
a)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
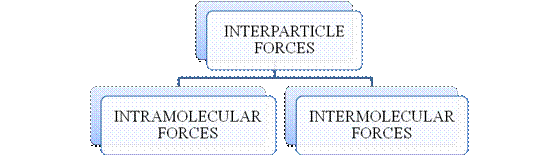
Figure 1
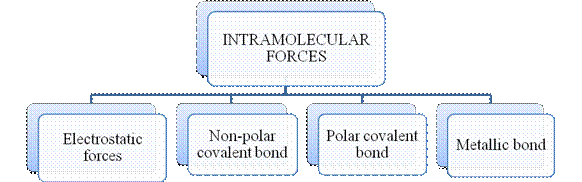
Figure 2
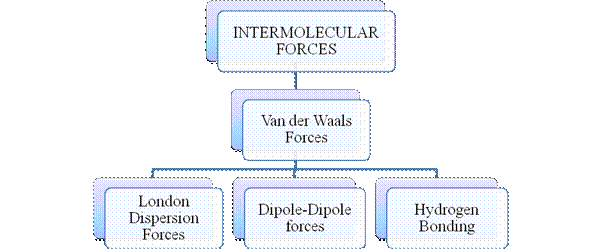
Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
b)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
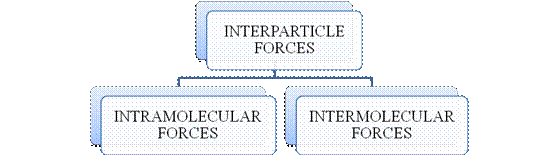
Figure 1
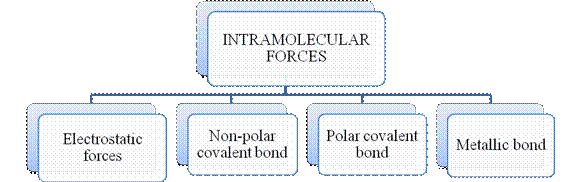
Figure 2
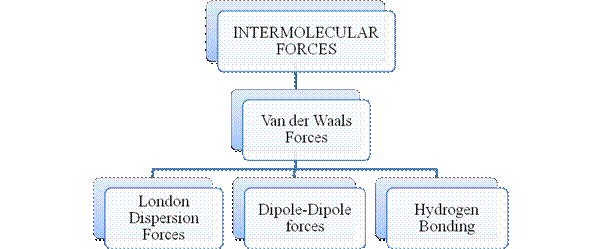
Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
c)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
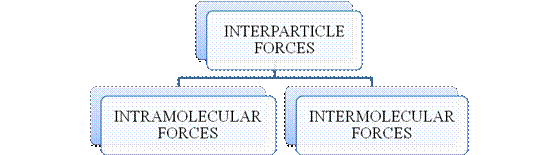
Figure 1

Figure 2
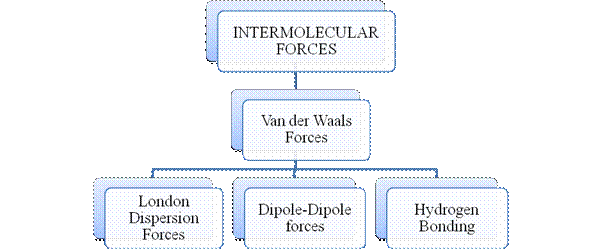
Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
d)
Interpretation:
The difference in the boiling points of the given set of compounds has to be rationalized.
Concept Introduction:
- Boiling point of any compound, depends upon its strength of Intramolecular force and Intermolecular force present in it.
- Intramolecular force refers to type of bonding between the atoms.
- Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind the molecules together to attribute to a stability of a compound.
- If the strength of intermolecular forces is high, boiling point will be high and if it is low, boiling point will be low.
- They are collectively known as “Interparticle forces”. The classification can be summarized as follows –
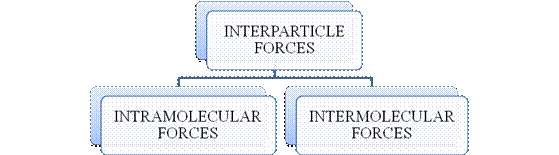
Figure 1

Figure 2

Figure 3
The type of bonding between atoms or ions is Intramolecular force. The intramolecular force in ionic compounds is electrostatic force of attraction between the ions of opposite charges. Usually ionic compounds are solids with high melting points. Covalent bonds are of two types, that is polar covalent bond and non-polar covalent bond. Covalent compounds are found as solids and liquids with moderate melting and boiling point. Metallic bond is formed between the metal atoms of an element.
Intermolecular forces are Van der Waals forces. They are weak and are of three types - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding is formed in polar covalent compounds containing hydrogen and other high electronegativity like fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. These atoms in a molecule partially bond to hydrogen of the other same molecule or within a molecule. It is relatively the strongest one. Hydrogen bonded compounds are usually liquids. They exhibit high boiling point.
London dispersion forces exist in all types of molecules. This is the force responsible for the condensation of non-polar compounds into liquids or solids under low temperature.
Dipole-dipole forces exist in polar covalent compounds. Hydrogen bonding exists in polar covalent compounds containing Fluorine, Oxygen or Nitrogen directly bonded to Hydrogen.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach, 2nd, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- Write the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M+ = 85.0899. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 1.008 12C 98.90 12.000 14N 99.63 14.003 160 99.76 15.995 Molecular formula (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forwardUse the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 59 3.0 58 64 43 100 15 23 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. •You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. + n[] 85 // ? CH4 Previous Nextarrow_forwardWrite the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M* = 128.0632. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 12C 98.90 14N 99.63 160 99.76 Molecular formula 1.008 12.000 14.003 15.995 (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this? And can I please the lowest possible significant number?arrow_forwardWhat is the molar mass of a gas that takes three times longer to effuse than helium?arrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism (with arows and structures) of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mecanism (with arrows and structures) for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion its not an examarrow_forward
- what is the skeletal structure of a tertiary alkyl fluoride with six carbon atoms and no rings.arrow_forwardOne step of glycolysis is a retro-aldol reaction (aldolase) to produce ATP.Below is the aldol reaction of the equilibrium. Show the mechanism for the base catalyzed reaction. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning





