
Concept explainers
Draw the organic products formed in each reaction.
a. 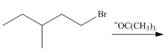 e.
e. 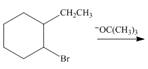 h.
h. 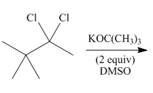
b. ![]() f.
f. 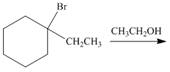 i.
i. 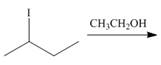
c. 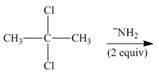 g.
g. ![]() j.
j. 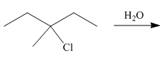
d. 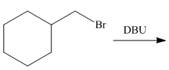
(a)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
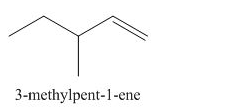
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves primary alkyl halide and strong bulky base. Primary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong and bulky; it undergoes elimination reaction through
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
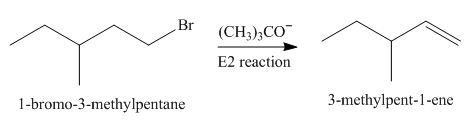
Figure 1
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic products formed in the given reaction are shown below.
![]()
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the alkyl halide is primary and ethoxide ion is a strong base. Primary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong, and also a strong nucleophile, the given halide undergoes substitution reaction through
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
![]()
Figure 2
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A carbon atom bonded to two halogen groups is called germinal dihalides. Geminal dihalides undergo double dehydrohalogenation reaction in the presence of excess base to form alkyne as the final product. The reaction prefers elimination pathway.
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
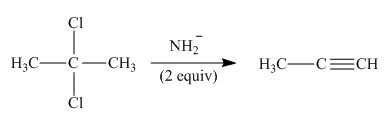
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, germinal dihalide is the starting material and amine base is strong, negatively charged and present in excess amount
The corresponding reaction is shown below.

Figure 3
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
In the given reaction, the alkyl halide is primary and base is strong, but non-nucleophilic. Primary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong and non-nucleophilic, it undergoes elimination reaction through E2 pathway.
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
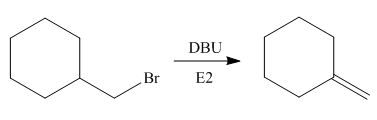
Figure 4
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
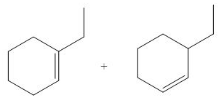
In the given reaction, the alkyl halide is secondary and base is a strong, negatively charged bulky base. Secondary alkyl halides can undergo substitution as well as elimination reactions. Since, the base is strong and bulky it undergoes elimination reaction through E2 pathway.
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
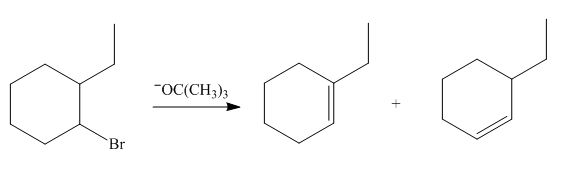
Figure 5
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
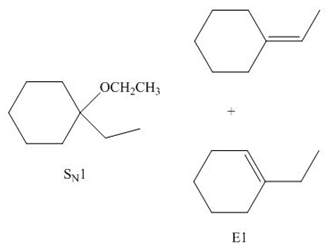
The given reaction involves tertiary alkyl halide, weak base that is also a weak nucleophile. These conditions make the given halide (tertiary) suitable to undergo either substitution by
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
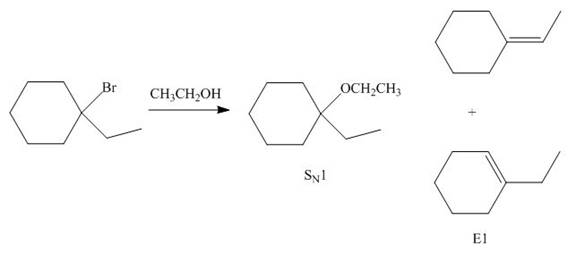
Figure 6
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
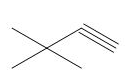
Concept introduction: Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of sodamide
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
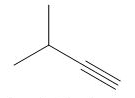
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is vicinal dihalide.
Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of sodamide
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
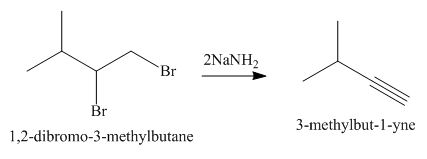
Figure 7
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of sodamide
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is vicinal dihalide.
Vicinal dihalides are the compounds in which the adjacent carbon atoms possess halogen groups (one on each carbon). These dihalides yield alkynes when treated with two equivalents of DMSO.
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
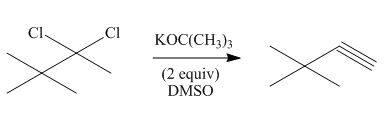
Figure 8
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
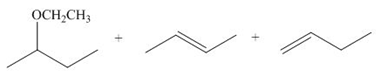
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction involves secondary alkyl halide and a base that is also a weak nucleophile. These conditions make the given halide (secondary) suitable to undergo either substitution by
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
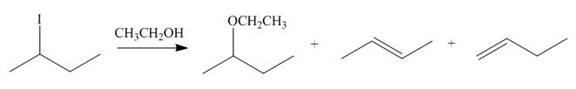
Figure 9
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of alkyl halide mostly favors
Answer to Problem 8.55P
The organic product formed in the given reaction is,
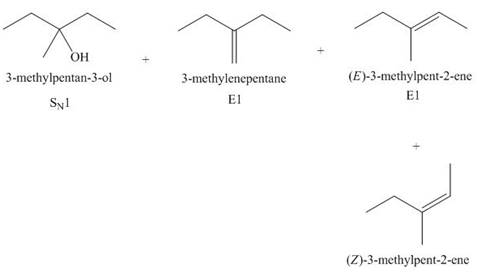
Explanation of Solution
The given alkyl halide is tertiary. Water is a weak base. These conditions make the given halide (tertiary) suitable to undergo substitution as well as elimination reaction
The corresponding reaction is shown below.
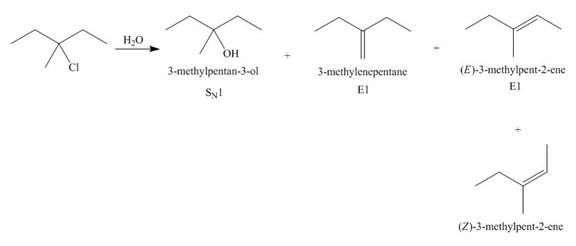
Figure 10
The organic product formed in the given reaction is drawn in Figure 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- H CH3 CH3 b) Write the products of your compound and the following reagents. If the reaction would not work for your compound, write "no reaction" and explain the problem. NaCN H* H₂NNHCH5 H* -à NaBH -à CH2MgBr Cro₁₂ --à H3O+ -à c) Would your compound give a positive Tollen's test? Why or why not?arrow_forwardHomework 4 Chem 204 Dr. Hellwig Consider this compound, which will be referred to as "your compound". a) Name your compound according to the IUPAC system. Include stereochemistry (E/Z/R/S) H CH3 CH3arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- 21.50 Determine the combinations of haloalkane(s) and alkoxide(s) that could be used to synthesize the following ethers through Williamson ether synthesis. (a) (c) (d) (e) (f) H₂COarrow_forward1. Arrange the following in order of increasing bond energy (lowest bond energy first, highest bond energy last). Provide your rationale. C=C, C-F, C=C, C-N, C-C List the bond order for each example.arrow_forwardWhat is the major enolate formed when treated with LDA? And why that one?arrow_forward
- 4. Calculate the total number of sigma bonds and total number of pi bonds in each of the following compounds. a. HH :D: +1 I H-N-C-C-O-H I H b. HH H Н :N=C-C-C=C-CEC-H :0: total o H-C-H H-C = `C-H I H. 11 H-C = C= CH H total o total π total π 1 Harrow_forwardIn the following reaction, what quantity in moles of CH₃OH are required to give off 4111 kJ of heat? 2 CH₃OH (l) + 3 O₂ (g) → 2 CO₂ (g) + 4 H₂O(g) ∆H° = -1280. kJarrow_forwardIndicate the processes in the dismutation of Cu2O.arrow_forward
- 1. Consider these three reactions as the elementary steps in the mechanism for a chemical reaction. 2600 2400 2200 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 Potential Energy (kJ) 600 400 200 0 -200- -400 -600- -800 (i) Cl₂ (g) + Pt(s) → 2Cl (g) + Pt(s) (ii) Cl (g)+ CO (g) + Pt (s) → CICO (g) + Pt (s) Ea = 1550 kJ Ea = 2240 kJ (iii) Cl (g) + CICO (g) → Cl₂CO (g) Ea = 2350 kJ AH=-950 kJ ΔΗ = 575 ΚΙ AH=-825 kJ a. Draw the potential energy diagram for the reaction. Label the data points for clarity. The potential energy of the reactants is 600 kJ Reaction Progress b. What is the overall chemical equation? c. What is the overall change in enthalpy for the above chemical reaction? d. What is the overall amount of activation energy for the above chemical reaction? e. Which reaction intermediate would be considered a catalyst (if any) and why? f. If you were to add 2700kJ of energy to the reaction (e.g. 2700 kl of heat or electricity), would you be able to make the reaction reverse itself (i.e. have…arrow_forwarddraw the enolate anion and the carbonyl that would be needed to make this product through an aldol addition reaction.arrow_forwardDraw the Michael Adduct and the final product of the Robinson annulation reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


