
EBK COMPUTER SCIENCE: AN OVERVIEW
12th Edition
ISBN: 8220102744196
Author: BRYLOW
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 35CRP
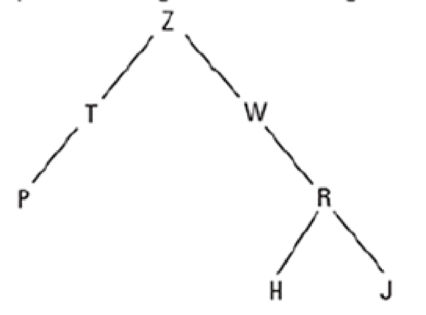
Draw a diagram showing how the binary tree below appears in memory when stored without pointers using a block of contiguous memory cells, as described in Section 8.3.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
In the diagram, there is a green arrow pointing from Input C (complete data) to Transformer Encoder S_B, which I don’t understand. The teacher model is trained on full data, but S_B should instead receive missing data—this arrow should not point there. Please verify and recreate the diagram to fix this issue. Additionally, the newly created diagram should meet the same clarity standards as the second diagram (Proposed MSCATN). Finally provide the output image of the diagram in image format .
Please provide me with the output image of both of them . below are the diagrams code
make sure to update the code and mentionned clearly each section also the digram should be clearly describe like in the attached image. please do not provide the same answer like in other question . I repost this question because it does not satisfy the requirment I need in terms of clarifty the output of both code are not very well details
I have two diagram :
first diagram code
graph LR subgraph Teacher Model (Pretrained) Input_Teacher[Input C (Complete Data)] --> Teacher_Encoder[Transformer Encoder T] Teacher_Encoder --> Teacher_Prediction[Teacher Prediction y_T] Teacher_Encoder --> Teacher_Features[Internal Features F_T] end subgraph Student_A_Model[Student Model A (Handles Missing Values)] Input_Student_A[Input M (Data with Missing Values)] --> Student_A_Encoder[Transformer Encoder E_A] Student_A_Encoder --> Student_A_Prediction[Student A Prediction y_A] Student_A_Encoder…
Why I need ?
Chapter 8 Solutions
EBK COMPUTER SCIENCE: AN OVERVIEW
Ch. 8.1 - Give examples (outside of computer science) of...Ch. 8.1 - Prob. 2QECh. 8.1 - Prob. 3QECh. 8.1 - Prob. 4QECh. 8.1 - Prob. 5QECh. 8.2 - In what sense are data structures such as arrays,...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 2QECh. 8.2 - Prob. 3QECh. 8.3 - Prob. 1QECh. 8.3 - Prob. 2QE
Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 3QECh. 8.3 - Prob. 4QECh. 8.3 - Modify the function in Figure 8.19 so that it...Ch. 8.3 - Prob. 7QECh. 8.3 - Prob. 8QECh. 8.3 - Draw a diagram representing how the tree below...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 1QECh. 8.4 - Prob. 2QECh. 8.4 - Prob. 3QECh. 8.4 - Prob. 4QECh. 8.5 - Prob. 1QECh. 8.5 - Prob. 3QECh. 8.5 - Prob. 4QECh. 8.6 - In what ways are abstract data types and classes...Ch. 8.6 - What is the difference between a class and an...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 3QECh. 8.7 - Suppose the Vole machine language (Appendix C) has...Ch. 8.7 - Prob. 2QECh. 8.7 - Using the extensions described at the end of this...Ch. 8.7 - In the chapter, we introduced a machine...Ch. 8 - Prob. 1CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 2CRPCh. 8 - (Asterisked problems are associated with optional...Ch. 8 - Prob. 4CRPCh. 8 - (Asterisked problems are associated with optional...Ch. 8 - Prob. 6CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 7CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 8CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 9CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 10CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 11CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 12CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 13CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 14CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 15CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 16CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 17CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 18CRPCh. 8 - Design a function to compare the contents of two...Ch. 8 - (Asterisked problems are associated with optional...Ch. 8 - (Asterisked problems are associated with optional...Ch. 8 - Prob. 22CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 23CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 24CRPCh. 8 - (Asterisked problems are associated with optional...Ch. 8 - Prob. 26CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 27CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 28CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 29CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 30CRPCh. 8 - Design a nonrecursive algorithm to replace the...Ch. 8 - Prob. 32CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 33CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 34CRPCh. 8 - Draw a diagram showing how the binary tree below...Ch. 8 - Prob. 36CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 37CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 38CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 39CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 40CRPCh. 8 - Modify the function in Figure 8.24 print the list...Ch. 8 - Prob. 42CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 43CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 44CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 45CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 46CRPCh. 8 - Using pseudocode similar to the Java class syntax...Ch. 8 - Prob. 48CRPCh. 8 - Identify the data structures and procedures that...Ch. 8 - Prob. 51CRPCh. 8 - In what way is a class more general than a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 53CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 54CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 55CRPCh. 8 - Prob. 1SICh. 8 - Prob. 2SICh. 8 - In many application programs, the size to which a...Ch. 8 - Prob. 4SICh. 8 - Prob. 5SICh. 8 - Prob. 6SICh. 8 - Prob. 7SICh. 8 - Prob. 8SI
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
While researching fluid dynamics, you came across a reference to the dimensionless number called the capillary ...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Determine the angle between the force and the line AO. Prob. F2-25
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
// Superclass public class Vehicle { private double cost; (Other methods ) } // Subclass public class Car exten...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
(Factorials) Factorials are used frequently in probability problems. The factorial of a positive integer n (wri...
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Describe two properties that each candidate key must satisfy.
Modern Database Management
Determine the internal normal force between lettered points on the cable and rod. Draw all necessary free-body ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Here are two diagrams. Make them very explicit, similar to Example Diagram 3 (the Architecture of MSCTNN). graph LR subgraph Teacher_Model_B [Teacher Model (Pretrained)] Input_Teacher_B[Input C (Complete Data)] --> Teacher_Encoder_B[Transformer Encoder T] Teacher_Encoder_B --> Teacher_Prediction_B[Teacher Prediction y_T] Teacher_Encoder_B --> Teacher_Features_B[Internal Features F_T] end subgraph Student_B_Model [Student Model B (Handles Missing Labels)] Input_Student_B[Input C (Complete Data)] --> Student_B_Encoder[Transformer Encoder E_B] Student_B_Encoder --> Student_B_Prediction[Student B Prediction y_B] end subgraph Knowledge_Distillation_B [Knowledge Distillation (Student B)] Teacher_Prediction_B -- Logits Distillation Loss (L_logits_B) --> Total_Loss_B Teacher_Features_B -- Feature Alignment Loss (L_feature_B) --> Total_Loss_B Partial_Labels_B[Partial Labels y_p] -- Prediction Loss (L_pred_B) --> Total_Loss_B Total_Loss_B -- Backpropagation -->…arrow_forwardPlease provide me with the output image of both of them . below are the diagrams code I have two diagram : first diagram code graph LR subgraph Teacher Model (Pretrained) Input_Teacher[Input C (Complete Data)] --> Teacher_Encoder[Transformer Encoder T] Teacher_Encoder --> Teacher_Prediction[Teacher Prediction y_T] Teacher_Encoder --> Teacher_Features[Internal Features F_T] end subgraph Student_A_Model[Student Model A (Handles Missing Values)] Input_Student_A[Input M (Data with Missing Values)] --> Student_A_Encoder[Transformer Encoder E_A] Student_A_Encoder --> Student_A_Prediction[Student A Prediction y_A] Student_A_Encoder --> Student_A_Features[Student A Features F_A] end subgraph Knowledge_Distillation_A [Knowledge Distillation (Student A)] Teacher_Prediction -- Logits Distillation Loss (L_logits_A) --> Total_Loss_A Teacher_Features -- Feature Alignment Loss (L_feature_A) --> Total_Loss_A Ground_Truth_A[Ground Truth y_gt] -- Prediction Loss (L_pred_A)…arrow_forwardI'm reposting my question again please make sure to avoid any copy paste from the previous answer because those answer did not satisfy or responded to the need that's why I'm asking again The knowledge distillation part is not very clear in the diagram. Please create two new diagrams by separating the two student models: First Diagram (Student A - Missing Values): Clearly illustrate the student training process. Show how knowledge distillation happens between the teacher and Student A. Explain what the teacher teaches Student A (e.g., handling missing values) and how this teaching occurs (e.g., through logits, features, or attention). Second Diagram (Student B - Missing Labels): Similarly, detail the training process for Student B. Clarify how knowledge distillation works between the teacher and Student B. Specify what the teacher teaches Student B (e.g., dealing with missing labels) and how the knowledge is transferred. Since these are two distinct challenges…arrow_forward
- The knowledge distillation part is not very clear in the diagram. Please create two new diagrams by separating the two student models: First Diagram (Student A - Missing Values): Clearly illustrate the student training process. Show how knowledge distillation happens between the teacher and Student A. Explain what the teacher teaches Student A (e.g., handling missing values) and how this teaching occurs (e.g., through logits, features, or attention). Second Diagram (Student B - Missing Labels): Similarly, detail the training process for Student B. Clarify how knowledge distillation works between the teacher and Student B. Specify what the teacher teaches Student B (e.g., dealing with missing labels) and how the knowledge is transferred. Since these are two distinct challenges (missing values vs. missing labels), they should not be combined in the same diagram. Instead, create two separate diagrams for clarity. For reference, I will attach a second image…arrow_forwardNote : please avoid using AI answer the question by carefully reading it and provide a clear and concise solutionHere is a clear background and explanation of the full method, including what each part is doing and why. Background & Motivation Missing values: Some input features (sensor channels) are missing for some samples due to sensor failure or corruption. Missing labels: Not all samples have a ground-truth RUL value. For example, data collected during normal operation is often unlabeled. Most traditional deep learning models require complete data and full labels. But in our case, both are incomplete. If we try to train a model directly, it will either fail to learn properly or discard valuable data. What We Are Doing: Overview We solve this using a Teacher–Student knowledge distillation framework: We train a Teacher model on a clean and complete dataset where both inputs and labels are available. We then use that Teacher to teach two separate Student models: Student A learns…arrow_forwardHere is a clear background and explanation of the full method, including what each part is doing and why. Background & Motivation Missing values: Some input features (sensor channels) are missing for some samples due to sensor failure or corruption. Missing labels: Not all samples have a ground-truth RUL value. For example, data collected during normal operation is often unlabeled. Most traditional deep learning models require complete data and full labels. But in our case, both are incomplete. If we try to train a model directly, it will either fail to learn properly or discard valuable data. What We Are Doing: Overview We solve this using a Teacher–Student knowledge distillation framework: We train a Teacher model on a clean and complete dataset where both inputs and labels are available. We then use that Teacher to teach two separate Student models: Student A learns from incomplete input (some sensor values missing). Student B learns from incomplete labels (RUL labels missing…arrow_forward
- here is a diagram code : graph LR subgraph Inputs [Inputs] A[Input C (Complete Data)] --> TeacherModel B[Input M (Missing Data)] --> StudentA A --> StudentB end subgraph TeacherModel [Teacher Model (Pretrained)] C[Transformer Encoder T] --> D{Teacher Prediction y_t} C --> E[Internal Features f_t] end subgraph StudentA [Student Model A (Trainable - Handles Missing Input)] F[Transformer Encoder S_A] --> G{Student A Prediction y_s^A} B --> F end subgraph StudentB [Student Model B (Trainable - Handles Missing Labels)] H[Transformer Encoder S_B] --> I{Student B Prediction y_s^B} A --> H end subgraph GroundTruth [Ground Truth RUL (Partial Labels)] J[RUL Labels] end subgraph KnowledgeDistillationA [Knowledge Distillation Block for Student A] K[Prediction Distillation Loss (y_s^A vs y_t)] L[Feature Alignment Loss (f_s^A vs f_t)] D -- Prediction Guidance --> K E -- Feature Guidance --> L G --> K F --> L J -- Supervised Guidance (if available) --> G K…arrow_forwarddetails explanation and background We solve this using a Teacher–Student knowledge distillation framework: We train a Teacher model on a clean and complete dataset where both inputs and labels are available. We then use that Teacher to teach two separate Student models: Student A learns from incomplete input (some sensor values missing). Student B learns from incomplete labels (RUL labels missing for some samples). We use knowledge distillation to guide both students, even when labels are missing. Why We Use Two Students Student A handles Missing Input Features: It receives input with some features masked out. Since it cannot see the full input, we help it by transferring internal features (feature distillation) and predictions from the teacher. Student B handles Missing RUL Labels: It receives full input but does not always have a ground-truth RUL label. We guide it using the predictions of the teacher model (prediction distillation). Using two students allows each to specialize in…arrow_forwardWe are doing a custom JSTL custom tag to make display page to access a tag handler. Write two custom tags: 1) A single tag which prints a number (from 0-99) as words. Ex: <abc:numAsWords val="32"/> --> produces: thirty-two 2) A paired tag which puts the body in a DIV with our team colors. Ex: <abc:teamColors school="gophers" reverse="true"> <p>Big game today</p> <p>Bring your lucky hat</p> <-- these will be green text on blue background </abc:teamColors> Details: The attribute for numAsWords will be just val, from 0 to 99 - spelling, etc... isn't important here. Print "twenty-six" or "Twenty six" ... . Attributes for teamColors are: school, a "required" string, and reversed, a non-required boolean. - pick any four schools. I picked gophers, cyclones, hawkeyes and cornhuskers - each school has two colors. Pick whatever seems best. For oine I picked "cyclones" and red text on a gold body - if…arrow_forward
- I want a database on MySQL to analyze blood disease analyses with a selection of all its commands, with an ER drawing, and a complete chart for normalization. I want them completely.arrow_forwardAssignment Instructions: You are tasked with developing a program to use city data from an online database and generate a city details report. 1) Create a new Project in Eclipse called "HW7". 2) Create a class "City.java" in the project and implement the UML diagram shown below and add comments to your program. 3) The logic for the method "getCityCategory" of City Class is below: a. If the population of a city is greater than 10000000, then the method returns "MEGA" b. If the population of a city is greater than 1000000 and less than 10000000, then the method returns "LARGE" c. If the population of a city is greater than 100000 and less than 1000000, then the method returns "MEDIUM" d. If the population of a city is below 100000, then the method returns "SMALL" 4) You should create another new Java program inside the project. Name the program as "xxxx_program.java”, where xxxx is your Kean username. 3) Implement the following methods inside the xxxx_program program The main method…arrow_forwardCPS 2231 - Computer Programming – Spring 2025 City Report Application - Due Date: Concepts: Classes and Objects, Reading from a file and generating report Point value: 40 points. The purpose of this project is to give students exposure to object-oriented design and programming using classes in a realistic application that involves arrays of objects and generating reports. Assignment Instructions: You are tasked with developing a program to use city data from an online database and generate a city details report. 1) Create a new Project in Eclipse called "HW7”. 2) Create a class "City.java" in the project and implement the UML diagram shown below and add comments to your program. 3) The logic for the method "getCityCategory" of City Class is below: a. If the population of a city is greater than 10000000, then the method returns "MEGA" b. If the population of a city is greater than 1000000 and less than 10000000, then the method returns "LARGE" c. If the population of a city is greater…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage

Systems Architecture
Computer Science
ISBN:9781305080195
Author:Stephen D. Burd
Publisher:Cengage Learning

C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337102087
Author:D. S. Malik
Publisher:Cengage Learning

New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript
Computer Science
ISBN:9781305503922
Author:Patrick M. Carey
Publisher:Cengage Learning

C++ for Engineers and Scientists
Computer Science
ISBN:9781133187844
Author:Bronson, Gary J.
Publisher:Course Technology Ptr

EBK JAVA PROGRAMMING
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337671385
Author:FARRELL
Publisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Programming Logic & Design Comprehensive
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337669405
Author:FARRELL
Publisher:Cengage
Instruction Format (With reference to address); Author: ChiragBhalodia;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lNdy8HREvgo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY