
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100663659
Author: ULABY
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 29P
The configuration shown in Fig. P9.29 depicts a satellite repeater with two antennas, one pointed towards the antenna of ground station 1 and the other towards the antenna of ground station 2. All antennas are parabolic dishes, antennas A1 and A4 are each 4 m in diameter, antennas A2 and A3 are each 2 m in diameter, and the distance between the satellite and each of the ground stations is 40,000 km. Upon receiving the signal by its antenna A2, the satellite transponder boosts the power gain by 80 dB and then retransmits the signal to A4. The system operates at 10 GHz with Pt = 1 kW. Determine the received power Pr. Assume all antennas to be lossless.
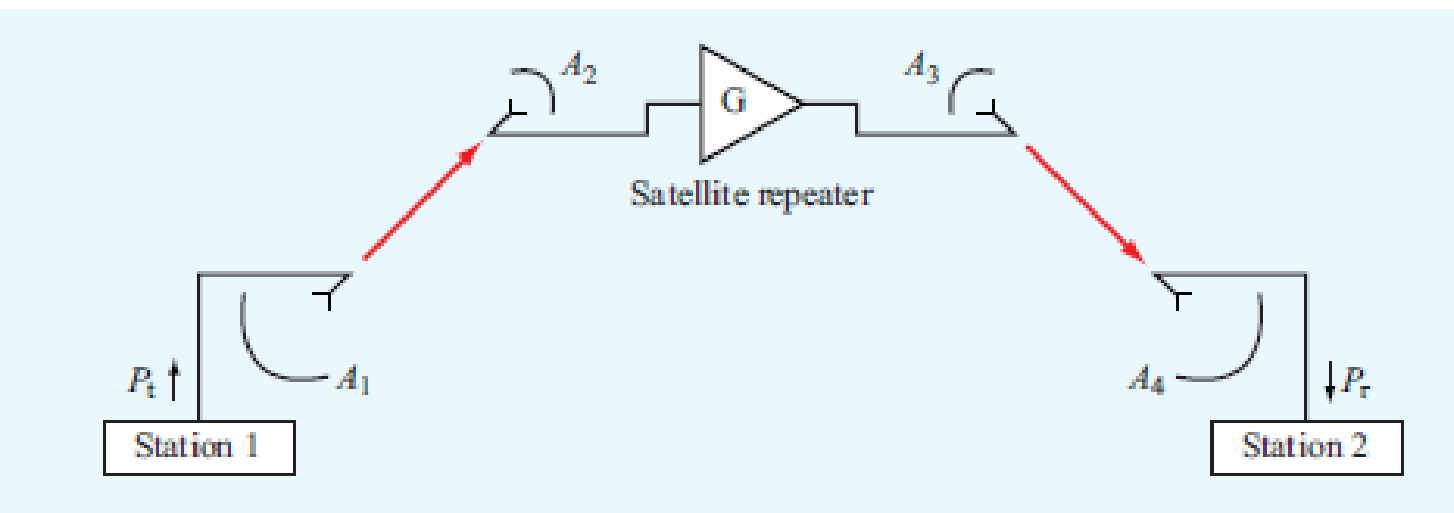
Figure P9.29 Satellite repeater system.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
when ever a flux linking a coil or current changes , an emf is induced in it this is known as
Draw a sample and hold electronic circuit using op-amp then explain its operation.
Note: For the thousandth time, I will raise this question and send the solution using intelligence. Please draw the circle by a human and not using intelligence, otherwise I will not raise the question here. I also have artificial intelligence.
Can you solve for the voltage across 1kohm resistor when both voltage sources are on. Additionally can you solve for when 2V is shorted and 5V is on. Then, when 2V is on and 5V is shorted
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLIED ELECTROMAGN
Ch. 9.1 - What does it mean to say that most antennas are...Ch. 9.1 - What is the radiated wave like in the far-field...Ch. 9.1 - In a Hertzian dipole, what is the underlying...Ch. 9.1 - Outline the basic steps used to relate the current...Ch. 9.1 - A 1 m long dipole is excited by a 5 MHz current...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 5CQCh. 9.2 - What is the magnitude of the directivity of an...Ch. 9.2 - An antenna has a conical radiation pattern with a...Ch. 9.2 - Prob. 3ECh. 9.3 - What is the physical length of a half-wave dipole...
Ch. 9.3 - How does the radiation pattern of a half-wave...Ch. 9.3 - How does the radiation efficiency of a...Ch. 9.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 9.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 9.5 - Prob. 6ECh. 9.5 - At 100 MHz, the pattern solid angle of an antenna...Ch. 9.6 - If the operating frequency of the communication...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 9ECh. 9.6 - Prob. 10ECh. 9.8 - Verify that Eq. (9.86) is a solution of Eq. (9.85)...Ch. 9.8 - Prob. 12ECh. 9.8 - What condition must be satisfied in order to use...Ch. 9.8 - Derive an expression for the array factor of a...Ch. 9.8 - Prob. 15ECh. 9.11 - Prob. 11CQCh. 9.11 - Prob. 12CQCh. 9.11 - Prob. 13CQCh. 9.11 - Prob. 14CQCh. 9.11 - Prob. 15CQCh. 9 - A center-fed Hertzian dipole is excited by a...Ch. 9 - A 50 cm long center-fed dipole directed along the...Ch. 9 - Prob. 3PCh. 9 - Determine the following: (a) The direction of...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 9.4 for an antenna with...Ch. 9 - A 2 m long center-fed dipole antenna operates in...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 9.6 for a 20 cm long antenna...Ch. 9 - Prob. 9PCh. 9 - An antenna with a radiation efficiency of 90% has...Ch. 9 - Prob. 11PCh. 9 - The normalized radiation intensity of a certain...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 9.6 for a 1 m long half-wave dipole...Ch. 9 - Prob. 14PCh. 9 - A 50 cm long dipole is excited by a sinusoidally...Ch. 9 - Prob. 16PCh. 9 - For a dipole antenna of length l = 3/2, (a)...Ch. 9 - Prob. 18PCh. 9 - Prob. 19PCh. 9 - Prob. 20PCh. 9 - A car antenna is a vertical monopole over a...Ch. 9 - Determine the effective area of a half-wave dipole...Ch. 9 - A 3 GHz line-of-sight microwave communication link...Ch. 9 - A half-wave dipole TV broadcast antenna transmits...Ch. 9 - A 150 MHz communication link consists of two...Ch. 9 - Consider the communication system shown in Fig....Ch. 9 - The configuration shown in Fig. P9.27 depicts two...Ch. 9 - Prob. 28PCh. 9 - The configuration shown in Fig. P9.29 depicts a...Ch. 9 - Prob. 30PCh. 9 - Prob. 31PCh. 9 - A uniformly illuminated rectangular aperture...Ch. 9 - An antenna with a circular aperture has a circular...Ch. 9 - Prob. 34PCh. 9 - Prob. 35PCh. 9 - Prob. 36PCh. 9 - Prob. 37PCh. 9 - Prob. 38PCh. 9 - Prob. 39PCh. 9 - Prob. 40PCh. 9 - Find and plot the normalized array factor and...Ch. 9 - Prob. 44PCh. 9 - A three-element linear array of isotropic sources...Ch. 9 - An eight-element linear array with /2 spacing is...Ch. 9 - A linear array arranged along the z axis consists...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a. A silicon sample maintained at room temperature is uniformly doped with ND=10¹6/cm³ donors. Calculate the resistivity of the sample. b. The silicon sample of part (a) is "compensated" by adding NA=1016/cm³ acceptors. Calculate the resistivity of the compensated sample. c. Compute the resistivity of intrinsic silicon at room temperature. d. A 500 resistor is to be made from a bar-shaped piece of n-type Si. The bar has a cross sectional area of 102 cm² and a current-carrying length of 1 cm. Determine the doping required. μn or μp (cm²/V-sec) 1000 Electrons Holes NA or ND (cm³) 1x1014 Мет Mp (cm2V-sec) 1358 461 2 1357 460 100 5 1352 459 1 x 1015 1345 458 2 1332 455 5 1298 448 1 x 1016.... 1248 437 2 1165 419 5 986 378 1 x 1017 801 331 10 1014 1015 1016 NA or ND (cm-³) 1017 1018 Silicon T = 300 Karrow_forward4. Two different silicon samples maintained at 300K are characterized by the energy band diagrams. Answer the questions that follow after choosing a specific diagram for analysis. a) Do equilibrium conditions prebail? How do you know? b) Sketch the electrostatic potential (V) inside the semiconductor as a function of x. c) Sketch the electric field (ε) inside the semiconductor as a function of x. EF Ec E₁ Ev E₁ EF Ev X X 0 L/2 L 0 L/2 L 3.arrow_forwardSee BOTH images to answer correctly thxarrow_forward
- a. An average hole drift velocity of 103 cm/sec results when 2V is applied across a 1 cm long semiconductor bar. What is the hole mobility inside the bar? b. Name the two dominant carrier scattering mechanisms in nondegeneratedly doped semiconductors of device quality. c. For a give semiconductor the carrier mobilities in intrinsic material are (choose one: higher than, lower than, the same as) those in heavily doped material. Briefly explain why the mobilites in intrinsic material are (chosen answer) those in heavily doped material.arrow_forwardFind the steady-state expression for vo(t) in the following circuit if vg (t) = 64 cos(8000t) V. 31.25 nF HE + Vg + - 2 ΚΩ Vo 500 mHarrow_forwardUse PSpice to model the differential amplifier circuit shown in Fig. 4 in DIBO mode (double input balanced output). Use 2N3904 BJTs and use appropriate values for resistors (you can choose the values that will not lead to excessive gain and saturation) to demonstrate that the circuit provides differential amplification. Use Vcc = 5 and Vee = 5. Use a pair of sinusoids with opposing polarity (180 degree phase shift) as the inputs to the differential amplifier. Recall from the theory ic is needed to compute re. Make sure that the conditions set in the analysis of DIBO circuit are satisfied. Assume Rs1 = Rs2 50 Ω. Does your simulation match the theoretical gain? Explain any differences.arrow_forward
- Derive the expression for the voltage gain of DIBO differential amplifier using AC analysis.arrow_forwardConsider the following circuit. + - 1.2 ΚΩ ig (1) vo ΣΕ ΚΩ € 50 nF 200 mH a) [6 pts] The frequency of the source current in the circuit is adjusted until vo is in phase with ig. What is the value of o in radians per second? (Hint: if vo is in phase with ig, the phase of total impedance must be zero (Ztot = vol ig), which means the phase of total admittance is zero. It will be easy to work with admittance in this question because the components are in parallel.) b) [2 pts] What is the total impedance at the frequency found in (a)? c) [2 pts] Ifig=2.5 cosoot mA (where o is the frequency found in [a]), what is the steady-state expression for vo?arrow_forwardConsider the following circuit with ig (t) = 200 cos(5000t) mA. 240 ΩΣ + 80 2: 2.5 µF 48 mH a) [3 pts] Obtain and draw the frequency-domain circuit. b) [3 pts] Use the current division to find the current flowing through the 240 2 resistor. c) [3 pts] Then calculate Vo in phasor form. d) [1 pts] Write the steady-state expression for vo(t).arrow_forward
- Q-Draw a sample and hold electronic circuit using op-amp then explain its operation. I hope the solution is from a human being and not from intelligencearrow_forwardDesign an AC-coupled (input and output) amplifier with a gain of -8 which has identical 3 dB corner frequencies of 10 kHz for high pass coupling at the input and output. Assume a power supply of 5 volts.arrow_forwardFind Laplace inverse for -25 -1 e S-1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Inside Wireless: Antenna Array; Author: RF elements s.r.o.;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vuz5zwbruTQ;License: Standard Youtube License