
Concept explainers
Three resonance structures are possible for dinitrogen monoxide, N2O.
- (a) Draw the three resonance structures.
- (b) Calculate the formal charge on each atom in each resonance structure.
- (c) Based on formal charges and electronegativity, predict which resonance structure is the most reasonable.
(a)
Interpretation:
The three resonance structure of
Concept Introduction:
Resonance structures: A molecule or ion which show more than structure but none of them are accurately correct show the known property of that molecule, and can lie between the canonical structure is known as resonance or canonical or contributing structure.
Explanation of Solution
The three resonance structure is drawn
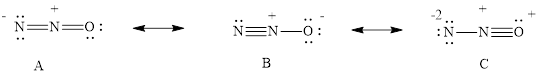
(b)
Interpretation:
Formal charge on each atom in each resonance structure has to be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Formal charge: It is the electrostatic charge that would reside on an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion if all bonding electron are shared equally between pairs of atoms.
Formal charge calculation: The formal charge for atom in a molecule or ion is calculated based on the Lewis structure of the molecule or ion by following the given equation below:

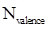 - Number of valence electrons
- Number of valence electrons
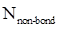 - Number of non-bonding electrons
- Number of non-bonding electrons
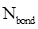 - Number of bonding electrons
- Number of bonding electrons
Explanation of Solution
The formal charges can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure A is given below,
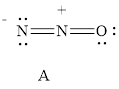
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure B is given below,
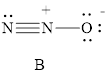
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure C, is given below,
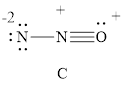
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
(c)
Interpretation:
From the resonance structure drawn, the most reasonable structure has to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
Formal charge: It is the electrostatic charge that would reside on an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ion if all bonding electron are shared equally between pairs of atoms.
Formal charge calculation: The formal charge for atom in a molecule or ion is calculated based on the Lewis structure of the molecule or ion by following the given equation below:

 - Number of valence electrons
- Number of valence electrons
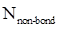 - Number of non-bonding electrons
- Number of non-bonding electrons
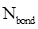 - Number of bonding electrons
- Number of bonding electrons
Resonance structures:
A molecule or ion which show more than structure but none of them are accurately correct show the known property of that molecule, and can lie between the canonical structure is known as resonance or canonical or contributing structure.
Explanation of Solution
The three resonance structure is drawn
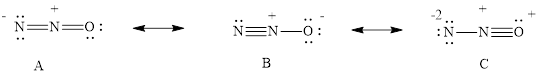
- (a) The formal charges can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure A
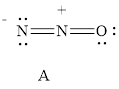
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure B
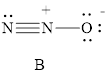
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
For resonance structure C
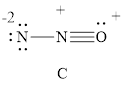
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on nitrogen
Formal charge on oxygen can be calculated as follows.
Thus from the formal charge given above, the Structure B is most reasonable
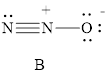
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
- Indicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forwardThe molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forward
- What characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forwardFor a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forward
- Describe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forwardState two similarities between fluorescence and phosphorescence.arrow_forwardState three photophysical processes that can be related to the effects of incident radiation on a molecule in its ground state. Consider that radiation can give rise to fluorescent emission, but not phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
