
Concept explainers
Three resonance structures are possible for dinitrogen monoxide, N2O.
- (a) Draw the three resonance structures.
- (b) Calculate the formal charge on each atom in each resonance structure.
- (c) Based on formal charges and electronegativity, predict which resonance structure is the most reasonable.
(a)
Interpretation:
The three resonance structure of
Concept Introduction:
Resonance structures: A molecule or ion which show more than structure but none of them are accurately correct show the known property of that molecule, and can lie between the canonical structure is known as resonance or canonical or contributing structure.
Explanation of Solution
The three resonance structure is drawn
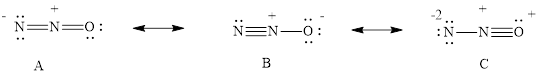
(b)
Interpretation:
Formal charge on each atom in each resonance structure has to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Formal charge: It is the electrostatic charge that would reside on an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion if all bonding electron are shared equally between pairs of atoms.
Formal charge calculation: The formal charge for atom in a molecule or ion is calculated based on the Lewis structure of the molecule or ion by following the given equation below:

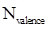 - Number of valence electrons
- Number of valence electrons
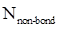 - Number of non-bonding electrons
- Number of non-bonding electrons
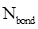 - Number of bonding electrons
- Number of bonding electrons
Explanation of Solution
The formal charges can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure A is given below,
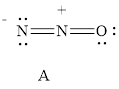
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure B is given below,
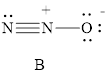
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure C, is given below,
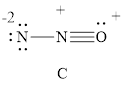
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
(c)
Interpretation:
From the resonance structure drawn, the most reasonable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Formal charge: It is the electrostatic charge that would reside on an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion if all bonding electron are shared equally between pairs of atoms.
Formal charge calculation: The formal charge for atom in a molecule or ion is calculated based on the Lewis structure of the molecule or ion by following the given equation below:

 - Number of valence electrons
- Number of valence electrons
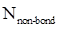 - Number of non-bonding electrons
- Number of non-bonding electrons
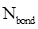 - Number of bonding electrons
- Number of bonding electrons
Resonance structures:
A molecule or ion which show more than structure but none of them are accurately correct show the known property of that molecule, and can lie between the canonical structure is known as resonance or canonical or contributing structure.
Explanation of Solution
The three resonance structure is drawn
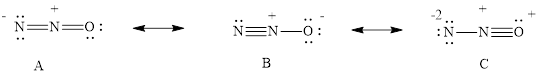
- (a) The formal charges can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure A
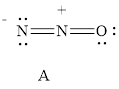
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure B
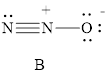
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure C
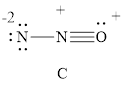
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
Thus from the formal charge given above, the Structure B is most reasonable
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- Please answer the questions in the photos and please revise any wrong answers. Thank youarrow_forward(Please be sure that 7 carbons are available in the structure )Based on the 1H NMR, 13C NMR, DEPT 135 NMR and DEPT 90 NMR, provide a reasoning step and arrive at the final structure of an unknown organic compound containing 7 carbons. Dept 135 shows peak to be positive at 128.62 and 13.63 Dept 135 shows peak to be negative at 130.28, 64.32, 30.62 and 19.10.arrow_forward-lease help me answer the questions in the photo.arrow_forward
- For the reaction below, the concentrations at equilibrium are [SO₂] = 0.50 M, [0] = 0.45 M, and [SO3] = 1.7 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K? 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) Report your answer using two significant figures. Provide your answer below:arrow_forwardI need help with this question. Step by step solution, please!arrow_forwardZn(OH)2(s) Zn(OH)+ Ksp = 3 X 10-16 B₁ = 1 x 104 Zn(OH)2(aq) B₂ = 2 x 1010 Zn(OH)3 ẞ3-8 x 1013 Zn(OH) B4-3 x 1015arrow_forward
- Help me understand this by showing step by step solution.arrow_forwardscratch paper, and the integrated rate table provided in class. our scratch work for this test. Content attribution 3/40 FEEDBACK QUESTION 3 - 4 POINTS Complete the equation that relates the rate of consumption of H+ and the rate of formation of Br2 for the given reaction. 5Br (aq) + BrO3 (aq) + 6H (aq) →3Br2(aq) + 3H2O(l) • Your answers should be whole numbers or fractions without any decimal places. Provide your answer below: Search 尚 5 fn 40 * 00 99+ 2 9 144 a [arrow_forward(a) Write down the structure of EDTA molecule and show the complex structure with Pb2+ . (b) When do you need to perform back titration? (c) Ni2+ can be analyzed by a back titration using standard Zn2+ at pH 5.5 with xylenol orange indicator. A solution containing 25.00 mL of Ni2+ in dilute HCl is treated with 25.00 mL of 0.05283 M Na2EDTA. The solution is neutralized with NaOH, and the pH is adjusted to 5.5 with acetate buffer. The solution turns yellow when a few drops of indicator are added. Titration with 0.02299 M Zn2+ requires 17.61 mL to reach the red end point. What is the molarity of Ni2+ in the unknown?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
