
Concept explainers
Consider an
molecular orbital is promoted to the lowest empty molecular orbital. (a) Identify the molecular orbitals involved, and sketch a diagram to show the transition. (b) Compare the bond order and bond length of
Interpretation:
The molecular orbitals involved in the transition of an electron in a
Concept introduction:
Two atomic orbitals combine in order to form a bonding and an antibonding molecular orbital. The orbitals that lie on internuclear axis combine to form
The molecular orbital formed by the combination of
Molecular orbital formed by the combination of
Molecular orbitals formed by combining
Electrons are filled in the molecular orbitals in increasing order of energy.
Bond order is determined by subtracting the number of electrons in antibonding orbitals from the number of electrons in bonding orbitals and dividing by two.
Higher the bond order, smaller is the bond length.
Paramagnetic substances possess net spin and a diamagnetic substance has zero spin.
The energy of the photon emitted is given by the expression as follows:
Here,
Answer to Problem 114AP
Solution:
a) One electron of

b) Bond order of
c)
d)
Explanation of Solution
a) The molecular orbitals involved to be identified and a diagram to show the transition.
The electronic configuration of a nitrogen atom is as follows:
The molecular orbital diagram for
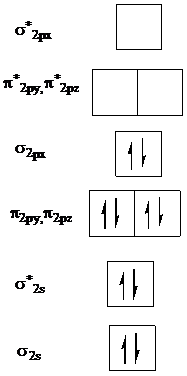
The highest occupied molecular orbital in
Thus, promote one electron of
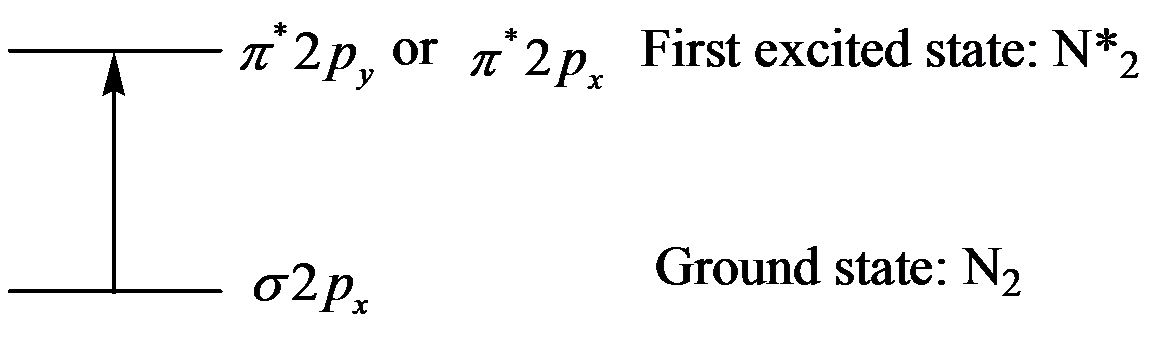
Explanation:
b) Comparison of bond order and bond length of
In
The bond order of
In
The bond order of
Hence bond order of
Thus, the bond length of
Explanation:
c)
The excited state of
Explanation:
d) The energy difference between two levels, when
The energy difference between the excited state and the ground state is equal to the energy of the photon emitted.
The energy of the photon is given by the expression as follows:
Here,
Here, the wavelength
Substitute
Hence, the energy difference between the ground state and excited state is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
BURDGE CHEMISTRY VALUE ED (LL)
- (2 Pts) Draw correct Lewis structures for two different molecules that have C3H6 as theirchemical formulaarrow_forwardSynthesize the following:arrow_forwardDid you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? Temperature of cold water (°C) 4.0 Temperature of hot water ("C) 87.0 Volume of cold water (mL) 94.0 Volume of hot water (mL) 78.0 Final temperature after mixing ("C) 41.0 Mass of cold water (g) 94.0 Mass of hot water (g) 78.0 Calorimeter constant (J/°C) 12.44 How to calculate the calorimeter constantarrow_forward
- please add appropriate arrows and tell me in detail where to add which or draw itarrow_forwardPart 1. Draw monomer units of the following products and draw their reaction mechanism (with arrow pushing) Temporary cross-linked polymer Using: 4% polyvinyl alcohol+ methyl red + 4% sodium boratearrow_forwardcan you please answer both these questions and draw the neccesaryarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
