
Concept explainers
Draw all products, including stereoisomers, in each reaction.
a. 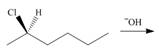 c.
c. 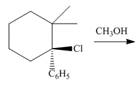 e.
e. 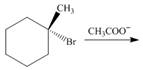
b. 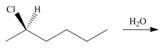 d.
d. 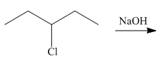 f.
f. 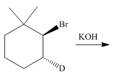
(a)
Interpretation: All products formed in the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The one-step bimolecular elimination reaction that favors the removal of a proton by a base from carbon adjacent to the leaving group that results in the formation of a carbocation is termed as
The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their bonds.
Answer to Problem 8.58P
The products that are formed in the given reaction are,
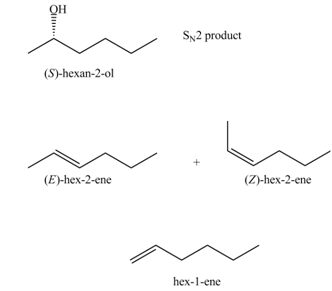
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the secondary alkyl halide is treated with a strong base due to which both substitution and elimination reactions takes place with the given secondary alkyl halide. This reaction results in the formation of three alkenes via
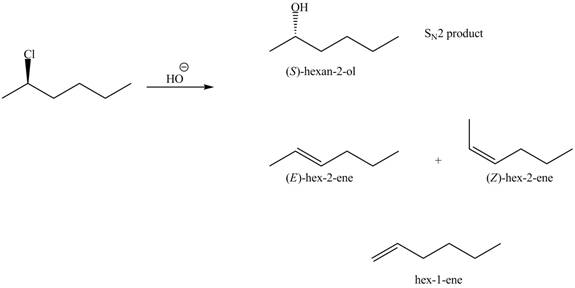
Figure 1
The products formed in the given reaction are shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: All products formed in the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The one-step bimolecular elimination reaction that favors the removal of a proton by a base from carbon adjacent to the leaving group that results in the formation of a carbocation is termed as
The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their bonds.
Answer to Problem 8.58P
The products that are formed in the given reaction are,
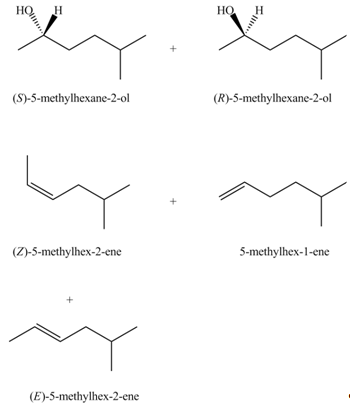
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the secondary alkyl halide is treated with a strong base due to which both substitution and elimination reactions takes place with the given secondary alkyl halide. This reaction results in the formation of three alkenes via
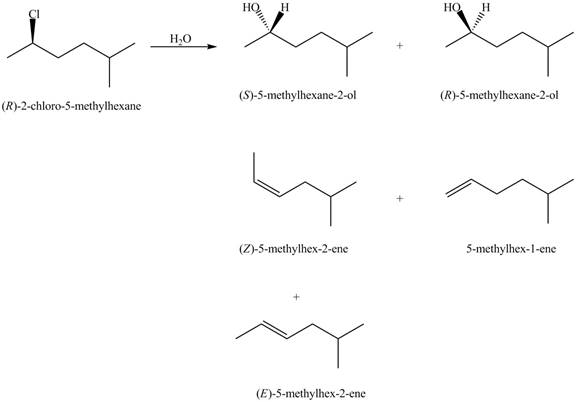
Figure 2
The products formed in the given reaction are shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: All products formed in the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The two-step unimolecular elimination reaction that favors the removal of a HX substituent and the formation of a carbocation intermediate takes place in its first step. In the second step of the reaction, the carbocation forms a double bond. This type of reaction is termed as
The two-step unimolecular reaction which favors the removal of a HX substituent and the formation of a carbocation intermediate takes place in its first step. Then, in the second step, the carbocation undergoes substitution. This type of reaction is termed as
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their bonds.
Answer to Problem 8.58P
The products that are formed in the given reaction are,
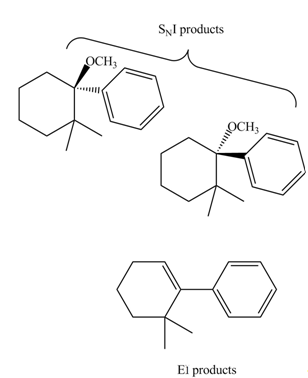
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction takes place between the tertiary alkyl halide and methanol that acts as a weak base as well as a weak nucleophile. The given tertiary alkyl halide undergoes elimination reaction via
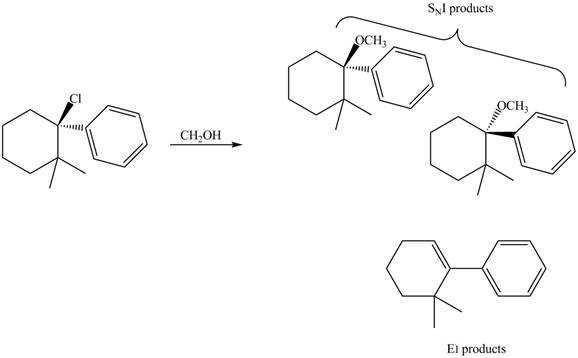
Figure 3
The products formed in the given reaction are shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: All products formed in the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their bonds.
Answer to Problem 8.58P
The products that are formed in the given reaction are,
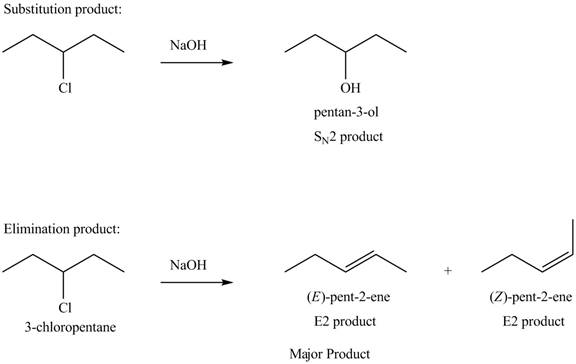
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is secondary alkyl halide. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base and strong nucleophile also. Therefore, the given alkyl halide reacts with
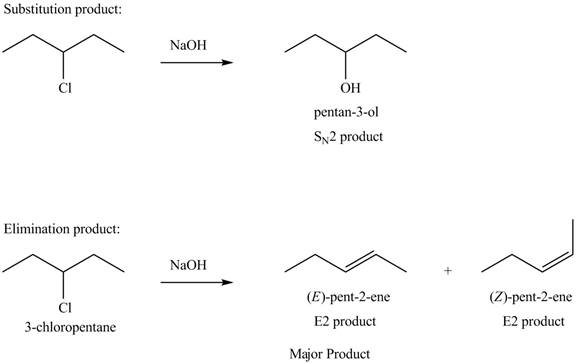
Figure 4
The products formed in the given reaction are shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: All products formed in the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their bonds.
Answer to Problem 8.58P
The products that are formed in the given reaction are,
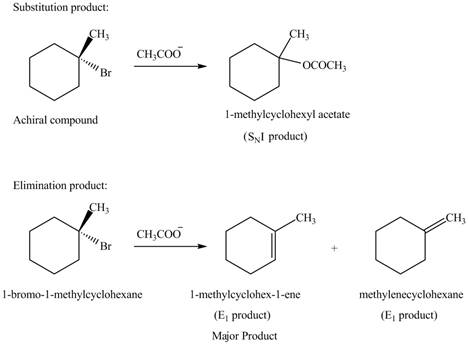
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is tertiary alkyl halide. The acetate ion is a weak base and weak nucleophile also. Therefore, the given alkyl halide reacts with
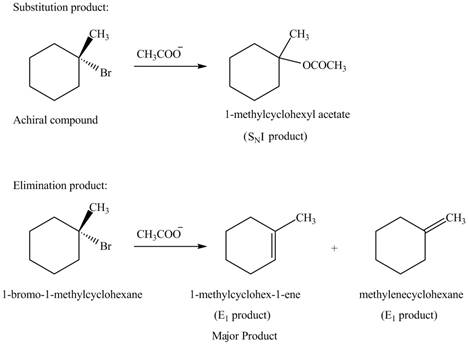
Figure 5
The products formed in the given reaction are shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: All products formed in the given reaction are to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The nucleophilic reaction that consists of bimolecular as well as bond-making and bond-breaking steps is termed as
Stereoisomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in the three-dimensional arrangement of their bonds.
Answer to Problem 8.58P
The products formed in the given reaction are shown below.
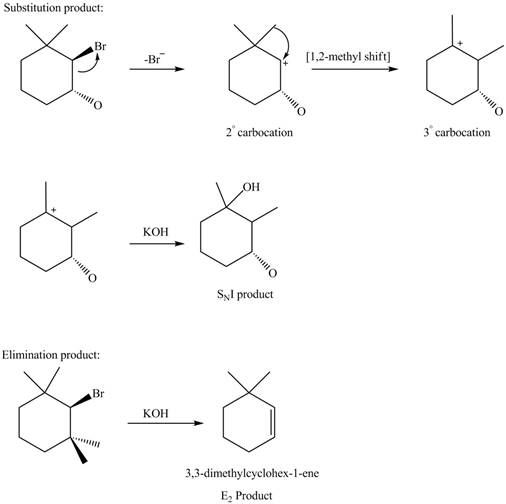
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the secondary alkyl halide is treated with a strong base due to which both substitution and elimination reactions takes place with the given secondary alkyl halide. After the removal of halide, there is a possibility of formation of tertiary carbocation also. Therefore, the given alkyl halide gives a mixture of both

Figure 6
The products formed in the given reaction are shown in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
- 3) Draw a detailed mechanism and predict the product of the reaction shown? 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+arrow_forwardHow to draw the mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward> H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





