
a)
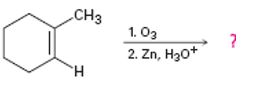
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Ozone adds to the double bond in
To give:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry.
b)
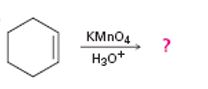
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
Potassium permanganate in neutral or acidic solution cleaves alkenes to give carbonyl containing products. If hydrogens are present on the double bond
To predict:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry.
c)
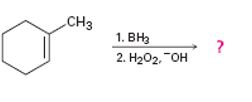
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
The hydroboration reaction takes place with syn stereochemistry and results in a non-Markovnikov addition of water to the double bond in the alkene. The resulting product has the hydroxyl group on the less highly substituted carbon.
To predict:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry.
d)
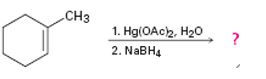
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
In the oxymercuration-demercuration process, in the first step, the electrophilic addition of Hg2+ to the alkene gives a mercurinium ion. In the next step the mercurinium ion reacts with water to yield an organomercury product. In the last step, reaction with NaBH4 removes mercury to give a more highly substituted alcohol, corresponding to Markovnikov regiochemistry, as the product.
To predict:
The product of the reaction given showing both regiochemistry and stereochemistry
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- Predict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain.arrow_forwardQ2: Explain why epoxides that react in an SN1 manner will not show any stereochemical inversion in the product. Q3: Rationalize why Alcohol B will react under the indicated reaction conditions, but Alcohol A will not. A ☑ OH B OH PBr3 R-Brarrow_forwardQ1: Predict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain. 1.) LDA, THF 2.) СОН CI OH H2SO4, heat OH m...... OH 1.) PCC, CH2Cl2 2.) CH3CH2MgBr, THF 3.) H3O+ 4.) TsCl, pyr 5.) tBuOK, tBuOH 1.) SOCI 2, CHCI 3 2.) CH3CH2ONA, DMF OH 1.) HBr 2.) Mg, THF 3.) H₂CO, THE 4.) H3O+ OH NaH, THFarrow_forward
- Problem 6-29 Identify the functional groups in the following molecules, and show the polarity of each: (a) CH3CH2C=N CH, CH, COCH (c) CH3CCH2COCH3 NH2 (e) OCH3 (b) (d) O Problem 6-30 Identify the following reactions as additions, eliminations, substitutions, or rearrangements: (a) CH3CH2Br + NaCN CH3CH2CN ( + NaBr) Acid -OH (+ H2O) catalyst (b) + (c) Heat NO2 Light + 02N-NO2 (+ HNO2) (d)arrow_forwardPredict the organic product of Y that is formed in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic product. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardPlease choose the best reagents to complete the following reactionarrow_forward
- Problem 6-17 Look at the following energy diagram: Energy Reaction progress (a) Is AG for the reaction positive or negative? Label it on the diagram. (b) How many steps are involved in the reaction? (c) How many transition states are there? Label them on the diagram. Problem 6-19 What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate? Problem 6-21 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction with Keq > 1. Label the overall AG°, transition states, and intermediate. Is AG° positive or negative? Problem 6-23 Draw an energy diagram for a reaction with Keq = 1. What is the value of AG° in this reaction?arrow_forwardProblem 6-37 Draw the different monochlorinated constitutional isomers you would obtain by the radical chlorination of the following compounds. (b) (c) Problem 6-39 Show the structure of the carbocation that would result when each of the following alkenes reacts with an acid, H+. (a) (b) (c)arrow_forwardPlease draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the carboxylic side productarrow_forward
