
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The pH values after the addition of each proportion of the base to the acid is to be determined. Also, the titration curve needs to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Titration curve is drawn to determine the change in pH of an acid or base with respect to the added volume of base or acid to it.
The titration curve can be drawn between a strong/weak acid and strong/weak base. The change in pH shows different patterns for different combinations of acids and bases.
Answer to Problem 69E
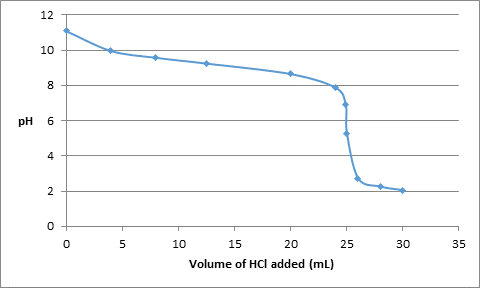
The change in pH due to addition of HCl is represented as follows:
| Volume of HCl added (mL) | pH |
| 0 | 11.1 |
| 4.0 | 9.97 |
| 8.0 | 9.58 |
| 12.5 | 9.25 |
| 20.0 | 8.65 |
| 24.0 | 7.87 |
| 24.9 | 6.9 |
| 25.0 | 5.28 |
| 26.0 | 2.71 |
| 28.0 | 2.24 |
| 30.0 | 2.04 |
The titration curve can be drawn as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Initial pH of the analyte solution; Ammonia is a weak base that forms an equilibrium when dissolved in water. The equilibrium is as follows.
The molarity of ammonia at 0 mL HCl is 0.100 M. The ICE table for its dissociation can be represented as follows:
| Reaction | Ammonia | Ammonium | OH- |
| Initial | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium | (0.1-x) | x | x |
The value of x can be calculated by solving the equation as follows:
Then the pH of the initial solution can be determined.
Thus, pH of solution when 0 mL of acid is added is 11.1.
Addition of
When 4.0 mL of acid is added the number of moles of ammonia and HCl can be calculated from their molarity and volume as follows:
The ICE table can be represented as follows:
| Reaction | Ammonia | HCl | Ammonium chloride |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0.0004 | 0 |
| Change | -0.0004 | -0.0004 | +0.0004 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0021 | 0 | 0.0004 |
The pH can be calculated using the Henderson-Hesselbalch equation as follows:
Now,
In the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, the pKa is used. therefore, the pKa for ammonia need to be calculated using its pKb.
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Thus, the pH of the solution is 9.97.
Addition of
Total amount of ammonia to be neutralized
Amount of acid added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Ammonia | HCl | Ammonium chloride |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0.0008 | 0 |
| Change | -0.0008 | -0.0008 | +0.0008 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0017 | 0 | 0.0008 |
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of ammonia to be neutralized
Amount of acid added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Ammonia | H+ | Ammonium chloride |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -0.00125 | -0.00125 | +0.00125 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00125 | 0 | 0.00125 |
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of ammonia to be neutralized
Amount of acid added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Ammonia | H+ | Ammonium |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -0.002 | -0.002 | +0.002 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0005 | 0 | 0.002 |
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of ammonia to be neutralized
Amount of acid added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Ammonia | HCl | Ammonium chloride |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -0.0024 | -0.0024 | 0.0024 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0001 | 0 | 0.0024 |
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of ammonia to be neutralized
Amount of acid added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Ammonia | HCl | Ammonium chloride |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -0.00249 | -0.00249 | -0.00249 |
| Equilibrium | 0.00001 | 0 | 0.00249 |
Applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation,
Addition of
Total amount of ammonia to be neutralized
Amount of acid added
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Ammonia | H+ | Ammonium |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | -0.0025 |
| Equilibrium | 0.0000 | 0 | 0.0025 |
From the number of moles of ammonium ion and total volume that is 0.05 L, the molarity of ammonium chloride solution can be calculated as follows:
The ammonium ion from salt can react with water to give back ammonia as follows:
The ICE table can be prepared as follows:
The acid dissociation constant can be represented as follow:
From the ICE table,
Since, the value of acid dissociation constant is very low thus; value of x can be neglected from denominator.
This is the concentration of hydrogen ion in the solution.
The pH can be calculated as follows:
Addition of 26 mL of the acid:
The number of moles of ammonia and acid will be:
The reaction is represented as follows:
| Reaction | Ammonia | HCl | Ammonium choride |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0.0026 | 0 |
| Change | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | +0.0025 |
| Equilibrium | 0 | 0.0001 | 0.0025 |
The pH depends only on the concentration of HCl as it is a strong acid.
The molarity of HCl using total volume of the solution will be:
The pH can be calculated as follows:
Addition of 28 mL of acid:
The number of moles of each species will be:
The reaction is represented as follows:
| Reaction | Ammonia | HCl | Ammonium choride |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0.0028 | 0 |
| Change | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | +0.0025 |
| Equilibrium | 0 | 0.0003 | 0.0025 |
The pH depends only on the concentration of HCl as it is a strong acid.
The molarity of HCl using total volume of the solution will be:
The pH can be calculated as follows:
Addition of
The number of moles of ammonia and HCl can be calculated as follows:
Then the ICE table after the addition of base is created in order to determine the pH of the solution using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
| Reaction | Ammonia | H+ | Ammonium | OH- |
| Initial | 0.0025 | 0.003 | 0 | 0 |
| Change | -0.0025 | -0.0025 | 0 | 0 |
| Equilibrium | 0 | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 |
Concentration of hydrogen ion
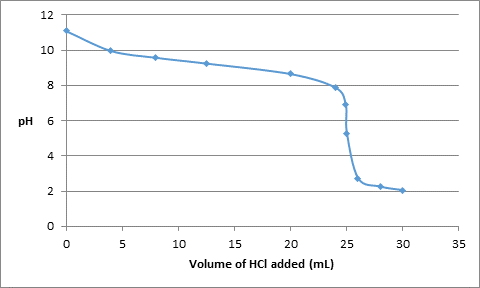
The data obtained from the above calculations will be:
| Volume of HCl added (mL) | pH |
| 0 | 11.1 |
| 4.0 | 9.97 |
| 8.0 | 9.58 |
| 12.5 | 9.25 |
| 20.0 | 8.65 |
| 24.0 | 7.87 |
| 24.9 | 6.9 |
| 25.0 | 5.28 |
| 26.0 | 2.71 |
| 28.0 | 2.24 |
| 30.0 | 2.04 |
The titration curve can be drawn as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- 2. Specify the solvent and reagent(s) required to carry out each of the following FGI. If two reagent sets must be used for the FGI, specify the solvent and reagent(s) for each reagent set. If a reaction cannot be carried out with reagents (sets) class, write NP (not possible) in the solvent box for reagent set #1. Use the letter abbreviation for each solvent; use a number abbreviation for reagent(s). Solvents: CH2Cl2 (A); H₂O (B); Reagents: HBr (1); R₂BH (6); H2SO4 (2); CH3OH (C); Br₂ (3); CH3CO₂H (D) NaHCO3 (4); Hg(OAc)2 (5); H₂O₂ / HO (7); NaBH4 (8) Reagent Set #1 Reagent Set #2 FGI хот Br Solvent Reagent(s) Solvent Reagent(s)arrow_forwardWhat is the correct chemical equation for the lattice formation reaction for CaBr2? Group of answer choices Ca2+(g) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s) ½ Ca2+(g) + Br−(g) → ½ CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + Br2(l) → CaBr2(s) Ca(s) + 2 Br−(g) → CaBr2(s)arrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER THE QUESTION!!!arrow_forward
- 3. SYNTHESIS. Propose a sequence of synthetic steps (FGI) that convert the starting material (SM) into the Target molecule. For each FGI in your proposed synthesis, specify the reagents / conditions, and draw the product(s) of that FGI. DO NOT INCLUDE the FGI mxn in the answer you submit. If an FGI requires two reagent sets, specify the order in which the reagent sets are added, e.g., i) Hg(OAc)2 / H₂O; ii) NaBH4/MeOH. Indicate the stereochemistry (if any) of the products of each FGI. FGI 1. Me Starting Material Source of all carbons in the Target molecule (can use multiple copies) Me Me Target molecule + enantiomerarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction mechanism stepsarrow_forwardIf is was a very hot day, what would the aldol condensation product be? *see imagearrow_forward
- Please help me with number 1-3. Thank you so much.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction ingnore the inorganic byproducts. 1. NaOCH2CH3 at 25 C 2. PhCH2Br (1 eq)arrow_forwardAt 90ºC the vapor pressure of ortho-xylene is 20 kPa and that of meta-xylene is 18 kPa. What is the composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a mixture in which the mole fraction of o-xylene is 0.60?arrow_forward
- Draw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





