
Concept explainers
Golden Earrings and the Golden Ratio A popular earring design features a circular piece of gold of diameter D with a circular cutout of diameter d, as shown in Figure 9-46. If this earring is to balance at the point P, show that the diameters must satisfy the condition D = φd, where φ =
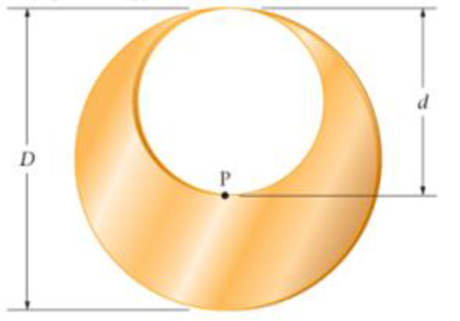
Figure 9-46
Problem 85
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics, Books a la Carte Edition (5th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
- Problem Seven. A football receiver running straight downfield at 5.60 m/s is 11.5 m in front of the quarterback when a pass is thrown downfield at an angle of 35.0° above the horizon. 8.) If the receiver never changes speed and the ball is caught at the same height from which it was thrown, find the distance between the quarterback and the receiver when the catch is made. (A) 21.3 (B) 17.8 (C) 18.8 (D) 19.9 (E) 67.5arrow_forward3 Consider a ball sliding down a ramp as shown above. The ball is already in motion at the position 1. Which direction best approximates the direction of instantaneous velocity vector V when the object is at position 3?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forward
- A car in a roller coaster moves along a track that consists of a sequence of ups and downs. Let the x axis be parallel to the ground and the positive y axis point upward. In the time interval from t 0 tot = = 4s, the trajectory of the car along a certain section of the track is given by 7 = A(1 m/s)ti + A [(1 m/s³) t³ - 6(1 m/s²)t²]ĵ where A is a positive dimensionless constant. At t car ascending or descending? = 2.0 S is the roller coaster Ascending. Descending.arrow_forwardneed help on first part its not 220arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardChildren playing in a playground on the flat roof of a city school lose their ball to the parking lot below. One of the teachers kicks the ball back up to the children as shown in the figure below. The playground is 6.10 m above the parking lot, and the school building's vertical wall is h = 7.40 m high, forming a 1.30 m high railing around the playground. The ball is launched at an angle of 8 = 53.0° above the horizontal at a point d = 24.0 m from the base of the building wall. The ball takes 2.20 s to reach a point vertically above the wall. (Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values-including answers submitted in WebAssign-in your calculations.) (a) Find the speed (in m/s) at which the ball was launched. 18.1 m/s (b) Find the vertical distance (in m) by which the ball clears the wall. 0.73 ✓ m (c) Find the horizontal distance (in m) from the wall to the point on the roof where the ball lands. 2.68 m (d) What If? If the teacher always launches the ball…arrow_forwardIt is not possible to see very small objects, such as viruses, using an ordinary light microscope. An electron microscope can view such objects using an electron beam instead of a light beam. Electron microscopy has proved invaluable for investigations of viruses, cell membranes and subcellular structures, bacterial surfaces, visual receptors, chloroplasts, and the contractile properties of muscles. The "lenses" of an electron microscope consist of electric and magnetic fields that control the electron beam. As an example of the manipulation of an electron beam, consider an electron traveling away from the origin along the x axis in the xy plane with initial velocity ₁ = vi. As it passes through the region x = 0 to x=d, the electron experiences acceleration a = ai +a, where a and a, are constants. For the case v, = 1.67 x 107 m/s, ax = 8.51 x 1014 m/s², and a = 1.50 x 10¹5 m/s², determine the following at x = d = 0.0100 m. (a) the position of the electron y, = 2.60e1014 m (b) the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardneed help with the first partarrow_forwardA ball is thrown with an initial speed v, at an angle 6, with the horizontal. The horizontal range of the ball is R, and the ball reaches a maximum height R/4. In terms of R and g, find the following. (a) the time interval during which the ball is in motion 2R (b) the ball's speed at the peak of its path v= Rg 2 √ sin 26, V 3 (c) the initial vertical component of its velocity Rg sin ei sin 20 (d) its initial speed Rg √ sin 20 × (e) the angle 6, expressed in terms of arctan of a fraction. 1 (f) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed found in (d) but at the angle appropriate for reaching the greatest height that it can. Find this height. hmax R2 (g) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed but at the angle for greatest possible range. Find this maximum horizontal range. Xmax R√3 2arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





