
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781133949640
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 85GQ
Acrolein is used to make plastics. Suppose this compound can be prepared by inserting a carbon monoxide molecule into the C—H bond of ethylene.
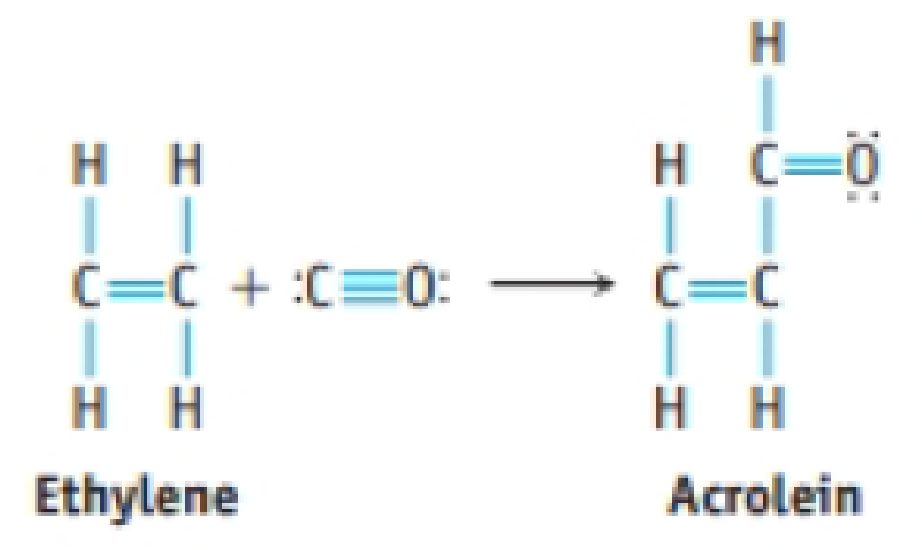
- (a) Which is the stronger carbon-carbon bond in acrolein?
- (b) Which is the longer carbon-carbon bond in acrolein?
- (c) Is ethylene or acrolein polar?
- (d) Use bond dissociation enthalpies to predict whether the reaction of CO with C2H4 to give acrolein is endothermic or exothermic.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electrons-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).
Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using
the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved
electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or
mechanistic step(s).
Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making
steps.
I
I
I
H
Select to Add Arrows
HCI, CH3CH2OH
Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and the follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Ch. 8.2 - Draw Lewis electron dot structures for CH3Cl...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 2CYUCh. 8.2 - Prob. 3CYUCh. 8.2 - Prob. 4CYUCh. 8.2 - Prob. 1RCCh. 8.2 - 2. Which one of the species in the list below is...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 3RCCh. 8.2 - Prob. 4RCCh. 8.3 - Prob. 1CYUCh. 8.3 - 1. What is the formal charge of the P atom in the...
Ch. 8.4 - Draw resonance structures for the bicarbonate ion,...Ch. 8.4 - 1. For which of the following species, SO32−, NO+,...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 2RCCh. 8.5 - Sketch the Lewis structures for CIF2+ and CIF2....Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 1QCh. 8.5 - Prob. 2QCh. 8.5 - Prob. 1RCCh. 8.5 - Prob. 2RCCh. 8.6 - What is the shape of the dichloromethane (CH2C12)...Ch. 8.6 - Give the electron-pair geometry and molecular...Ch. 8.6 - Draw the Lewis structure for lCl2, and then decide...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 4CYUCh. 8.6 - Which of the following species has...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 2RCCh. 8.6 - What is the approximate ClCCl bond angle in...Ch. 8.6 - 4. What is the molecular geometry of N2O (where...Ch. 8.7 - Draw the resonance structures for SCN. What are...Ch. 8.7 - For each of the following molecules, decide...Ch. 8.7 - Prob. 1RCCh. 8.7 - 2. Which of the following best describes the...Ch. 8.7 - Three resonance forms can be drawn for the...Ch. 8.8 - The electrostatic potential surface for SOCl2 is...Ch. 8.8 - Using the bond dissociation enthalpies in Table...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 1RCCh. 8.8 - Prob. 2RCCh. 8.9 - 1. Which of the following species has the longest...Ch. 8.9 - 2. Which of the following species has the largest...Ch. 8.9 - 3. Use bond dissociation enthalpies to estimate...Ch. 8 - Give the periodic group number and number of...Ch. 8 - Give the periodic group number and number of...Ch. 8 - For elements in Groups 4A-7A of the periodic...Ch. 8 - Prob. 4PSCh. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Show all possible resonance structures for each of...Ch. 8 - Show all possible resonance structures for each of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 11PSCh. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Determine the formal charge on each atom in the...Ch. 8 - Determine the formal charge on each atom in the...Ch. 8 - Determine the formal charge on each atom in the...Ch. 8 - Determine the formal charge on each atom in the...Ch. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 18PSCh. 8 - Prob. 19PSCh. 8 - The following molecules or ions all have three...Ch. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following...Ch. 8 - Give approximate values for the indicated bond...Ch. 8 - Give approximate values for the indicated bond...Ch. 8 - Phenylalanine is one of the natural amino acids...Ch. 8 - Acetylacetone has the structure shown here....Ch. 8 - For each pair of bonds, indicate the more polar...Ch. 8 - For each of the bonds listed below, tell which...Ch. 8 - Urea, (NH2)2CO, is used in plastics and...Ch. 8 - Considering both formal charges and bond...Ch. 8 - Considering both formal charge and bond...Ch. 8 - Three resonance structures are possible for...Ch. 8 - Three resonance structures are possible for the...Ch. 8 - Compare the electron dot structures of the...Ch. 8 - Compare the electron dot structures of the...Ch. 8 - The chemistry of the nitrite ion and HNO2: (a) Two...Ch. 8 - Draw the resonance structures for the formate ion,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 39PSCh. 8 - Consider the following molecules: (a) CH4 (b)...Ch. 8 - Which of the following molecules is(are) polar?...Ch. 8 - Prob. 42PSCh. 8 - Give the bond order for each bond in the following...Ch. 8 - Prob. 44PSCh. 8 - In each pair of bonds, predict which is shorter....Ch. 8 - In each pair of bonds, predict which is shorter....Ch. 8 - Prob. 47PSCh. 8 - Compare the carbon-oxygen bond lengths in the...Ch. 8 - Consider the carbon-oxygen bond in formaldehyde...Ch. 8 - Compare the nitrogen-nitrogen bond in hydrazine,...Ch. 8 - Ethanol can be made by the reaction of ethylene...Ch. 8 - Methanol can be made by partial oxidation of...Ch. 8 - Hydrogenation reactions, which involve the...Ch. 8 - Phosgene, Cl2CO, is a highly toxic gas that was...Ch. 8 - The compound oxygen difluoride is quite reactive,...Ch. 8 - Oxygen atoms can combine with ozone to form...Ch. 8 - Prob. 57GQCh. 8 - Prob. 58GQCh. 8 - Which of the following compounds or ions do not...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60GQCh. 8 - Draw resonance structures for the formate ion,...Ch. 8 - Prob. 62GQCh. 8 - Prob. 63GQCh. 8 - What is the principle of electroneutrality? Use...Ch. 8 - Prob. 65GQCh. 8 - Draw resonance structures for the SO2 molecule,...Ch. 8 - What are the orders of the NO bonds in NO2 and...Ch. 8 - Which has the greater ONO bond angle, NO2 or NO2+?...Ch. 8 - Compare the FClF angles in CIF2+ and ClF2. Using...Ch. 8 - Draw an electron dot structure for the cyanide...Ch. 8 - Draw the electron dot structure for the sulfite...Ch. 8 - Dinitrogen monoxide, N2O, can decompose to...Ch. 8 - The equation for the combustion of gaseous...Ch. 8 - The cyanate ion, OCN, has the least...Ch. 8 - Vanillin is the flavoring agent in vanilla extract...Ch. 8 - Explain why (a) XeF2 has a linear molecular...Ch. 8 - The formula for nitryl chloride is ClNO2 (in which...Ch. 8 - Hydroxyproline is a less-common amino acid. (a)...Ch. 8 - Amides are an important class of organic...Ch. 8 - Prob. 81GQCh. 8 - The molecule shown here. 2-furylmelhanethiol, is...Ch. 8 - Dihydroxyacetone is a component of quick-tanning...Ch. 8 - It is possible to draw three resonance structures...Ch. 8 - Acrolein is used to make plastics. Suppose this...Ch. 8 - Molecules in space: (a) In addition to molecules...Ch. 8 - 1,2-Dichloroethylene can be synthesized by adding...Ch. 8 - The molecule pictured below is epinephrine, a...Ch. 8 - You are doing an experiment in the laboratory and...Ch. 8 - Prob. 90ILCh. 8 - A paper published in the research Journal Science...Ch. 8 - Uracil is one of the bases in RNA, a close...Ch. 8 - Prob. 93SCQCh. 8 - Prob. 94SCQCh. 8 - Bromine-containing species play a role in...Ch. 8 - Acrylamide, H2C=CHCONH2, is a known neurotoxin and...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the curved arrows to draw the intermediates and product of the following reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Use the reaction conditions provided and follow the arrows to draw the intermediate and the product in this reaction or mechanistic step(s).arrow_forwardLook at the following pairs of structures carefully to identify them as representing a) completely different compounds, b) compounds that are structural isomers of each other, c) compounds that are geometric isomers of each other, d) conformers of the same compound (part of structure rotated around a single bond) or e) the same structure.arrow_forward
- Given 10.0 g of NaOH, what volume of a 0.100 M solution of H2SO4 would be required to exactly react all the NaOH?arrow_forward3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forward3.50 g of Li are combined with 3.50 g of N2. What is the maximum mass of Li3N that can be produced? 6 Li + N2 ---> 2 Li3Narrow_forward
- Concentration Trial1 Concentration of iodide solution (mA) 255.8 Concentration of thiosulfate solution (mM) 47.0 Concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution (mM) 110.1 Temperature of iodide solution ('C) 25.0 Volume of iodide solution (1) used (mL) 10.0 Volume of thiosulfate solution (5:03) used (mL) Volume of DI water used (mL) Volume of hydrogen peroxide solution (H₂O₂) used (mL) 1.0 2.5 7.5 Time (s) 16.9 Dark blue Observations Initial concentration of iodide in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of thiosulfate in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mA) Initial Rate (mA's)arrow_forwardDraw the condensed or line-angle structure for an alkene with the formula C5H10. Note: Avoid selecting cis-/trans- isomers in this exercise. Draw two additional condensed or line-angle structures for alkenes with the formula C5H10. Record the name of the isomers in Data Table 1. Repeat steps for 2 cyclic isomers of C5H10arrow_forwardExplain why the following names of the structures are incorrect. CH2CH3 CH3-C=CH-CH2-CH3 a. 2-ethyl-2-pentene CH3 | CH3-CH-CH2-CH=CH2 b. 2-methyl-4-pentenearrow_forward
- Draw the line-angle formula of cis-2,3-dichloro-2-pentene. Then, draw the line-angle formula of trans-2,3-dichloro-2-pentene below. Draw the dash-wedge formula of cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. Then, draw the dash-wedge formula of trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane below.arrow_forwardRecord the amounts measured and calculate the percent yield for Part 2 in the table below. Dicyclopentadiene measured in volume Cyclopentadiene measured in grams 0 Measured Calculated Mol Yield Mass (g) or Volume (mL) Mass (g) or Volume (ml) 0.6 2.955 Part 2 Measurements and Results Record the amounts measured and calculate the percent yield for Part 2 in the table below. 0.588 0.0044 2.868 0.0434 N/A Table view List view Measured Calculated Mol $ Yield Melting Point (C) Mass (g) or Volume (ml) Mass (g) or Volume (ml.) Cyclopentadiene 0.1 0.08 0.001189 measured in volume Maleic Anhydride 0.196 N/A cis-norbornene-5,6-endo- dicarboxylic anhydride 0.041 0.0002467 N/A N/A N/A 0.002 N/A N/A 128arrow_forwardDraw the condensed structural formula and line-angle formula for each: 2,3-dimethylheptane 3-bromo-2-pentanol 3-isopropyl-2-hexene 4-chlorobutanoic acidarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning
INTRODUCTION TO MOLECULAR QUANTUM MECHANICS -Valence bond theory - 1; Author: AGK Chemistry;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U8kPBPqDIwM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY