
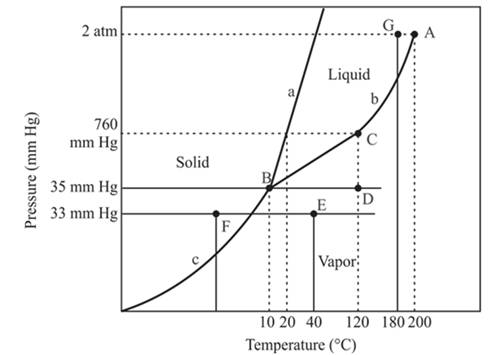
Consider the phase diagram of the compound in Problem 17 to answer the following questions.
(a) What is the physical state of the compound at 35 mm Hg and 120°C?
(b) What is the normal freezing point of the compound?
(c) What is the point A called?
(d) What is the point B called?
(e) What is the point C called?
(f) What change occurs when at a constant pressure of 33 mm Hg, the temperature is decreased from 40°C to -20°C?
(g) Will the solid float on the liquid?
(h) Can the compound exist as a liquid at 180°C and 2 atm pressure?
(a)
Interpretation:
Refer to the given phase diagram of compound X. The physical state of compound X is to be determined at pressure 35mmHg and temperature 120°C.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
The physical state of compound X is vapor determined at pressure 35mmHg and temperature 120°C.
Explanation of Solution
Given Infromation:
The phase diagram of the compound X is as follows:
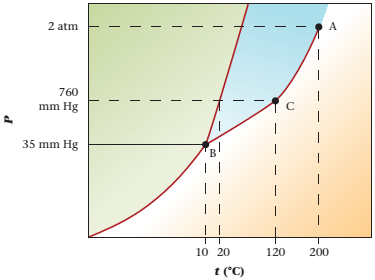
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of pure substance. The phase diagram is shown below-
In the below diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
Given values-
Pressure = 35mmHg
Temperature = -50°C
These two given values are intersecting at point D and point D lies in the vapor phase region.
Hence,
At pressure 35 mmHg and at temperature 120°C, the physical state of the compound is vapor.
(b)
Interpretation:
The normal freezing point of a compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
The normal freezing point of a compound is 20°C.
Explanation of Solution
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of pure substance. The phase diagram is shown below-
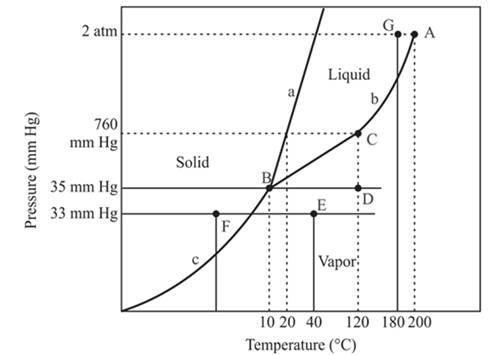
In the above diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
The normal boiling temperature is the temperature at which compound start freezing which is basically atmospheric pressure. Therefore pressure for the freezing point is 760mmHg. At atmospheric pressure of freezing point, if at the particular temperature the liquid and vapor phase of a substance are at equilibrium then that temperature is the freezing point temperature. From the phase diagram of the compound, at temperature 20°C liquid and vapor phase of a substance is at the equilibrium.
Hence, the freezing point temperature is 20°C.
(c)
Interpretation:
The name for the point A is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
The A is the critical point of the phase diagram of the compound.
Explanation of Solution
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of water. The phase diagram is shown below-
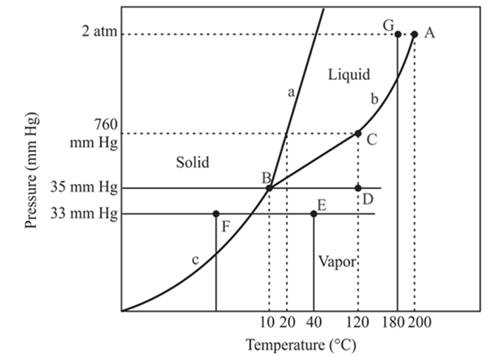
In the above diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
From the above diagram, the critical point of a substance is represented by the end of that curve which shows the equilibrium condition between the liquid phase and vapor phase. This curve is curved b and it ends at point A at temperature 200°C and at pressure 2 atm.
Hence, the point A is called a critical point.
(d)
Interpretation:
The name for the point B is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
The point B is the triple point in the phase diagram.
Explanation of Solution
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of water. The phase diagram is shown below-
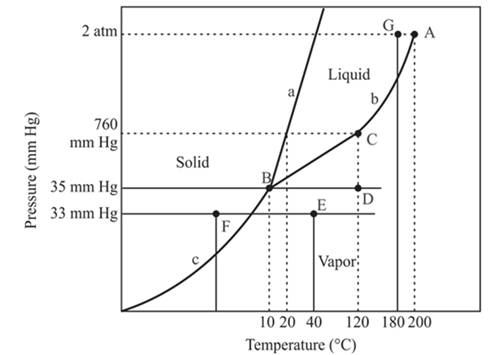
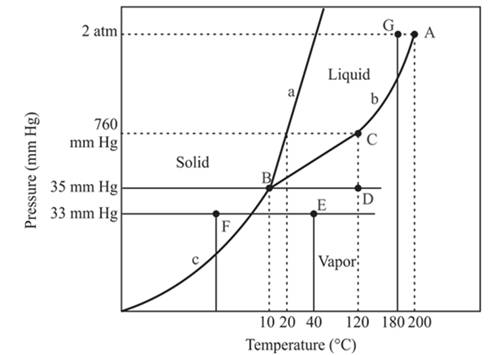
In the above diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
The triple point represents the equilibrium among all the phases which are solid, liquid and gas of compound. Hence, the intersection point of all curves am and c will represent the triple point. From the graph, the intersection point of these three curves is existing at point B.
Therefore, point B will represent the triple point of the compound.
(e)
Interpretation:
The name for the point C is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
The point C is the normal boiling point for the compound.
Explanation of Solution
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of water. The phase diagram is shown below-
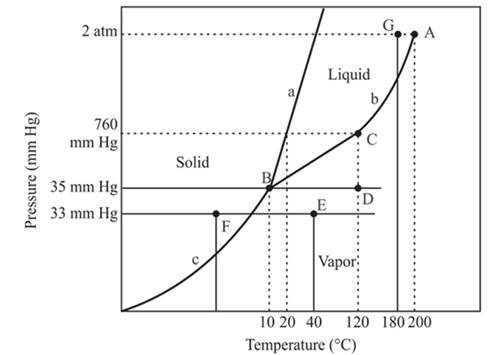
In the above diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
The point C is the normal boiling point at which the compound starts boiling and the pressure for this is atmospheric pressure or 1 atm or 760 mmHg.
(f)
Interpretation:
The changes are to be determined at constant pressure 33mmHg and the temperature is changing from 40°C to -20°C.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
At constant pressure 33mmHg and the process of changing of temperature from 40°C to -20°C is occurred between point E and F. In this process-
There is a change of phase.
Explanation of Solution
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of water. The phase diagram is shown below-
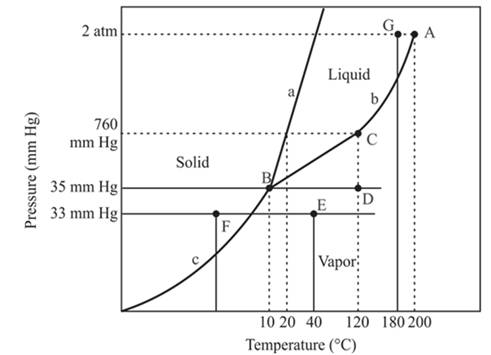
In the above diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
In this process the, the pressure is constant and the temperature varies from 40°C to -20°C which is represented by point E and F. The starting point is E and endpoint is F and both have different phases. The point E or starting point occurs in the vapor phase and the ending point, point F lies in the solid phase. So, there is an occurrence of a change of phase.
(g)
Interpretation:
The statement that solid float on liquid is to be checked.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
The densest phase is a solid phase.
Explanation of Solution
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of water. The phase diagram is shown below-
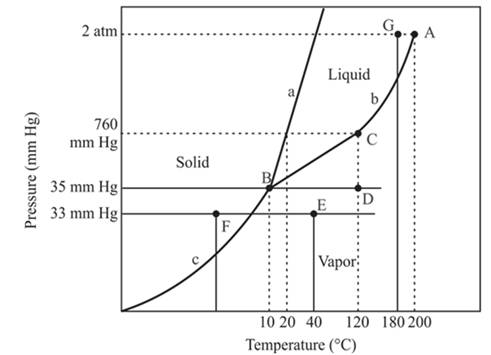
In the above diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
The floating of solid on liquid depends on the density of these two phases. In the case of the solid phase of water, it will float on the liquid phase of water. But this condition is not the same in all condition because the solid iron piece will not be able to float on the liquid water otherwise it will sink in the water.
(h)
Interpretation:
The existence of compound at pressure 2 atm and at temperature 180°C is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Phase diagram can be defined as the representation of pressure and temperature quantities of any pure substance. At these values of temperature and pressure, the different phases of the pure substance are equilibrium to each other.
Answer to Problem 18QAP
The compound at pressure 2 atm and at temperature 180°C will exist as a liquid.
Explanation of Solution
The triple point is defined as the equilibrium condition among all the three phases of any pure substance which is solid, liquid and gas. The curves are used for the equilibrium condition between two phases of water. The phase diagram is shown below-
In the above diagram −
a = solid-liquid phase in equilibrium
b = liquid-vapor phase in equilibrium
c = solid-vapor phase in equilibrium
The compound with pressure 2 atm and at temperature 180°C is occurred at point G which exist at the left of the critical point or point A. The pressure of this pint is less than the critical point hence it will exist in the critical limits. Therefore, the phase of the compound at this point is the liquid phase. Therefore, compound will exist as a liquid at given quantities.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
- in the scope of the SCH4U course! please show all steps as im still learning how to format my answers in the format given, thank you!arrow_forwardhelp me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forward
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





