
Concept explainers
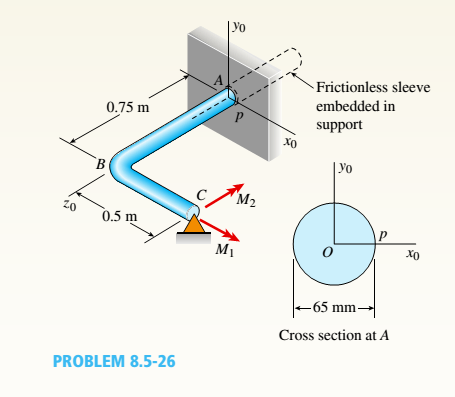
A horizontal bracket ABC consists of two perpendicular arms AB of a length 0.75 m and BC of a length 0,5 m. The bracket has a solid, circular cross section with a diameter equal to 65 mm. The bracket is inserted in a friction less sleeve at A (which is slightly larger in diameter), so it is free to rotate about the r0 axis at A and is supported by a pin at C Moments are applied at point C M{=1.5 kN -m in the x direction and A/3 = L0 kN-m acts in the — z direction.
Considering only the moments Mxand M2, calculate the maximum tensile stress
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
- Space Frame ABC is clamped at A, except it is free to rotate at A about the x and y axes. Cables DC and EC support the frame at C. Force Py= - 50 lb is applied at the mid-span of AS, and a concentrated moment Mx= -20 in-lb acts at joint B. (a) Find reactions at support A. (b) Find cable tension Forces.arrow_forwardA plane frame is constructed by using a pin connection between segments ABC and CDE. The frame has pin supports at A and E and joint loads at B and D (see figure). (a) Find reactions at supports A and E. (b) Find the resultant force in the pin at C.arrow_forwardFind support reactions at 4 and Band then use the method of joints to find all member forces. Let b = 3 m and P = 80 kN.arrow_forward
- Repeat Problem 11.2-3 assuming that R= 10 kN · m/rad and L = 2 m.arrow_forwardFrame ABC has a moment release just left of joint B. Find axial force N, shear force V, and moment M at the top of column AB. Write variables N, V, and M in terms of variables P and L.arrow_forward.17 A mountain-bike rider going uphill applies torque T = Fd(F = l5lb, d = 4 in.) to the end of the handlebars ABCD by pulling on the handlebar extenders DE. Consider the right half of the handlebar assembly only (assume the bars are fixed at the fork at A). Segments AB and CD are prismatic with lengths L, = 2 in.andL3 = 8.5 in, and with outer diameters and thicknesses d01 = 1.25 in. 101 = 0.125 in. and d03 = O.87in.,i03 = 0.ll5in, respectively as shown. Segment BC’ of length L, = 1.2 in. however. is tapered, and outer diameter and thickness vary linearly between dimensions at B and C. Consider torsion effects only. Assume G = 4000 ksi is constant. Derive an integral expression for the angle of twist of half of the handlebar tube when it is subjected to torque T = Fd acting at the end. Evaluate ‘b1-, for the given numerical1ues.arrow_forward
- Solve the preceding problem for the following data: b = 6 in., b = 10 in, L = 110 ft, tan a = 1/3, and q = 325 lb/ft.arrow_forwardAn L-shaped reinforced concrete slab 12 Ft X 12 ft, with a 6 Ft X 6 ft cut-out and thickness t = 9.0 in, is lifted by three cables attached at O, B, and D, as shown in the figure. The cables are are combined at point Q, which is 7.0 Ft above the top of the slab and directly above the center of mass at C. Each cable has an effective cross-sectional area of Ae= 0.12 in2. (a) Find the tensile force Tr(i = 1, 2, 3) in each cable due to the weight W of the concrete slab (ignore weight of cables). (b) Find the average stress ov in each cable. (See Table I-1 in Appendix I for the weight density of reinforced concrete.) (c) Add cable AQ so that OQA is one continuous cable, with each segment having Force T, which is connected to cables BQ and DQ at point Q. Repeat parts (a) and (b). Hini: There are now three Forced equilibrium equations and one constrain equation, T1= T4.arrow_forwardTwo separate cables AC and BC support a sign structure of weight W = 1575 lb attached to a building. The sign is also supported by a pin support at O and a lateral restraint in the '-direction at D. (a) Find the tension in each cable. Neglect the mass of the cables. (b) Find the average stress in each cable if the area of each cable is Ae= 0.471 in2.arrow_forward
- A simply supported beam ABC is loaded at the end of a bracket BDE (see figure). Draw axial-force, shear-force, and bending-moment diagrams for ABC.arrow_forwardRepeat Problem 11.3-9. Use two C 150 × 12.2 steel shapes and assume that E = 205 GPa and L = 6 m.arrow_forwardA long re Lai nine: wall is braced by wood shores set at an angle of 30° and supported by concrete thrust blocks, as shown in the first part of the figure. The shores are evenly spaced at 3 m apart. For analysis purposes, the wall and shores are idealized as shown in the second part of the figure. Note that the base of the wall and both ends of the shores are assumed to be pinned. The pressure of the soil against the wall is assumed to be triangularly distributed, and the resultant force acting on a 3-meter length of the walls is F = 190 kN. If each shore has a 150 mm X 150 mm square cross section, what is the compressive stressarrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
