
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133949640
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 65SCQ
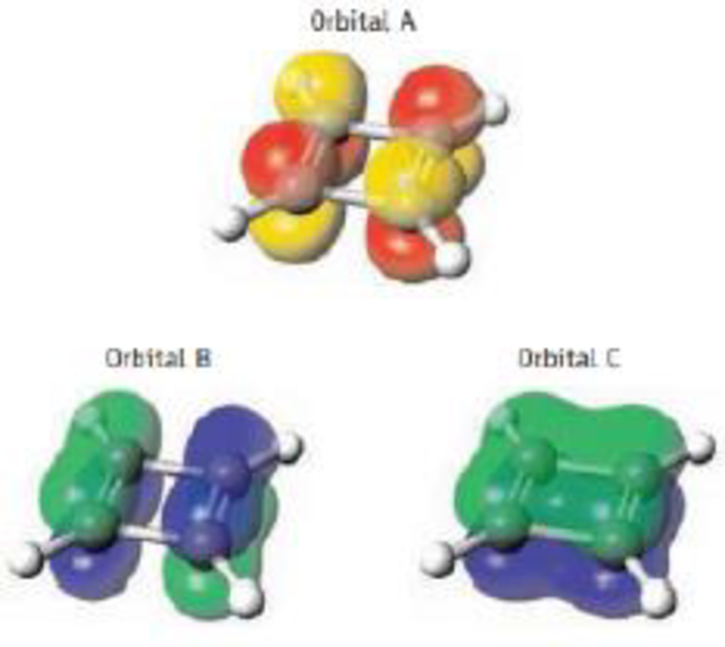
Three of the four π molecular orbitals for cyclobutadiene are pictured here. Place them in order of increasing energy. (See Figures 9.13, 9.15, 9.16, and 9.18 and the relation of orbital energy and nodes.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
in the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!
help me solve this HW
Molecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Ch. 9.2 - Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in...Ch. 9.2 - Identify the hybridization of each underlined atom...Ch. 9.2 - Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in...Ch. 9.2 - What is the hybridization of the S atom (the...Ch. 9.2 - 2. Which of the following is incorrect?
The...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 3RCCh. 9.2 - Prob. 4RCCh. 9.3 - What is the electron configuration of the H2+ ion?...Ch. 9.3 - Could the anion Li2 exist? What is the ions bond...Ch. 9.3 - The cations O2+ and N2+ are formed when molecules...
Ch. 9.3 - What is the NO bond order in nitrogen monoxide,...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 2RCCh. 9.3 - Prob. 3RCCh. 9.3 - 4. Among the known dioxygen species (O2+, O2, O2−...Ch. 9.3 - What is the empirical formula of Tynan purple?Ch. 9.3 - Butter yellow absorbs light with a wavelength of...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 3CSCh. 9.A - Photoelectron spectroscopy is s1milar to the...Ch. 9.A - What is the energy of a photon with a wavelength...Ch. 9.A - Using the accompanying figure, state which...Ch. 9.A - The kinetic energy of an electron ejected from the...Ch. 9.A - The N2+ ions that are formed when electrons with...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for chloroform, CHCl3....Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for NF3. What are its...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for hydroxylamine, H2NOH....Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for 1,...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for carbonyl fluoride,...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structure for acetamide, CH3CONH2....Ch. 9 - Specify the electron-pair and molecular geometry...Ch. 9 - Specify the electron-pair and molecular geometry...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9PSCh. 9 - What is the hybrid orbital set used by each of the...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structures of the acid HPO2F2 and...Ch. 9 - Draw the Lewis structures of the arid HSO3F and...Ch. 9 - What is the hybridization of the carbon atom in...Ch. 9 - What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in...Ch. 9 - What is the electron-pair and molecular geometry...Ch. 9 - Prob. 17PSCh. 9 - For each compound below, decide whether cis and...Ch. 9 - Molecular Orbital Theory (See Examples 9.49.6.)...Ch. 9 - Give the electron configurations for the ions Li2+...Ch. 9 - Platinum hexafluoride is an extremely strong...Ch. 9 - When potassium and oxygen react, one of the...Ch. 9 - Among the following, which has the shortest bond...Ch. 9 - Consider the following list of small molecules and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 27PSCh. 9 - The nitrosyl ion. NO+, has an interesting...Ch. 9 - These questions are not designated as to type or...Ch. 9 - What is the OSO angle and the hybrid orbital set...Ch. 9 - Sketch the resonance structures for the nitrite...Ch. 9 - Sketch the resonance structures for the nitrate...Ch. 9 - Sketch the resonance structures for the N2O...Ch. 9 - Compare the structure and bonding in CO2 and CO32...Ch. 9 - Numerous molecules are detected in deep space....Ch. 9 - Acrolein, a component of photochemical smog, has a...Ch. 9 - The organic compound below is a member of a class...Ch. 9 - The compound sketched below is acetylsalicylic...Ch. 9 - Phosphoserine is a less-common amino acid. (a)...Ch. 9 - Lactic acid is a natural compound found in sour...Ch. 9 - Cinnamaldehyde ocaus naturally in cinnamon oil....Ch. 9 - The ion Si2 was reported in a laboratory...Ch. 9 - The simple valence bond picture of O2 does not...Ch. 9 - Nitrogen, N2, can ionize to form N2+ or add an...Ch. 9 - Which of the homonuclear, diatomic molecules of...Ch. 9 - Which of the following molecules or ions are...Ch. 9 - Prob. 47GQCh. 9 - The structure of amphetamine, a stimulant, is...Ch. 9 - Menthol is used in soaps, perfumes, and foods. It...Ch. 9 - Prob. 50GQCh. 9 - Suppose you carry out the following reaction of...Ch. 9 - Ethylene oxide is an intermediate in the...Ch. 9 - The sulfamate ion, H2NSO3, can be thought of as...Ch. 9 - The compound whose structure is shown here is...Ch. 9 - Prob. 55ILCh. 9 - Carbon dioxide (CO2), dinitrogen monoxide (N2O),...Ch. 9 - Draw the two resonance structures that describe...Ch. 9 - Draw a Lewis structure for diimide, HNNH. Then,...Ch. 9 - Prob. 59SCQCh. 9 - Consider the three fluorides BF4, SiF4, and SF4....Ch. 9 - When two amino acids react with each other, they...Ch. 9 - What is the connection between bond order, bond...Ch. 9 - When is it desirable to use MO theory rather than...Ch. 9 - Show how valence bond theory and molecular orbital...Ch. 9 - Three of the four molecular orbitals for...Ch. 9 - Lets look more closely at the process of...Ch. 9 - Borax has the molecular formula Na2B4O5(OH)4. The...Ch. 9 - A model of the organic compound allene is shown...Ch. 9 - Prob. 69SCQCh. 9 - Prob. 70SCQCh. 9 - Bromine forms a number of oxides of varying...Ch. 9 - Prob. 72SCQCh. 9 - Urea reacts with malonic acid to produce...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
- Describe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardState two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
INTRODUCTION TO MOLECULAR QUANTUM MECHANICS -Valence bond theory - 1; Author: AGK Chemistry;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8kPBPqDIwM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY