
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for the given molecule should be determined. The electron-pair geometry and molecular geometry around central atom should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
- Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the
chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds. - It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
- The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then tend to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Electron-Pair geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering all valence electrons and bond pairs around central atom.
Molecular geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering only the directly bonded atoms with the central atom.
(a)
Answer to Problem 18PS
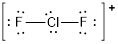
The electron pair geometry around chlorine is Trigonal bipyramidal and the molecular geometry is linear.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.

The electron pair geometry around chlorine is Trigonal bipyramidal and the molecular geometry is linear since there are two bond pairs and three lone pairs around the chlorine atom.
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for the given molecule should be determined. The electron-pair geometry and molecular geometry around central atom should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
- Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
- It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
- The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then tend to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Electron-Pair geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering all valence electrons and bond pairs around central atom.
Molecular geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering only the directly bonded atoms with the central atom.
(b)
Answer to Problem 18PS
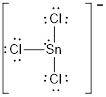
Electron pair geometry around
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.

Electron pair geometry around
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for the given molecule should be determined. The electron-pair geometry and molecular geometry around central atom should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
- Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
- It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
- The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then tend to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Electron-Pair geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering all valence electrons and bond pairs around central atom.
Molecular geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering only the directly bonded atoms with the central atom.
(c)
Answer to Problem 18PS
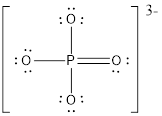
The electron pair and the molecular geometry around the central atom is tetrahedral.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.

The electron pair and the molecular geometry around the central atom is tetrahedral since there are only four bond pairs and no lone pairs around the Phosphorus atom.
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for the given molecule should be determined. The electron-pair geometry and molecular geometry around central atom should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
- Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the chemical bonding of covalently bonded molecules and coordination compounds.
- It is also known as Lewis dot structures which represent the bonding between atoms of a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule.
- The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Lewis structure for any molecule is drawn by using the following steps,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
VSEPR Theory:
As the name itself indicates that the basis for this theory is the electron pair that is bonded electron present in either single or double bonds or lone pair electrons, present in the valence shell tends to repel each other which then tend to be in position in order to minimize the repulsions. The steps involved in the theory in describing the geometry is as follows,
- The first step is to draw the correct Lewis structure for the molecule.
- Then, the electron domain around the central atom should be counted and the geometry that matches with that type of domain in VSEPR should be determined.
- Finally, the geometry is predicted by using the orientation of atoms.
The molecules with considering the domains of type
Electron Domain: In VSEPR theory, both the lone pair and the bonded pair are together considered as electron domain regardless of the type of bond in which the bonded pair presents.
Electron-Pair geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering all valence electrons and bond pairs around central atom.
Molecular geometry: It is the geometry obtained by considering only the directly bonded atoms with the central atom.
(d)
Answer to Problem 18PS
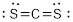
Electron pair geometry around C is linear. The molecular geometry is also linear.
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis electron dot structure for given molecules are determined by first drawing the skeletal structure for the given molecules, then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecules are determined.
The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it.
Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed considering each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
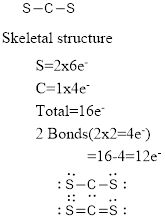
The electron pair geometry and the molecular geometry around carbon is linear since there are no lone pairs around the central atom.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- Indicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forward
- Name an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forwardGiven the hydrazones indicated, draw the structures of the enamines that can be formed. Indicate the most stable enamine (explain). C6H5 C6H5 H C6H5 Harrow_forward
- 4. Propose a Synthesis for the molecule below. You may use any starting materials containing 6 carbons or less (reagents that aren't incorporated into the final molecule such as PhзP do not count towards this total, and the starting material can have whatever non-carbon functional groups you want), and any of the reactions you have learned so far in organic chemistry I, II, and III. Your final answer should show each step separately, with intermediates and conditions clearly drawn.arrow_forwardIndicate the importance of the indole ring. Find a representative example and list 5 structures.arrow_forwardΌΗ 1) V2 CO 3 or Nalt In منهarrow_forward
- 6. The equilibrium constant for the reaction 2 HBr (g) → H2(g) + Br2(g) Can be expressed by the empirical formula 11790 K In K-6.375 + 0.6415 In(T K-¹) - T Use this formula to determine A,H as a function of temperature. Calculate A,-H at 25 °C and at 100 °C.arrow_forward3. Nitrosyl chloride, NOCI, decomposes according to 2 NOCI (g) → 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) Assuming that we start with no moles of NOCl (g) and no NO(g) or Cl2(g), derive an expression for Kp in terms of the equilibrium value of the extent of reaction, Seq, and the pressure, P. Given that K₂ = 2.00 × 10-4, calculate Seq/ of 29/no when P = 0.080 bar. What is the new value по ƒª/ at equilibrium when P = 0.160 bar? Is this result in accord with Le Châtelier's Principle?arrow_forwardConsider the following chemical equilibrium: 2SO2(g) + O2(g) = 2SO3(g) • Write the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction. Now compare it to the equilibrium constant expression for the related reaction: • . 1 SO2(g) + O2(g) = SO3(g) 2 How do these two equilibrium expressions differ? What important principle about the dependence of equilibrium constants on the stoichiometry of a reaction can you learn from this comparison?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning



