
Concept explainers
(a)
The slope-intercept form equation for the equation of the line of fit with the help of the following graph:
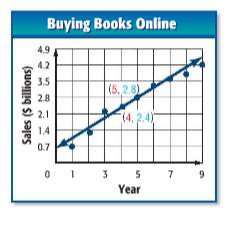
(a)
Answer to Problem 2CYU
The final slope intercept form equation is derived as
Explanation of Solution
Given:
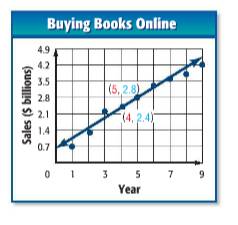
Concept Used:
The slope intercept form equation is
Where;
Slope:
Y-intercept:
Calculation:
Consider,
Year:
Sales:
There are two points are given in the graph:
Now use any two points to calculate the slope intercept from equation:
Now, the slope intercept form equation is written as:
Now put the value of
So, the final slope intercept form equation is:
Conclusion:
Hence, slope-intercept form is derived with the help of the line of fit.
(b)
The number of sales of books in the year
(b)
Answer to Problem 2CYU
There are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept Used:
The slope intercept form equation is
Where;
Slope:
Y-intercept:
Calculation:
From the first subpart:
The final slope intercept form equation is derived as:
Now, to calculate the number of books sales
So, for the year
Conclusion:
Hence, sales books in the year
Chapter 8 Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
College Algebra (7th Edition)
College Algebra with Modeling & Visualization (5th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
- Evaluate the following expression and show your work to support your calculations. a). 6! b). 4! 3!0! 7! c). 5!2! d). 5!2! e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardAmy and Samiha have a hat that contains two playing cards, one ace and one king. They are playing a game where they randomly pick a card out of the hat four times, with replacement. Amy thinks that the probability of getting exactly two aces in four picks is equal to the probability of not getting exactly two aces in four picks. Samiha disagrees. She thinks that the probability of not getting exactly two aces is greater. The sample space of possible outcomes is listed below. A represents an ace, and K represents a king. Who is correct?arrow_forwardConsider the exponential function f(x) = 12x. Complete the sentences about the key features of the graph. The domain is all real numbers. The range is y> 0. The equation of the asymptote is y = 0 The y-intercept is 1arrow_forward
- The graph shows Alex's distance from home after biking for x hours. What is the average rate of change from -1 to 1 for the function? 4-2 о A. -2 О B. 2 О C. 1 O D. -1 ty 6 4 2 2 0 X 2 4arrow_forwardWrite 7. √49 using rational exponents. ○ A. 57 47 B. 7 O C. 47 ○ D. 74arrow_forwardCan you check If my short explantions make sense because I want to make sure that I describe this part accuratelyarrow_forward
- 9! is 362, 880. What is 10!?arrow_forwardBruce and Krista are going to buy a new furniture set for their living room. They want to buy a couch, a coffee table, and a recliner. They have narrowed it down so that they are choosing between \[4\] couches, \[5\] coffee tables, and \[9\] recliners. How many different furniture combinations are possible?arrow_forwardCan you check if my step is correct?arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





