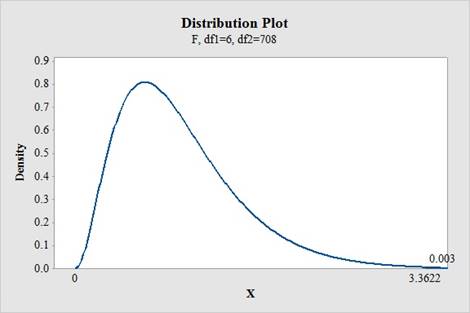
From the MINITAB output, the value of
The ANOVA table is,
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F | P |
| Base | 3 | 13,495 | 4498.3 | 7.5308 | 0.000 |
| Instrument | 2 | 90,990 | 45,495 | 76.164 | 0.000 |
| Interaction | 6 | 12,050 | 2,008.3 | 3.3622 | 0.003 |
| Error | 708 | 422,912 | 597.33 | ||
| Total | 719 | 539,447 |
Conclusion:
Base (Block):
Here, the P-value is less than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Thus, it can be concluded that there is a significant difference between block effects.
Instrument (Treatment):
Here, the P-value is less than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Thus, it can be concluded that there is a significant difference between treatment effects.
Interaction:
Here, the P-value is less than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Thus, it can be concluded that there is a significant effect of the interaction between the base (block) and instrument (treatment).
b.
Decide whether it is appropriate to treat the randomized complete block design with base stations as blocks to determine the interest that the mean error differs among the instruments.
Answer to Problem 9SE
No, it is not appropriate to treat the data with a randomized complete block design with base stations as blocks.
Explanation of Solution
In randomized complete block design, there must be no the interaction between the treatment factor and the blocking factor, so that the treatment factor may be interpreted in RBD. However, here, the interaction effect is significant, suggesting that it is not possible to use randomized complete block design.
Thus, the suggestion given by the surveyor to treat the randomized complete block design with base station as blocks is not appropriate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Statistics for Engineers and Scientists
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Finite Mathematics for Business, Economics, Life Sciences and Social Sciences
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
- Question 2 The data below provides the battery life of thirty eight (38) motorcycle batteries. 100 83 83 105 110 81 114 99 101 105 78 115 74 96 106 89 94 81 106 91 93 86 79 103 94 108 113 100 117 120 77 93 93 85 76 89 78 88 680 a. Test the hypothesis that mean battery life is greater than 90. Use the 1% level of significance. b. Determine if the mean battery life is different from 80. Use the 10% level of significance. Show all steps for the hypothesis test c. Would your conlcusion in part (b) change at the 5% level of significance? | d. Confirm test results in part (b) using JASP. Note: All JASP input files and output tables should be providedarrow_forwardSuppose that 80% of athletes at a certain college graduate. You randomly select eight athletes. What’s the chance that at most 7 of them graduate?arrow_forwardSuppose that you flip a fair coin four times. What’s the chance of getting at least one head?arrow_forward
- Suppose that the chance that an elementary student eats hot lunch is 30 percent. What’s the chance that, among 20 randomly selected students, between 6 and 8 students eat hot lunch (inclusive)?arrow_forwardBob’s commuting times to work are varied. He makes it to work on time 80 percent of the time. On 12 randomly selected trips to work, what’s the chance that Bob makes it on time at least 10 times?arrow_forwardYour chance of winning a small prize in a scratch-off ticket is 10 percent. You buy five tickets. What’s the chance you will win at least one prize?arrow_forward
- Suppose that 60 percent of families own a pet. You randomly sample four families. What is the chance that two or three of them own a pet?arrow_forwardIf 40 percent of university students purchase their textbooks online, in a random sample of five students, what’s the chance that exactly one of them purchased their textbooks online?arrow_forwardA stoplight is green 40 percent of the time. If you stop at this light eight random times, what is the chance that it’s green exactly five times?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





